(a)(i) Mention two forms in which specimen J (Guinea Grass) could be preserved.
(ii) State three qualities of each of the preserved forms of specimen J mentions in 4(a)(i)
(b) State three advantages of growing specimens J and K (Pueraria) together on a pasture.
(c) List four management practices that could be adopted to improve a pasture on which specimen J and K are grown.
(a) State four ways of controlling specimen G (Rat) on an animal farm.
(b) State four effects of specimen H (Tick) on cattle.
(c) Mention three other organisms which have similar effects as specimen H on farm animals.
(d) State four ways of controlling specimen H.
(a) Give four reasons why farmers keep specimen E.
(b) Mention two products that could be obtained from specimen E.
(c) If specimen E was serviced on 12th May 2016 and conceived on the same day, calculate the expected kindling date.
(d) Sate two ways of controlling ear manage on specimen E.
(e) Mention two endoparasites and two ectoparasites that could infest specimen E.
Study specimen C(Cattle Hoof) ,D ,E(Rabbit) and F and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Mention two other farm animals from which; (i) specimen A (Chicken Egg) could be obtained (ii) specimen B (Cattle Horn) could be obtained (iii) specimen C could be obtained
(b) State four ways in which specimen A is important.
(c) State one function of each specimen B and C in farm animals
(d) List three products that could be obtained from specimen B.
(a) Name five agents involved in the marketing of animal products.
(b)(i) Define the term pasteurization as used in milk processing. (ii) State two ways in which pasteurisation of milk is important.
(iii) List four milk products.
(c) State four factors that affect the yield of milk in cows.
(d)(i) Give one reason why it is important to starve an animal before slaughtering. (ii) List two pre-slaughtering activities.
(a) State five differences between the digestive systems of a goat and a chicken.
(b) Explain each of the following terms as used in animal production:
(I) rumination;
(ii) coprophagy.
(c) Give one reason for carrying out each of the following practices in livestock production:
(i) creep feeding; (ii) steaming-up; (iii) flushing.
(d)(i) State four ways in which rangelands are important. (ii) List four practices that could be carried out to improve pastures.
(a)(i) List five external parts of a cock. (ii) Name three viral diseases that could affect poultry.
(b) State five signs that could be observed in a sick farm animal.
(c) Explain each of the following terms as used in livestock production: (i) drenching; (ii) dipping.
(d) Name three body systems in farm animals.
(a) Name four parts of the reproductive system of each of the following farm animals: (i) bull; (ii) hen.
(b) Give one function of each of the parts named in 3(a).
(c) Describe the process of cassava tuber in the mouth of a pig.
(a) State three ways in which each of the following factors hinders livestock production in West Africa: (i) breeding; (ii) nutrition; (iii) healthcare; (iv) government policy; (v) finance.
(b) Mention five factors that affect productivity of pastures.
(a) Explain the term ration as used in animal production.
(b) Explain how each of the following factors influence feed formulation for farm animals: (i) physiological status of animal;
(ii) age of animal; (iii) purpose of production; (iv) availability of feed ingredients.
(c) Describe the process of preparing palm kernel cake.
(d) Give two differences between broiler starter mash and broiler finisher mash.
Which of the following agents usually sells animal products in large quantity
- A. consumer
- B. producer
- C. retailer
- D. wholesaler
In rabbit production, nesting is a sign that the animal is approaching
- A. conception
- B. ill-health
- C. ovulation
- D. parturition
Malnutrition in animals could result in
- A. anthrax
- B. brucellosis
- C. erysipelas
- D. ketosis
The alimentary canals of fowl and pig end respectively as
- A. rectum an cloaca
- B. caeca and cloaca
- C. colon and rectum
- D. cloaca and rectum
During artificial insemination, the arge rubber tube used in introducing semen into the vagina of the female is called
- A. catheter
- B. ejaculator
- C. insemination machine
- D. speculum
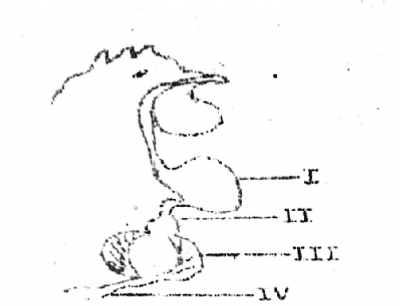
Digestive enzymes are secreted in the parts labeled
- A. I and II only
- B. II and III only
- C. II and IV only
- D. I, II and IV only
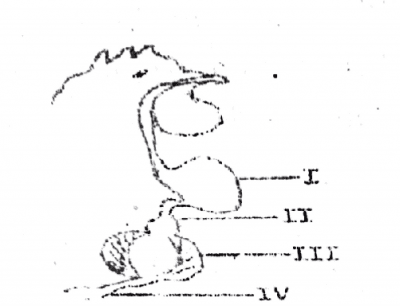
The part labeled III is used for
- A. ingesting food
- B. grinding food particles
- C. storing food materials
- D. absorbing food nutrients
The diagram below illustrates a portion is the digestive system. Study it carefully and use it to answer questions 33, 34, and 35.
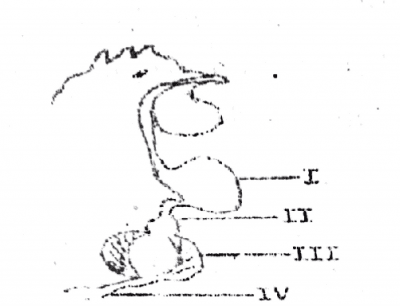
The part which functions as temporary storage for food is labeled as
- A. I
- B. II
- C. III
- D. IV
Which of the following activities are routine management practices in animal husbandry? I Feeding II. Slaughtering III. Vaccination
- A. I and II only
- B. I and III only
- C. II and III only
- D. I, II, and III
To control the apread of diseases on a farm, the farmer needs to
- A. Isolate sick animals
- B. vaccinate sick animals
- C. introduce sick animals
- D. quarantine sick animals
A sow was served on the 7th July, 2012 and it concieved on the same day. What was the expected farrowing date of the sow?
- A. 7th October, 2012
- B. 10th October, 2012
- C. 31st October, 2012
- D. 27th April, 2013


