(a) ldentify specimens N,0, P and Q.
(b) Name the classes of farm animals from which each of specimens N and O can be obtained.
(c) State two functions of specimens N,O, and P that are Common to farm animals.
(d) Mention: (i) one industrial use of specimen O, (i) one parasite of specimen O.
(e) Name the condition in which an animal does not possess specimen Q.
(f) State two importance of specimen Q to each farm animal and man respectively.
(a) ldentify specimens J, K , L and M
(b) Enumerate four types of damages done to crops by each of specimens K and L.
(c) State five methods of controlling specimen J..
(a) ldentify specimens D, E, F, G, H and I.
(b) State one function of each of specimens D, E, F, G, H and I.
(c) Mention one method of maintaining each of specimens D,E, F, G, Hand I.
(a) Identify specimens A, B, and C.
(b) State the main nutrient(s) which can be released to the soil for crop’s use by each of specimens A, B, and C.
(C) Name two other chemical substances which can be used as substitutes for specimen B.
(d) State the major adverse effect of repeated applications of specimen B on a soil.
(e) Mention the role of specimen C in (i) crop production (ii) fish production.
(f) Name other substances that can be used and substituted for specimen C.
a.i Main agricultural extension methods that could be used to create awareness of the disease among poultry farmers. (ii) Most appropriate extension method to create awareness of the disease among poultry farmers (iii) Reasons for the choice of the mass method (iv) problems likely to be encountered by the use of the mass method
b. problems faced by farm managers
c. Breeds of goat found in West Africa
a. Reasons why farm operations are important on (i) Prunning of cocoa trees (ii) parboiling of paddy rice
b. Ways of eradicating guinea grass in a farmland
c. uses of ornamental plants
a. i. Explanation of selective exploitation as used in forest management.
ii. Advantages of selective exploitation of forest trees
b. Distinction between field pests and storage pests of crops
c. I.Examples of storage insect pests of crops
ii. Examples of field insect pests of crops
d. Ways of conserving water in the soil
a. State the roles played by the following factors in soil formation (i)Time (ii) Rainfall (iii) parent material
b. Principles which should be followed in a good crop rotation plan |
c. Uses of forage crops
a. State the roles of government of West African countries in agricultural development on (i) Agricultural finance. (ii) Agricultural education (iii) Agricultural extension services (iv) Agricultural policies and programmes services
b. State structural differences between disc plough and disc harrow
c. State the effects of the frequent use of disc plough on the soil.
Which of the following problems of agriculture could be solved through farmers’ adoption of research findings?
- A. Unpredictable climate
- B. Environmental degradation
- C. poor extension services
- D. Insufficient basic amenities
A long-term loan for an agricultural enterprise could be obtained from
- A. micro-finance banks
- B. commercial banks
- C. money lenders
- D. cooperative societies
The table below illustrates the supply schedule of maize. Use it to answer this question.
| PRICE(#) | QUANTITY SUPPLIED(kg) |
| 24 | 480 |
| 16 | 400 |
Determine the elasticity of supply for maize
- A. 0.3
- B. 0.4
- C. 0.5
- D. 0.6
The table below illustrates the supply schedule of maize. Use it to answer this question.
| PRICE(#) | QUANTITY SUPPLIED (kg) |
| 24 | 480 |
| 16 | 400 |
Calculate the percentage change in price for maize
- A. 8.0%
- B. 33.3%
- C. 50.0%
- D. 66.7%
The table below illustrates the supply schedule of maize. Use it to answer this question.
| PRICE(#) | QUANTITY SUPPLIED(kg) |
| 24 | 480 |
| 16 | 400 |
The percentage change in quantity supplied for maize is
- A. 16.7%
- B. 20%
- C. 80%
- D. 83.3%
In sheep production, tapeworm could be controlled by
- A. dusting
- B. spraying
- C. dipping
- D. drenching
Formation of blisters on the mouth and the skin around the hoof of farm animals is a symptom of
- A. rinderpest
- B. anthrax
- C. Newcastle disease
- D. foot and mouth disease
The diagram below illustrates a tool used in animal production. use it to answer this question.

The illustrated tool is used for
- A. castrating the bull calf
- B. cutting the horns of the animal
- C. collecting semen from the bull
- D. identifying the animal
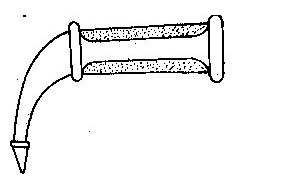
The diagram above illustrates a tool used in animal production. use it to answer this question.
The illustrated tool is
- A. an elastrator
- B. a burdizzo
- C. an electric dehorner
- D. an artificial vagina
An advantage of zero-grazing is that it
- A. requires a lot of labour
- B. prevents livestock from physical exercises
- C. prevents depletion of pasture
- D. increases the cost of pasture management
Feeds that have more than 18% fibre are classified as
- A. concentrates
- B. additives
- C. supplements
- D. roughages
If 0.7kg of feed was fed to chicks per week, determine the cost of feeding the birds for 6 weeks. (1kg of feed costs #5)
- A. #4.20
- B. #11.70
- C. #21.00
- D. #30.00


