A secondary reason for keeping dairy cow is for
- A. milk production.
- B. work purposes
- C. mutton production.
- D. breeding purposes
During Artificial Insemination, semen is diluted with glycerol to
- A. provide nutrients for the spermatozoa.
- B. provide antibacterial action to the spermatozoa.
- C. serve as lubricant to the spermatozoa.
- D. buffer the pH of the semen.
Use this information to answer this question, Guinea grass was planted on 40 m x 100 m land with a spacing of 0.5 m x 0.75 m.
If the percentage germination of Guinea grass is 80%, determine the plant population.
- A. 1,200
- B. 4,266
- C. 6,400
- D. 8,533
Use this information to answer this question, Guinea grass was planted on 40 m x 100 m land with a spacing of 0.5 m x 0.75 m.
Determine the population of the Guinea grass
- A. 1,500
- B. 5,333
- C. 8,000
- D. 10,666
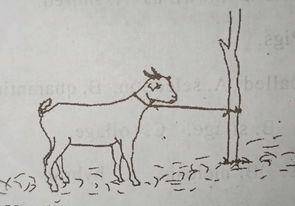
The management practice is mainly done to prevent the animal from?
- A. attacking the farmer
- B. attacking other animals
- C. roaming about
- D. destroying crops
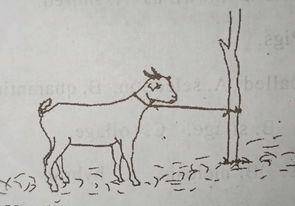
The illustrated method above is?
- A. paddocking
- B. hobbling
- C. ranching
- D. tethering

The pie chart above illustrates the record of sales of a livestock farmer. Study it carefully and use it to answer this question.
In apiculture, honey production is carried out by the
- A. brood
- B. worker
- C. queen
- D. drone

The pie chart above illustrates the record of sales of a livestock farmer. Study it carefully and use it to answer this question.
If the total income of the farmer is ₦1,544,200.00, calculate the income for dairy products.
- A. ₦1,962,514.00
- B. ₦4,040,470.00
- C. ₦5,194,890.00
- D. ₦6,002,984.00

The pie chart above illustrates the record of sales of a livestock farmer. Study it carefully and use it to answer this question.
What is the percentage contribution of dairy products?
- A. 17%
- B. 35%
- C. 45%
- D. 52%
The use of local herbs, shrubs and roots to treat sick animals is described as
- A. orthodox veterinary practices.
- B. trado-veterinary medicine
- C. ethno-veterinary practices
- D. pathological practices
Natural immunity in young farm animals could be acquired from
- A. vacination
- B. colostrum
- C. antibiotics
- D. disinfection
In ruminants, volatile fatty acids are produced in the
- A. rumen
- B. reticulum
- C. omasum
- D. abomasum
The causative organism of contagious abortion in cattle is called
- A. Brucella abortus
- B. Brucella suis
- C. Bacillus anthracis
- D. Salmonella sp
Which of the following feed ingredients contains the highest amount of protein?
- A. Whole maize
- B. Groundnut cake
- C. Wheat offal
- D. Fish meal
Which of the following diseases is transmitted by tick?
- A. Babesiosis
- B. Coccidiosis
- C. Sleeping sickness
- D. Night blindness
Farm animals with four-chambered stomach are referred to as
- A. ruminants
- B. pseudoruminants
- C. monogastrics
- D. omnivores
Specimen K (Head of cock)
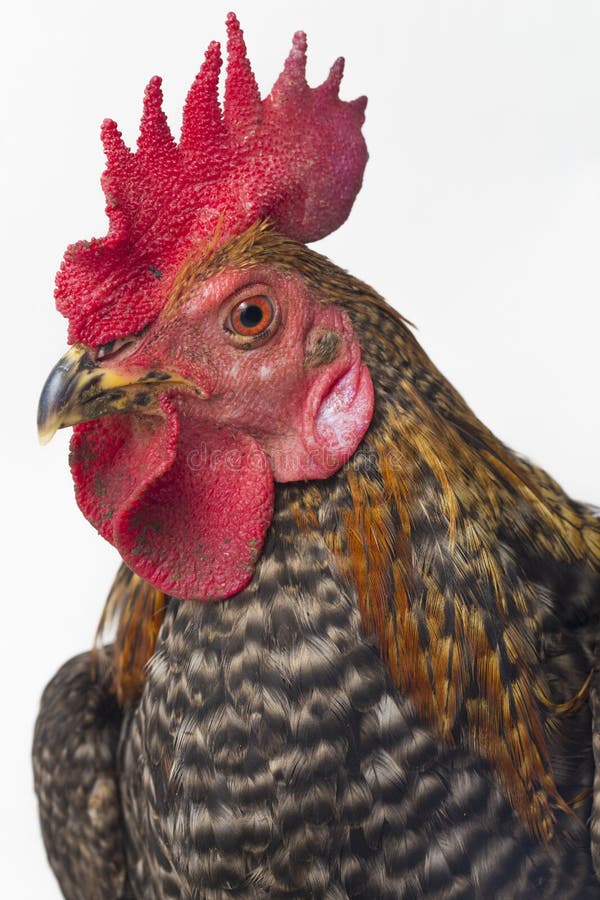

(a) Draw and label five parts of specimen K.
(b) Mention one function of each of the labelled parts of specimen K.
(c) Mention two management practices that could be carried out on specimen K.
Specimen L (Pair of scissors)
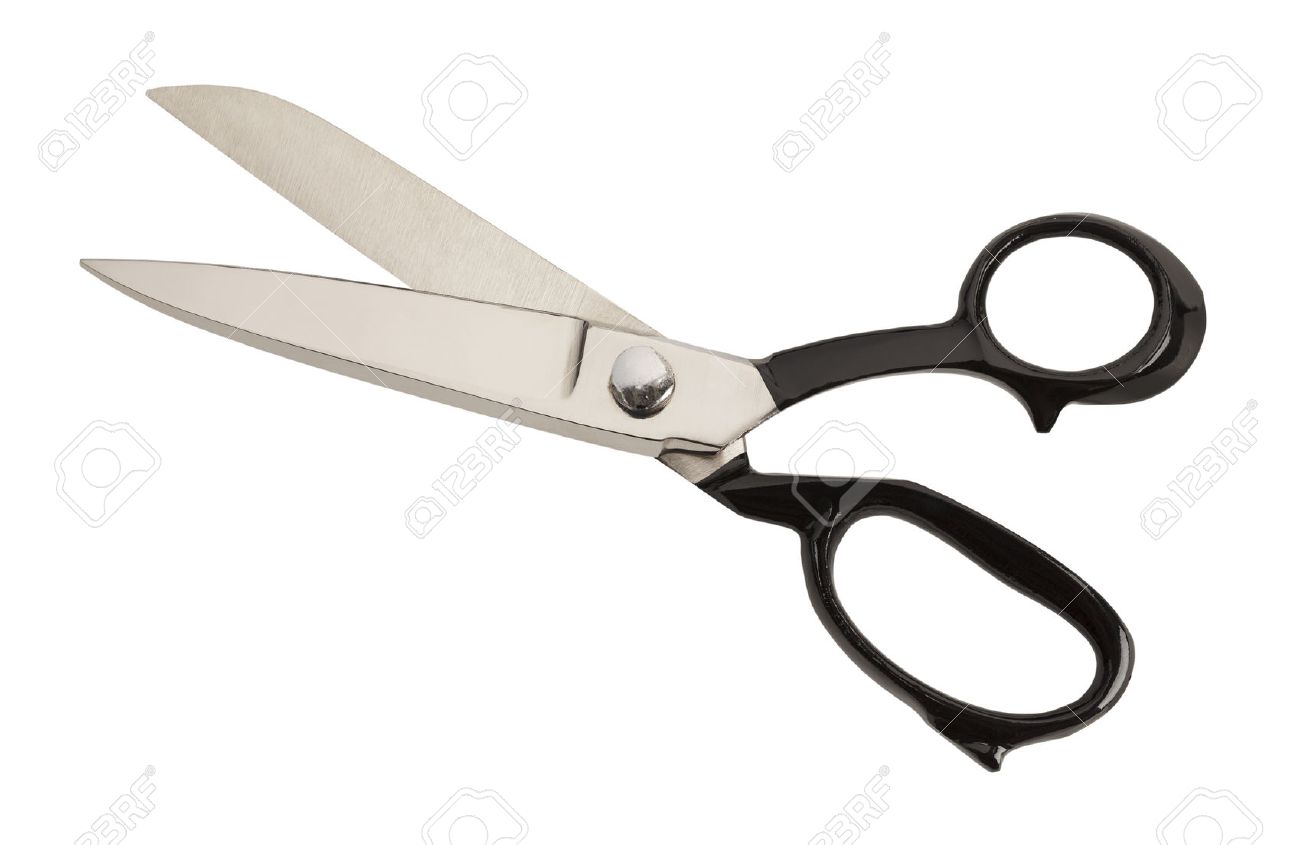

(d) Name one toll which could be used in place of specimen L to carry out the management practices on specimen K.
Specimen H (Plastic bucket)
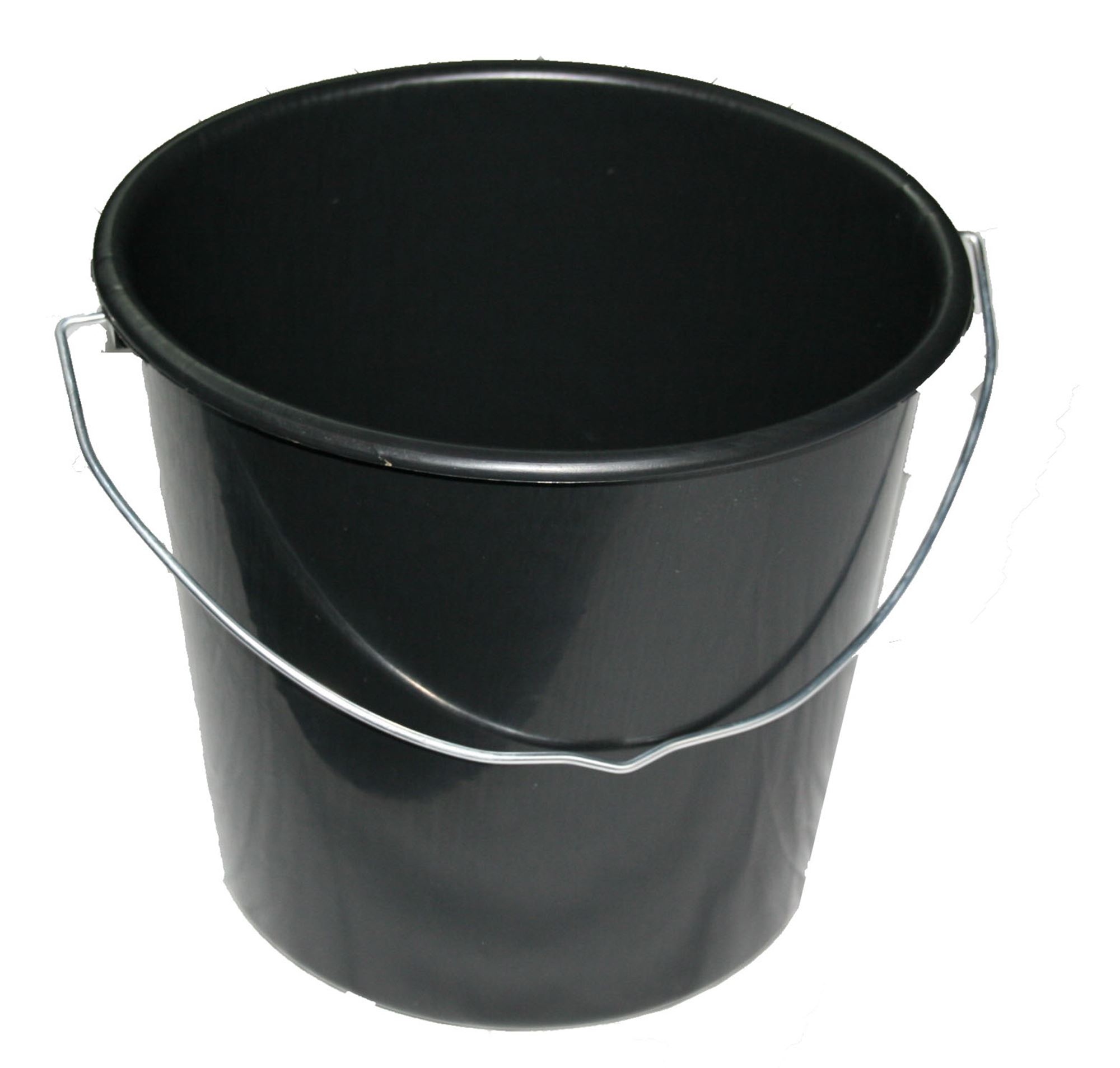

(a)(i) State five ways in which specimen H could be used in poultry production.
(ii) Mention two advantages of using specimen H in animal production
(iii) State two disadvantages of using specimen H in animal production.
Specimen I (Mercury in glass thermometer)
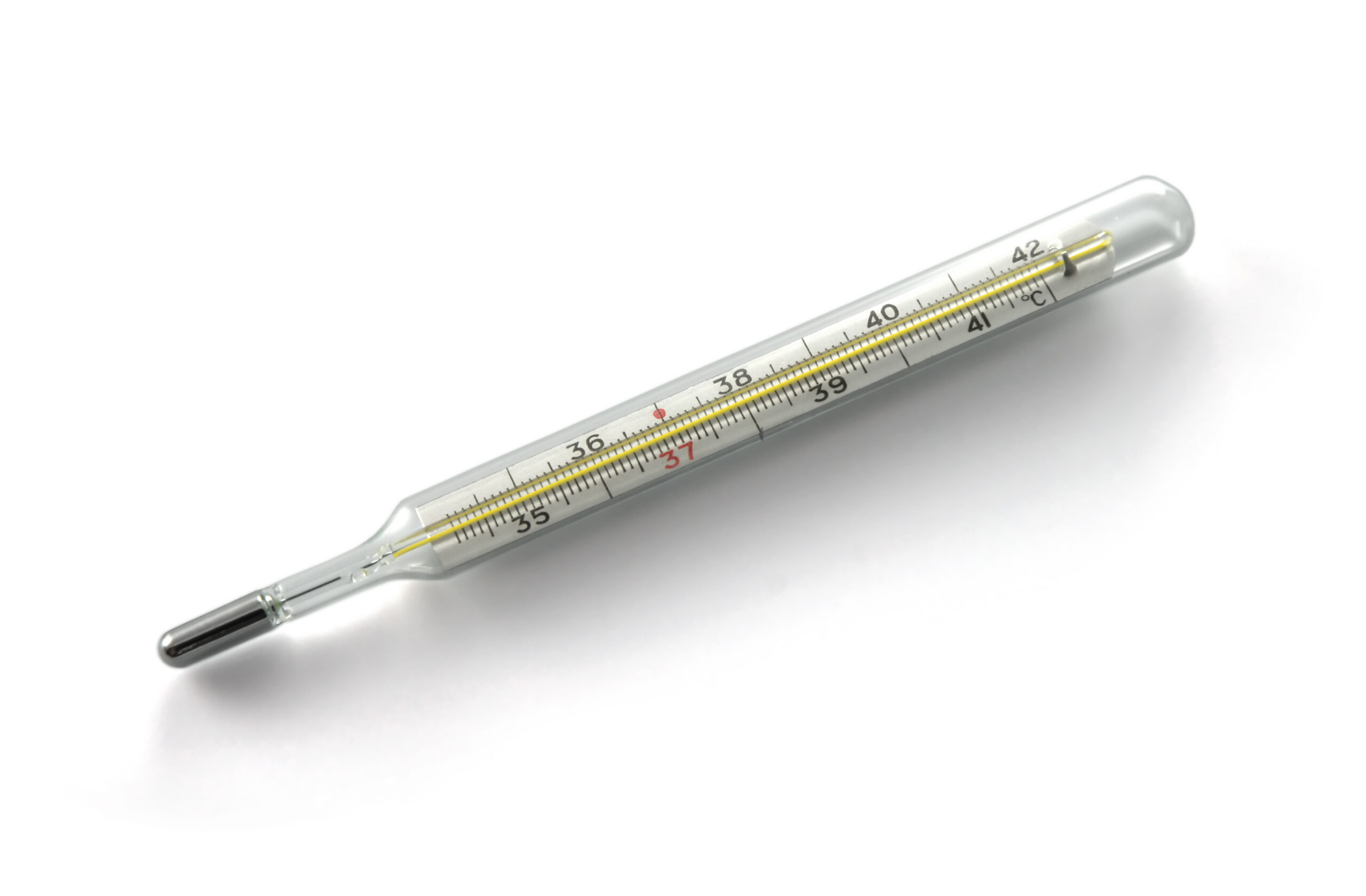

(b) Give one reason for using specimen I in the brooding of chicks
Specimen J (Ear tag)

(c)(i) State two ways in which the use of specimen J is important in animal production.
(ii) Name three farm animals on which specimen J could be used.
Specimen E (Land snail)
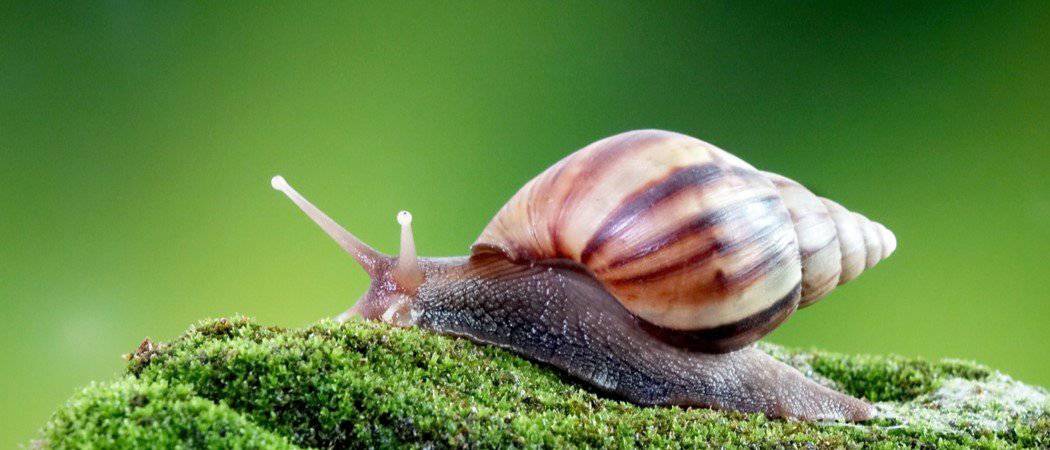

(a)(i) Name two external parts of the body of specimen E.
(ii) State five which could be derived from rearing specimen E.
(iii) Name three pests that could attack specimen E.
Specimen F (Bamboo)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-grow-golden-bamboo-5077107-hero-50c7b729a702412b8e106469b2431368.jpg)
(b)(i) State three uses of specimen F on an animal farm.
(ii) Give two disadvantages of using specimen F on an animal farm
Specimen A (Dry groundnut haulm)
(a)i. Outline the procedure for obtaining specimen A.
(ii) State three benefits that farm animals could derive from feeding on specimen A.
Specimen B (Guinea grass)
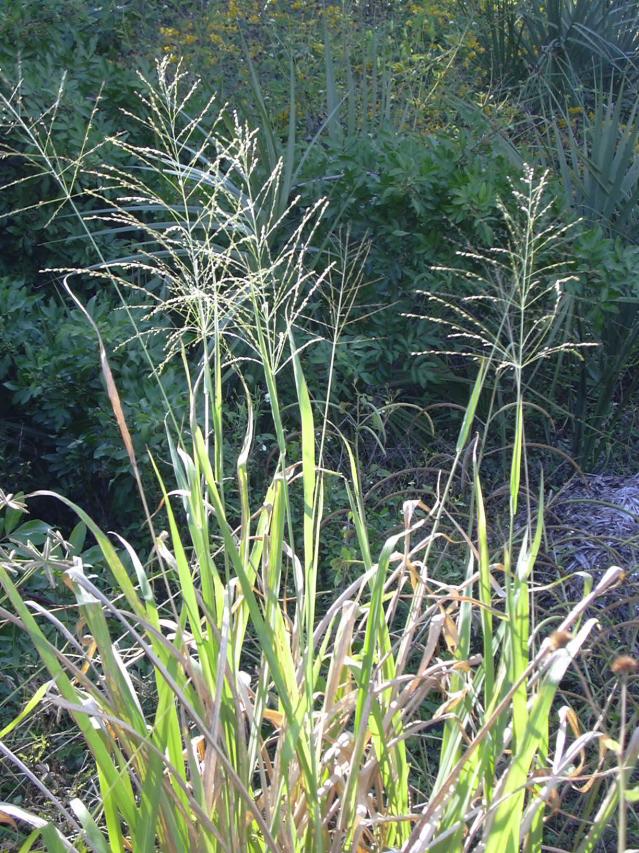

(b)(i) Mention two each that could be used to propagate specimen B;
(ii) preserve specimen B.
Specimen C (Kitchen knife)
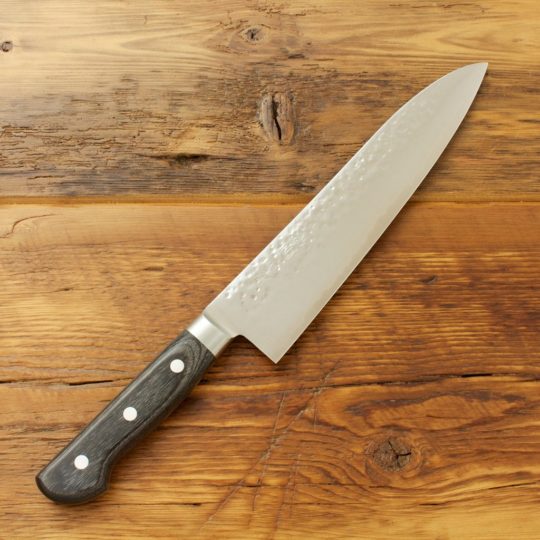

(c) State four of specimen C in animal production
(a)i) Explain the term brooding as used in animal husbandry.
(ii) State four routine activities which are carried out in a brooder house.
(b) State four effects of parasites in livestock production.
(c) Mention four ways of controlling liver fluke in sheep production.
(d) Define the term artificial insemination as used in animal production.
(ii) State four advantages of artificial insemination in cattle production.


