(a) Name three farm animal hosts of specimen O (TICK)
(b) State four damages done by each of specimens N (LIVER FLUKE) and O on their farm animal hosts.
(c) Enumerate four ways of controlling specimen O
(a) Name the organism which causes the damage observe on each of specimen J, K, L and M.
(b) State three ways in which the organism which caused the damage on specimen J is of economic importance.
(c) State two ways of controlling each of the organisms which caused damage to specimens J,K, L and M.
(a) With the aid of the litmus paper and water provided, classify specimens G, H and I.
(b) Outline the steps taken in classifying specimen G (NEUTRAL SOIL), H (ACIDIC SOIL) and I (ALKALINE / BASIC SOIL)
(c)(i) If the pH value of one of the soil samples provided is 4.5, what condition does this pH value indicate in the soil sample?
(ii) State three effects of the condition indicated in (c)(i) on crop production.
(iii) List Three factors that could cause the condition indicated in (c)(i).
(a) State three uses of each of specimens A (AXE), B(SPADE), D(HAND TROWEL) and F(HAND FORK)
(b) State three ways of maintaining specimen A.
(a) State four characteristics of igneous rocks. .
(b) The table below illustrates the combined demand and supply schedule for maize.
Use it to answer the questions that follow.
|
Price |
Quantity of maize demanded |
Quantity of maize supplied (kg) |
|
20 |
50 |
340 |
|
16 |
70 |
300 |
|
12 |
125 |
250 |
|
8 |
200 |
200 |
|
4 |
350 |
130 |
(i) Draw the demand and supply curves to show the equilibrium price of maize.
(ii) Determine the excess demand for maize at a unit price of ₦4.
(iii) Determine the excess supply for maize at a unit price of ₦12.
(a) Discuss the cultivation of maize under the following headings.
(i) soil requirements;
(ii) method of propagation;
(iii) spacing;
(iv) weed control;
(v) two fungal diseases;
(vi) harvesting.
(b) Describe each of the following farm records:
(i) production record;
(ii) farm inventory;
(iii) cash book;
(iv) labour record
(a) Explain briefly two types of soil water.
(b) State four management practices carried out during the brooding of chicks.
(c) Complete the table below on diseases of farm animals.
| Disease |
Causal organism |
Vaccine/drug administered |
|
Marek’s disease |
(i) |
(ii) |
|
(iii) |
(iv) |
NDV La Sota |
|
Coccidiosis |
(v) |
(vi) |
|
Anthrax |
(vii) |
(viii) |
(a) Give two examples of each of the following classes of crops:
(i) roots and tubers;
(ii) oil crops;
(iii) grain legumes;
(iv)cereals.
(b) State five differences between the digestive system of a goat and a chicken.
(c) Give five reasons why farmers keep records.
(a) State six problems of agricultural development in West Africa.
(b) Explain each of the following farm practices:
(i) crop rotation;
(ii) mixed farming.
(c) State three advantages of each of the following farm practices:
(i) crop rotation;
(ii) mixed farming.
(a) State seven ways in which agriculture is important to the economy of West Africa.
(b) Give two advantages of each of the following sources of farm power:
(i) internal combustion engine;
(ii) electricity;
(iii) wind.
(c) State five operations in poultry production which could be carried out through the use of
electrical power.
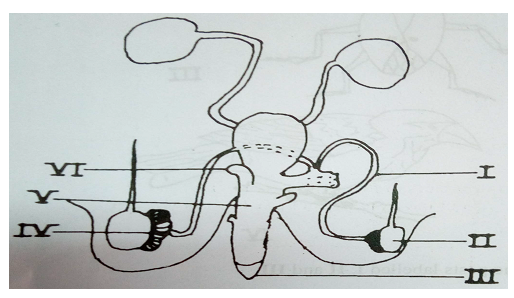
The diagram below illustrates the reproductive parts of livestock. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Name the parts labelled I, II, III, IV, V and VI.
(b) State one function of each of the parts labelled I, II, III, IV, V and VI.
(c) To prevent indiscriminate mating in the herd, a farmer decided to carry out a management practice to alter the functioning of the parts illustrated above.
(i) Name the management practice.
(ii) Name the two main parts of the illustrated diagram that would be of utmost benefit to the farmer in carrying out the management practice named in (c)(i).
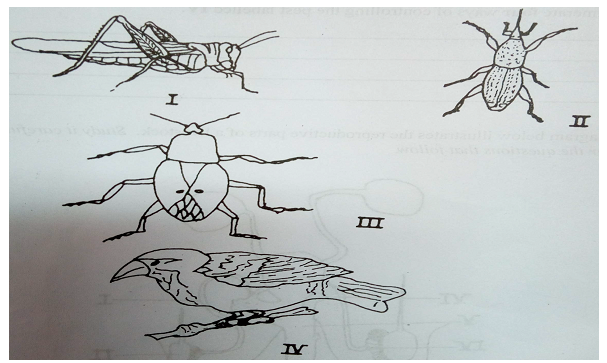
The diagrams below illustrate pests of crops. Study them and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Name each of the pests labelled I, II and III.
(b) Describe the life cycle of the pest labelled I.
(c) State four damages caused by the pest labelled III on crops.
(d) Enumerate four ways of controlling the pest labelled IV.
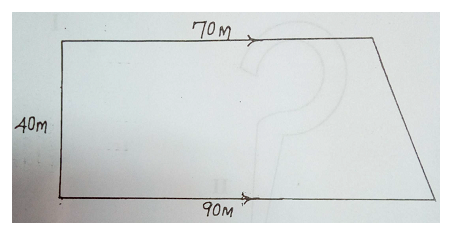
The plan below represents the survey of a farm. Use it to answer questions (a) and (b).
(a) Calculate the area of the farmland.
(b) If the farmland is planted with banana at a spacing of 4 m x 4 m, what will be the population of banana plants on the farm?
(c) Study the diagrams labelled I and II below and answer the questions that follow.
(i) Name the tools labelled I and II.
(ii) State two uses of each of the tools labelled I and II.
(iii) State one general way of maintaining the tools labelled I and II.
The diagram below illustrates an experimental set-up in soil analysis. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
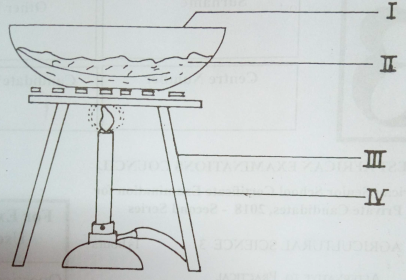
(a) State the aim of the illustrated experiment.
(b) Name the part labelled I, II, III and IV.
(c) A fresh sample of soil weighed 60 g. A container weighing 35 g was used to dry the soil. If both the soil and the container weighed 80 g after the experiment, determine the:
(i) weight of the dried soil;
(ii) weight of the water lost from the soil;
(iii) percentage of water lost from the soil.
(d) List three forms in which water exists in the soil.
(a) What is Colotrum?
(b) Draw and label the transverse section of an egg.
(c) Complete this table on Law of Diminishing Returns
(i) — (ii) 3kg (ii) 11kg (iv) 28kg (v) 40kg (vi) 8kg (vii) 1 kg (viii) 0kg
(a) List four management practices carried out in poultry production.
(b) Discuss four advantages of dehorning in cattle production.
(c) State five marketing services in Agricultural Production
(d) Briefly state five problems of agricultural marketing in West Africa
(a) What is Land Tenure System
(b) Define Weed
(c) Discuss Groundnut rosette disease under the following sub-headings.
(i) Causal organism (ii) Mode of transmission (iii) Symptoms (iv) Control
(d) List the characteristics of the following factors of production (i) Land (ii) Capital
(a) Briefly discuss the cultivation of cassava under the following:
(i) Soil requirement (ii) Land Preparation (iii) Spacing (iv) Weed Control (iv) Fertilizer Requirement (vii) Harvesting (viii) Storage
(b) Complete the following table under the following.
|
|
Name of Diseases | Causal Organism | Farm animal | Symptoms |
Control |
| i | Coccidiosis | ||||
| ii | Rinderpes |
(a) List four functions of soil water to crops.
(b) Enumerate five factors that could cause low soil pH.
(c) Briefly discuss the life cycle of Liver Fluke.
(a) List and discuss the factors hindering Agricultural development in West Africa under the following headings:
(i) Basic amenities
(ii) Farm inputs
Which of the following agricultural extension methods is aimed at reaching an individual farmer at a particular time?
- A. film show
- B. farm visit
- C. electronic media
- D. field trip