SECTION B
Answer all the questions in this section
Study specimens L, M, P, and Q and answer questions 3(a) to 3(d).
(a) Name the region of the human body where each of specimens L and Q are located.
L:
Q:
b(i) State four observable differences between specimens L and Q.
| L | Q |
(ii) State four observable similarities between specimens L and Q.
c(i) Name two bones each that articulate with specimens M and P.
(ii) Name one vertebra each that is located and after each of specimens L and Q in the vertebral column.
Before After
L: …………………………… ………………………………
Q: ………………………….. ……………………………….
(d) Complete the table below by using tick (✔) to indicate presence and cross (X) to indicate absence of the following features in each of specimens L, M, P and Q.
| Specimen | Features | |||
| Neural canal | Rounded head | Neural spine | Long shaft | |
| L | ||||
| M | X | |||
| P | ||||
| Q | ✔ | |||
Study specimens F, H and K and answer questions 2(a) to 2(d).
(a) State four functions of specimen H to the plant from which it was obtained.
b(i) State one function each of specimen F and K to the plants from which they were obtained.
F:
K:
(ii) Give one reason for the answers in 2b(i)
F:
K:
(iii) What part of the plant is modified for the function stated in 2b(i)?
F:
K:
c(i) State four observable differences between specimens F and K.
| F | K |
(ii) State one similarity between specimens F and K.
(d) Make a drawing; 6 cm to 8 cm long of the specimen H and label fully.
SECTION A
Study specimens B, D and E and answer questions 1(a) to 1(f).
(a) Name the phylum and class of the organism that possesses specimen D.
Phylum:
Class:
(b) State three observable features of Specimen B.
c(i) Give three functions of specimen B to the organism from which it was obtained
(ii) State one function each of specimens D and E to the organism from which they were obtained.
D:
E:
(iii) Mention one adaptation each of specimens D and E to the function stated in 1c(ii)
D:
E:
d(i) Use the office pin provided to prick the dark green structure attached to specimen B. Touch the fluid oozing from the structure with each of the red and blue litmus
papers at intervals. Record the observations and inferences on the table below:
| Test | Observation | Inferences |
| Red litmus paper + fluid | ||
| Blue litmus paper + fluid |
(ii) Give three functions of the fluid tested in 1d(i) to the organism that possesses it.
e(i) Name the biological system in the body of vertebrates that specimens D and E belongs to.
(ii) Which of specimens B, D or E is absent in humans?
f(i) Name the mode of feeding of the organism that possesses specimen E.
(ii) Name one type of food that the organism that possesses specimen D consumes.
SECTION B
a(i)What is competition?
(ii)List two types of competition.
(iii)List four factors that organisms compete for in a habitat.
(iv)Explain briefly the relationship between competition and succession.
b(i)What is structural adaptation?
(ii)State four types of structural adaptations in animals.
(c)List four features of variation in humans that are used in crime detection.
(d)Complete the table below by listing three types of adaptive colouration in animals and give one example each of animals that show the colourations.
| Three types of adaptive colouration in animals | One example of animal that show the type of colouration |
(e) Give three examples of plants found in a tropical Rainforest.
a(i)Complete the table below by stating the type of cell division and the type of set of chromosomes for the listed cells.
| Cell | Type of cell division | set of chromosomes |
| Onion cell | mitosis | |
| Sperm cell | ||
| Pollen grain | ||
| Ovum | ||
| Guard cell | ||
| Cheek cell | diploid |
(ii) What is mitosis?
(b)Explain briefly how parents with blood groups A or B could have an offspring with blood group O.
(c)Explain briefly how genes are involved in the process of evolution.
(a)A piece of raw meat was left in an uncovered bowl for seven days. Use the information to answer questions 3(a) and 3(b).
(i) State four likely changes that would be observed in the meat.
(ii) Name the biological process that led to the changes that are observed in the meat.
(iii)On the table below, list four methods of preserving meat to prevent it from the changes stated in 3a(i) and mention the principle involved in the methods.
| Four methods of preserving the meat | One principle involved in the preservation method |
(iv)Name two environmental factors that may be responsible for the changes in 3a(i)
(b) Name one method of preserving the following food items:
(i) dried maize grains; (ii) fresh tomatoes; (iii) vegetables; (iv) beans; (v) milk
An individual ate a hot and large meal of cassava with salty groundnut soup. The individual was sweating profusely and did not drink water after the meal.
(a) State one role each played by the following organs involved in the activity above:
(i) mouth; (ii) skin; (iii) tongue; (iv) kidney; (v) stomach; (vi) small intestine; (vii) large intestine; (viii) liver.
(b) Name three of the organs listed in 2(a) that contain enzymes needed to breakdown the food.
(c) Name three digestive enzymes that would be involved in the digestion of the meal.
(d) Name two end products of the meal after digestion.
(e)(i) State one effect that the excess salt in the meal might have on the individual.
(ii) State three advantages that the individual would derive from the meal.
(a)State one function each of the following parts of the nephron:
(i) glomerulus (ii)Bowman’s capsule (iii)proximal convoluted tubule (iv) distal convoluted tubule
(b) Complete the table below.
| Organism | Structure for excretion | Form in which waste is excreted by organism |
| contractile vacuole | ||
| Flatworm | ||
| Earthworm | ||
| Cockroach | ||
| Human | Liquid | |
| Stomata pore |
(c) List five excretory products of plants.
Which of the scientists were involved in the study of evolution?
Scientist Famous work
I. Charles Darwin → Preservation of some food with heat
II. Gregor Mendel → Natural selection
III. Jean Baptiste Lamarck → Inheritance of acquired characteristics
IV. Louis Pasteur → Independent assortment of genes.
- A. I and III
- B. II and III
- C. I, II and IV
- D. II. III and IV
In a test, a student paired some scientists with their famous work as shown below. Use it to answer questions 49 and 50.
Scientist Famous work
I. Charles Darwin → Preservation of some food with heat
II. Gregor Mendel → Natural selection
III. Jean Baptiste Lamarck → Inheritance of acquired characteristics
IV. Louis Pasteur → Independent assortment of genes.
The Scientists that are not correctly paired with their famous work are
- A. I and II only
- B. II and III only
- C. I, II and IV.
- D. II, III and IV.
Which type of breeding is represented by industrial melanism in peppered moths?
- A. Artificial selection
- B. Natural selection
- C. Inbreeding
- D. Outbreeding
The male and female gametes which bear genes for inheritance in plants are located in the
- A. anthers and petals
- B. sepals and petals
- C. stamens and pistils
- D. stamens and petals
Mutation leads to evolution because it
- A. kills all organisms where it has occurred.
- B. gives rise to offspring having same characteristics as the parents
- C. does not confer adaptability to the offspring
- D. gives rise to new individuals that differ from their parents
The physical appearance of an organism is described as its
- A. phenotype
- B. genotype
- C. allele
- D. chromosome
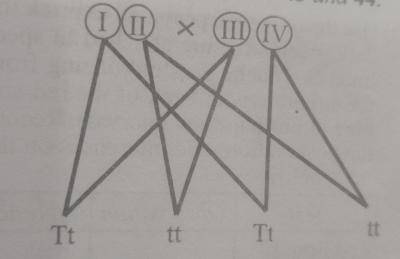
Which of the following statements is correct about the cross?
- A. Both parents are heterozygous
- B. The male is not heterozygous
- C. The female is homozygous
- D. Both parents are homozygous
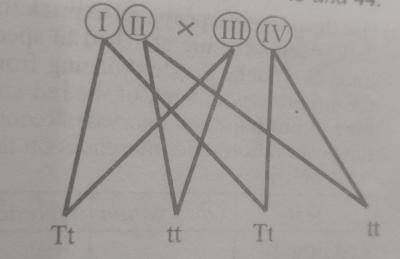
The diagram above is an illustration of genetic cross between two parents. The parental gametes I, II, III and IV gave rise to the offspring below. Study it and answer questions 43 and 44.
Gametes I, II, III and IV, respectively are
- A. T,T,T and t
- B. T, t, t, and t
- C. T, T, t and t
- D. T, t, T and t
A woman with blood group A gives birth to a child with blood group O. Which of the following blood groups cannot belong to the father?
- A. B
- B. A
- C. AB
- D. O
Which of the following statements is correct about the ABO blood group system?
- A. Antigens are located on the surface of white blood cells
- B. Antibodies are located in the blood plasma
- C. Antibodies are located on the surface of the red blood cells
- D. Antigens are located in the blood plasma
Which of the following traits is not inheritable? Ability to
- A. taste P.T.C
- B. roll the tongue
- C. move the ear
- D. roll the eyeball
An individual found a strange bird that is tagged as an endangered specie. What should the individual do?
- A. Kill it
- B. Take it to an aquatic environment
- C. Return it to its natural habitat
- D. Sell it at a very high price
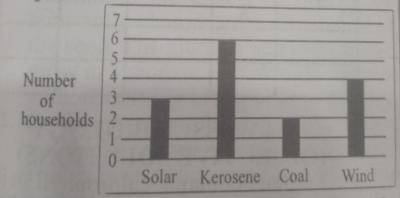
The two sources of energy that would mostly lead to pollution in the community are
- A. solar and kerosene
- B. coal and wind
- C. kerosene and coal
- D. solar and wind


