(a) Outline the steps involved in processing specimen P into blood meal.
(b) Name two nutrients supplied by blood meal.
(c) Name two types of housing units for keeping specimen Q.
(d) Mention four products that could be obtained from specimen Q.
(e) Name two ectoparasites that could infest specimen Q.
(a) State three disadvantages of using specimen J (Hurricane Lantern) in a poultry house.
(b) Mention two precautions that should be taken using specimen J.
(c) State three uses of specimen K (Snail).
(d) Mention three feedstuffs that could be used in feeding specimen K.
(e) Enumerate four uses of specimen L (knife) on an animal farm.
(a) Mention three nutrients that could be found in specimen G.
(b) List three ways of preserving specimen G.
(c) State two functions of specimen H in farm animals.
(d) Describe two features of specimen H which enables it to perform the functions stated in 2(c) above.
(e) Name three farm animals which possess specimen H.
(a) Stat three ways in which specimen A (Tapeworm) is of economic importance.
(b) State four ways of controlling specimen A
(c) List three nutrients contained in specimen B (Fish meal)
(d) Name two ectoparasites that could infest the farm animal from which specimen C (Hide of cattle) was obtained.
(e) Mention three uses of specimen C
(a) Mention three equipment used in incubation of eggs
(b) State five measures a livestock farmer could adopt to control diseases on the farm
(c) enumerate four advantages of artificial insemination
(d) Discuss two methods of animal improvement.
(a) Explain each of the following terms as used in animal nutrition (i) ration (ii) balanced diet (iii) maintenance ration (iv) production ration (v) malnutrition.
(b) Give two uses of each of the following animal products: (i) honey (ii) wool (iii) horn (iv) milk (d) egg.
(a) State five objectives of animal improvement.
(b) Mention live signs that indicate that a pregnant animal is approaching parturition. (c) Name two disease causing organisms in livestock production.
(d) copy and complete the table below:
| Nutrients | One Function | One deficiency symptom |
| Calcium | ||
| Iodine | ||
| Vitamin A | ||
| Vitamin E |
(a) Mention four parasites of farm animals.
(b) Enumerate five ways in which the keeping of ruminants is important to the economy of your country.
(c) List In management practices undertaken in caulk production.
(d) State two ways in which each of the following management practices is important: (i) brooding (ii) debeaking (iii) culling.
(a) State five ways of improving pasture.
(b) Name live organs of the digestive system of a. rabbit.
(c) State five precautions that should be taken in dipping of sheep.
(a) State five management practices that are carried out daily on a livestock farm
(b) Mention five devices that could be used in restraining farm animals.
(c) Name four structures used for housing livestock.
(d) Outline the steps involved in branding cattle.
Farm animals producing milk, egg and wool would require
- A. maintenance ration
- B. balance ration
- C. weaning ration
- D. production ration
Which of the following disease would directly affect milk production in cows
- A. Mastitis
- B. Rinderpest
- C. Trypanosomiasis
- D. Tuberculosis
The fundamental principles underlying animal breeding is based on
- A. genetics
- B. management
- C. physiology
- D. selection
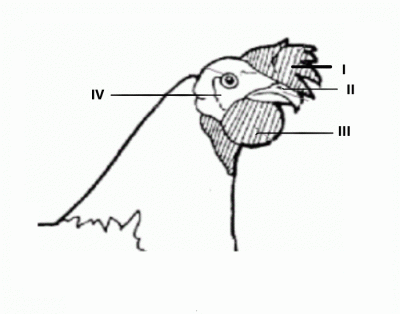
Use the diagram below to answer questions 36 and 37

Which of the labelled part is used to determine a good layer?
- A. I and II only
- B. II and III only
- C. I and III only
- D. II and IV only
Which of the following farm animals is a monogastric?
- A. Bullock
- B. Boar
- C. Heifer
- D. Wether
The endoparasite that creates sores in the liver and lungs of farm animals as it bores through them is
- A. hookworm
- B. pinworm
- C. roundworm
- D. tapeworm
Which of the following statements about ovulation in rabbits is correct?
- A. Eggs are released every 21 days
- B. Eggs are released every 26 days
- C. Eggs are released in the absence of a buck
- D. Eggs are released in the presence of a buck
If the oestrus cycle of a goat is 27 days, how many times will it come on heat in a year?
- A. 14 times
- B. 28 times
- C. 30 times
- D. 60 times
Which of the following factors affects the productivity of pasture? I Soil fertility II. Climate III. Weeds
- A. I and II
- B. I and III only
- C. II and III only
- D. I, II and III
A disadvantage of prolonged inbreeding in farm animals it that it leads to
- A. reduced vigour among offspring
- B. increased vigour among offspring
- C. production of pure breeds
- D. production of animals with uniform characteristics