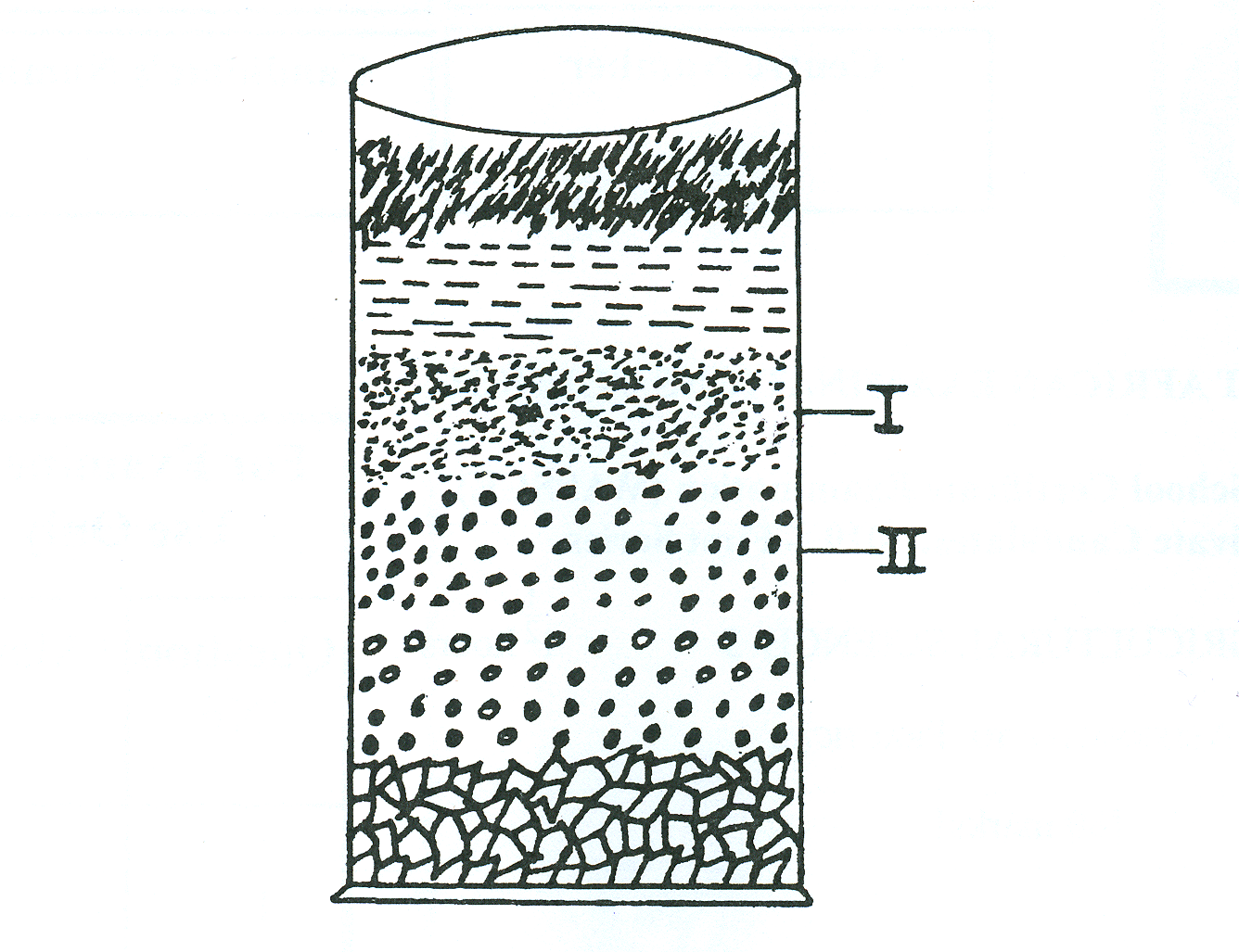
The diagram below illustrates an experimental set-up on soil. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
a) (i) State the aim of the experiment.
(ii)Name the parts labelled I and II in the diagram.
b) Describe how the experiment is carried out.
c) State four properties of sandy soils.
d) Describe a test for soil acidity using litmus paper.
Explanation
(a)(i) Aim of the experiment
- Separation of soil into its fractions/determination of soil texture by sedimentation
(ii) Naming of the parts labelled I and II
I – Clay in suspension/Clay
II – Silt
(b) Description of the experiment
- Place a glass jar on a surface
- Weigh about 70 – 100g of the soil
- Add the weighed soil into an equivalent quantity of water in a glass jar
- Add suitable dispersing agent e,g, NaOH, NaHCO3
- Shake the glass jar vigorously to disperse any soil clods
- Allow the glass jar to settle for an hour
- Observe the result
(c) Properties of sandy soils
- Low cation exchange capacity
- Diameter is between 0.02 mm – 2m2
- Well drained, loose and highly aerated
- Low plant nutrients
- Low buffering capacity
- Leaching of nutrients is high/supports leaching
- Easily gets hot and cold
- Low water holding capacity
- Particles are light and easy to till
- Gritty/rough/coarse in nature
- High percolation rate
- Low capillary action
- Cannot be moulded
(d) Testing soil acidity using litmus paper
- Mix the soil very well
- Moisten with distilled water
- Dip red and blue litmus paper into moistened soil
- If blue litmus paper changes pink/red, the soil is acidic
- If red litmus paper changes blue, the soil is basic/alkaline
- If there is no colour change, the soil is neutral