Specimen K (Head of cock)
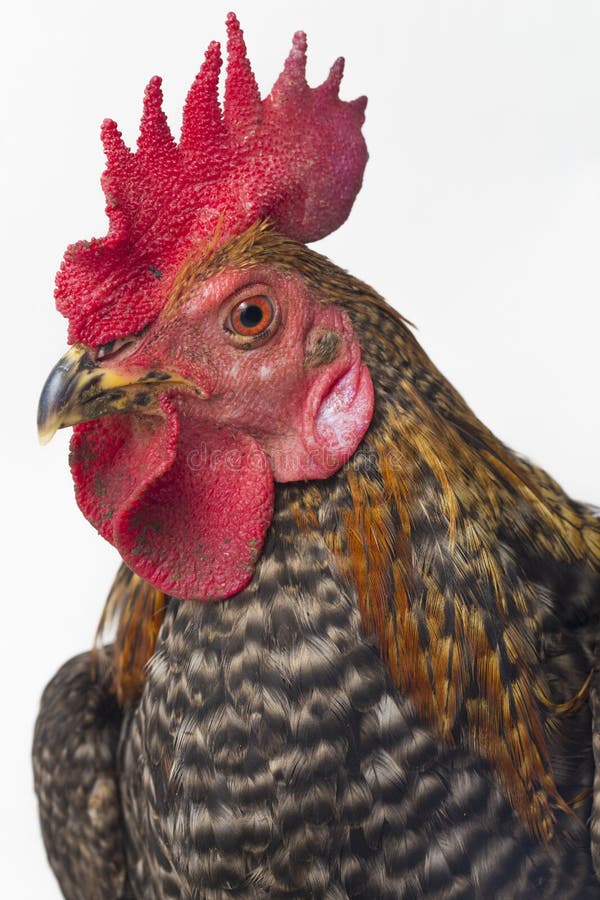

(a) Draw and label five parts of specimen K.
(b) Mention one function of each of the labelled parts of specimen K.
(c) Mention two management practices that could be carried out on specimen K.
Specimen L (Pair of scissors)
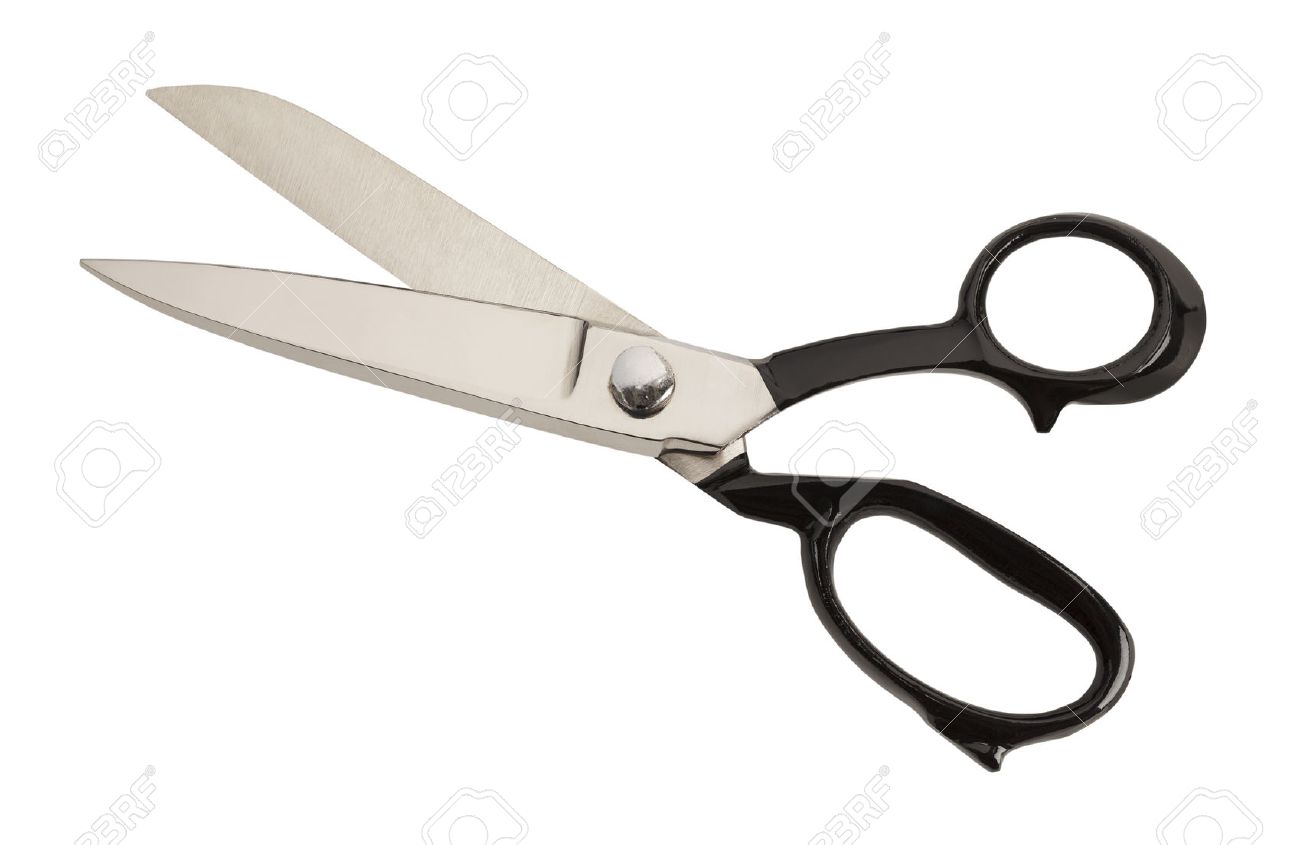

(d) Name one toll which could be used in place of specimen L to carry out the management practices on specimen K.
Specimen H (Plastic bucket)
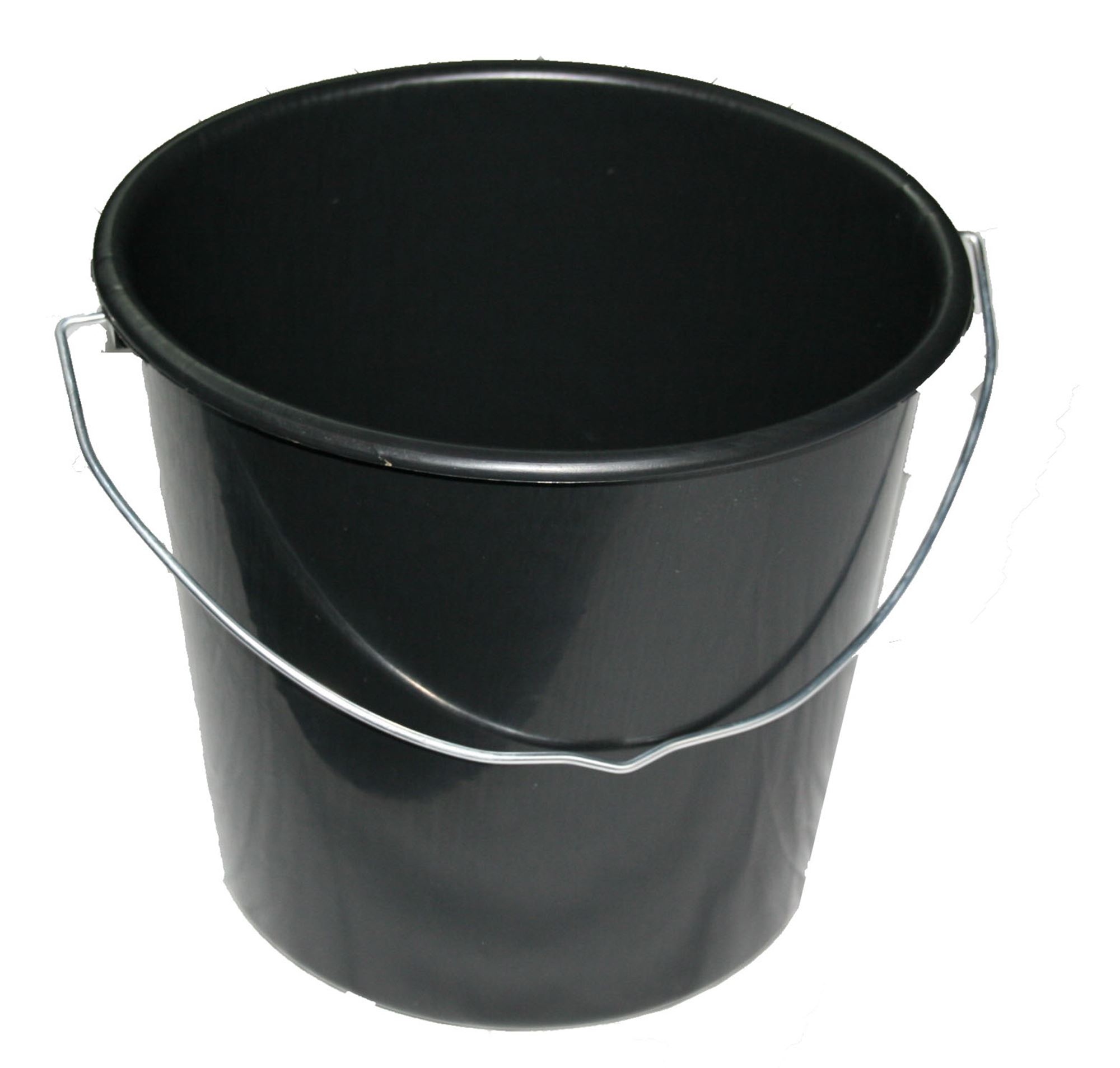

(a)(i) State five ways in which specimen H could be used in poultry production.
(ii) Mention two advantages of using specimen H in animal production
(iii) State two disadvantages of using specimen H in animal production.
Specimen I (Mercury in glass thermometer)
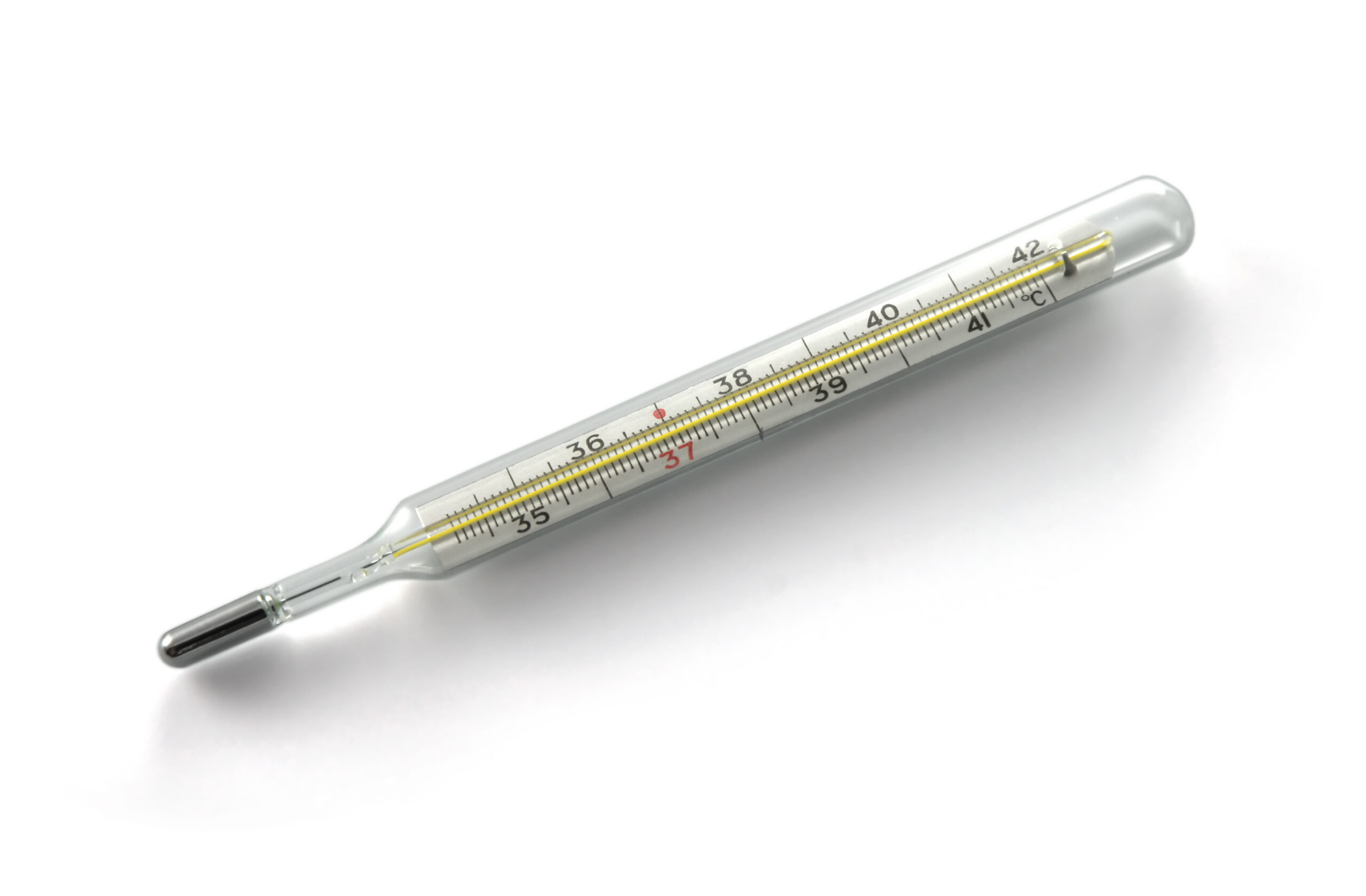

(b) Give one reason for using specimen I in the brooding of chicks
Specimen J (Ear tag)

(c)(i) State two ways in which the use of specimen J is important in animal production.
(ii) Name three farm animals on which specimen J could be used.
Specimen E (Land snail)
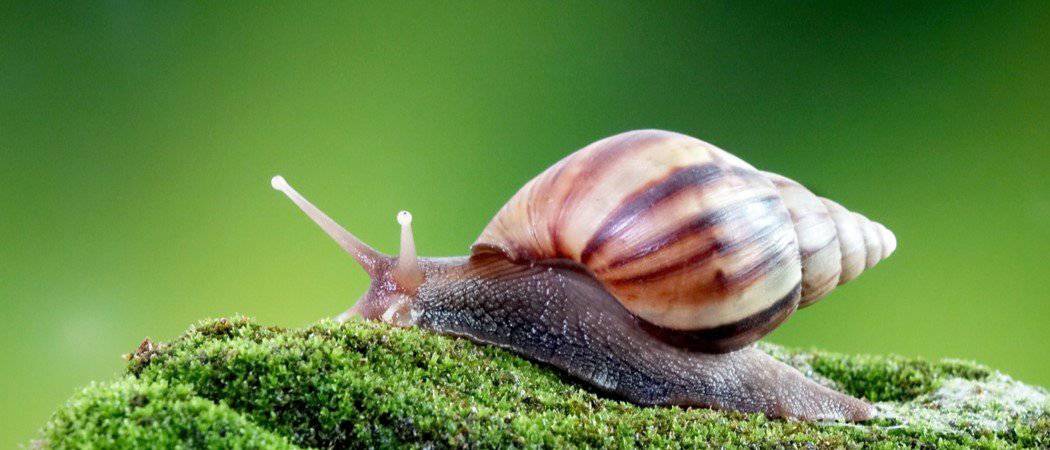

(a)(i) Name two external parts of the body of specimen E.
(ii) State five which could be derived from rearing specimen E.
(iii) Name three pests that could attack specimen E.
Specimen F (Bamboo)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-grow-golden-bamboo-5077107-hero-50c7b729a702412b8e106469b2431368.jpg)
(b)(i) State three uses of specimen F on an animal farm.
(ii) Give two disadvantages of using specimen F on an animal farm
Specimen A (Dry groundnut haulm)
(a)i. Outline the procedure for obtaining specimen A.
(ii) State three benefits that farm animals could derive from feeding on specimen A.
Specimen B (Guinea grass)

(b)(i) Mention two each that could be used to propagate specimen B;
(ii) preserve specimen B.
Specimen C (Kitchen knife)

(c) State four of specimen C in animal production
(a)i) Explain the term brooding as used in animal husbandry.
(ii) State four routine activities which are carried out in a brooder house.
(b) State four effects of parasites in livestock production.
(c) Mention four ways of controlling liver fluke in sheep production.
(d) Define the term artificial insemination as used in animal production.
(ii) State four advantages of artificial insemination in cattle production.
(a) Explain each of the following terms as used in the slaughtering of farm animals:
(i) scalding
(ii) singeing:
(iii) evisceration.
(b) Name four agents involved in the marketing of farm animals and animal products
(c) State five marketing functions that could be performed to facilitate the sale of chicken and eggs.
(d) Name three stages in the life cycle of a roundworm.
(e) Mention two methods of animal improvement.
(a) State four ways in which livestock 1s important
(b)i. Mention sIx organs associated with the digestive system in rabbits.
(ii) State two functions of the alimentary canal in livestock
(c)i. State lour functions of the liver in farm animals
(ii) Mention two parasites that could be found in the liver of cattle
(d) State two differences between the digestive s systems of a goat and a rabbit
(a) Mention five ways of preventing malnutrition in farm animals.
(b) Discuss rickets in farm animals stating two points each under the following headings.
(i) causes:
(ii) symptoms:
(iii) control measures
(iv) animals which could be affected
(c) Explain the term additive as used in animal nutrition
(d) State five reasons why additives are included in animal feed
(a) Complete the table below on forage crops
| Botanical name | Common name | Types of forage |
| Pennisetum purpureum | (i) | Grass |
| Calopogonium mucunoides | (ii) | (iii) |
| (iv) | stylo | (v) |
| Panicum maxinium | (vi) | (vii) |
| Mucuna utilis | (viii) | Legume |
(b)i. Define the term pasture
ii. State four ways in which grass-legume mixture is important in livestock production
(c) State six characteristics of rangelands
(a) State 6 activities that could be carried out in the brooding of chicks
(b) Explain each of the following management practices in poultry production
i. deworming
ii. culling
iii. debeaking
iv. delousing
(c) State four signs of ill health in poultry
(d) Mention to organs in the circulatory system of farm animals
The diagram below illustrates the life of an endoparasite of livestock. Use it to answer the question below

The stage of the life cycle labelled II enters the secondary host is called
- A. bladder worm
- B. miracidium
- C. sporocyst
- D. redia
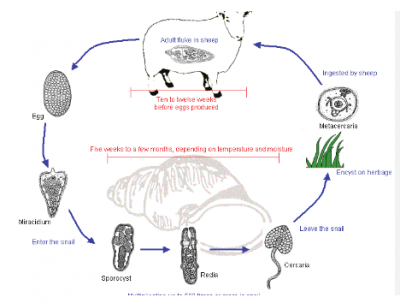
The diagram above illustrates the life of an endoparasite of livestock. Use it to answer the question below
The secondary host of the parasite is
- A. pig
- B. human
- C. water snail
- D. domestic fowl
The diagram below illustrates the life of an endoparasite of livestock. Use it to answer the question below

The diagram illustrates the developmental stage of
- A. liver fluke
- B. tapeworm
- C. roundworm
- D. hookworm
Which of the following animals is usually classified as a non-traditional farm animal
- A. cattle
- B. goat
- C. pig
- D. snail
The extent to which a farm animal readily consumes a feed is referred to as
- A. Acceptability
- B. Digestability
- C. Salivation
- D. utilization
Formation of the eggshell membrane occurs in the
- A. infundibulum
- B. isthhhmus
- C. magnum
- D. uterus
The meat of a calf that is less than six months old and fed exclusively on milk is called
- A. beef
- B. chevon
- C. mutton
- D. veal
Grass legume mixture for pasture production is used to
- A. Supply additives to animals
- B. Control disease outbreak
- C. Reduce energy level of forage
- D. Improve nutrient level of forage
The background below illustrates an organ of a farm animal. Use it to answer the question below.

This synthesis of milk occurs in the part labeled
- A. I
- B. II
- C. III
- D. IV
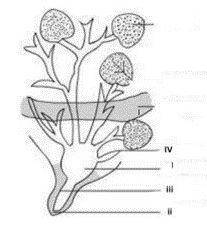
The diagram above illustrates an organ of a farm animal. Use it to answer the question below.
The part labeled III is the?
- A. small duct
- B. large duct
- C. gland cistern
- D. teat cistern
Which of the following measures could be used to maintain productivity of pasture
- A. mulching
- B. crop rotation
- C. Optimum stocking rate
- D. spraying with herbicides


