(a) State the main nutrient obtainable from each of the Specimen G (BONE), and P ( DRIED ANIMAL BLOOD) and two main nutrients obtainable from Specimen T (FISH)
(b) State three functions for each of the two main nutrients obtainable from specimen T
(c) Name one feed ingredient that can be prepared from each of specimens G, P, and T.
(d) Give two disadvantages of using the ingredient prepared from specimen P in compounding livestock feed.
(a) Identify specimens L, N, and Q
Specimen L; Specimen N; Specimen Q;
(b) State three agricultural uses of each specimen N and Q
(c) List two crops each which require each of the specimens L, N and Q in large quantities for good yields
(d) State three methods of applying specimen L on a farm
(a) State three functions and two methods of maintaining each of specimens F (HOE), H (RAKE), and K (PLIERS).
(a) (i) Describe the physical properties of each of Specimens B (SAND), C (CLAY), and D (LOAM)
(ii) To about 10ml each of the specimens B, C and D, add about 5ml of specimen O and using the hand, mix well. Describe the physical properties of each specimen?
(b) Which of the specimens B, C, and D should be considered of greater value to farmers? Give two reasons for your answers
(c) State three ways of improving each of the other two specimens not mentioned in (b) above
Discuss each of rinderpest and Newcastle diseases under the following headings (i0 host organism (2 marks) (ii) Casual organsim (2 marks) (iii) Mode of transmission (4 marks) (iv) Symptoms (4 marks) (v) Control (4 marks)
(a) List four marketing agents [2 marks]
(b) State (i) four characteristic features and (ii) four advantages of co-operative societies in agriculture [8 marks]
(c)(i) Give three merits of individual contact in extension method [3 marks] (ii) List three Agricultural Extension Programmes in your country. [3 marks]
a) Name and explain three factors of production in agriculture [12 marks] (b) Mention four functions of a farm manager [4 marks]
(a) Mention four factors that should be considered when siting a fish pond. [4 marks] (b) Explain six ways of maintaining a fish pond. [12 marks] Discuss each of rinderpest and Newcastle diseases under the following headings: (i) host organism; [2 marks] (ii) causal organism; [2 marks] (iii) mode of transmission; [4 marks] (iv) symptoms; [4 marks] (v) control [4 marks]
(a) Outline the life cycle of the bean beetle [6 marks] (b)(i) Describe briefly four damages done by cotton stainer to cotton plants on the field. [6 marks] (ii) Name four alternate hosts of cotton stainer [4 marks]
The plan below represents the survey of a school farm.
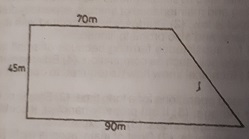
Use it to answer Questions (a) and (b).
(a) Calculate the area of the land in hectares [4 marks] 70m
(b) If the school plans to cultivate plantain at a spacing of 4m x 4m on 80% of the land and pineapple at a spacing of 2m x 2.5m on 20% of the land, calculate the number of plantain and pineapple planting materials that would be required for the farm. [12 marks]
(a) State four functions of each of the following macro-nutrients in plant nutrition: (i) nitrogen; (ii) phosphorus; (iii) potassium. [12 marks] (b) List four factors that affect the availability of nutrients to crops. [4 marks]
(a) What is land? [1 mark] (b) Mention six uses of land [6 marks] (c) State four ways through which an agricultural land may appreciate in value [4 marks] (d) State five benefits derived from soil organisms in agriculture [5 marks]
(a) List six sources of farm power [3 marks] (b) Explain how five of the sources of farm power listed in 2(a) are utilised on the farm. [5 marks] (c) Give two disadvantages each, of any four sources of farm power listed in 2(a). [8 marks]
(a) Mention three ways each of the following affect agrocultural development (i) poor tools and implements (ii) poor storage facilities (6 marks)
(b) Suggest one solution to the problem of poor tools and implements (1 mark)
(c) State three objectives each of (i) Land Use Act (ii) Quarantine programme (iii) government agricultural loan and subside schemes [9 marks]
The best method of introducing a new pesticide to rural farmers is through
- A. farmers co-operatives
- B. circular letters
- C. demonstration
- D. field trips
The activities of middlemen may cause the following problems except
- A. reducing the profit margin of farmers
- B. artificial scarcity of produce
- C. inflation of prices
- D. inadequate storage facilities
Farm records are important for the following reasons except
- A. supplying information for future planning
- B. determining profit and loss made on the farm
- C. assessing the quality of farm produce
- D. determining the credit worthiness of farmers
The major advantage of inbreeding in animals is that it
- A. increases hybrid vigour
- B. increases multiple births
- C. eliminates undesirable traits
- D. reduces the number of meals needed in a herd
The resulting calf from crossing white fulani with a muturu cow is a
- A. kuri
- B. keteku
- C. ndama
- D. bororo
Fish products include the following except
- A. fish meal
- B. fish silage
- C. oil
- D. leather
Coccidiosis can be treated with
- A. sulphamethazine
- B. iodised salt
- C. piperazine citrate
- D. ferrous oxide


