Specimen G is a paste made from a food material. Carry out the following tests to identify the food substances contained in specimen G. Wash the test tube after each use to ensure that the next sample is not contaminated. All tests and observations should be recorded in a table as shown below.
| Test | observation | inference |
(a) (i) Pour 5 cm/(^3/) of specimen G into a test tube and add three drops of sodium hydroxide solution. Shake two test tube. Record your observation. Then add three drops of copper (ii) tetraoxosulphate (VI) solution (CuSO/(_4/)). Shake the test tube. Record your observations and inference (b) Pour 5 cm/(^3/) of specimen G into a test tube and three drops of Sudan IIl. Shake the mixture. Record your observation and inference (d) To another 5 cm/(^3/) of specimen G add four drops of Fehling’s solution. Shake the test tube. Warm the mixture. Record your observation and inference
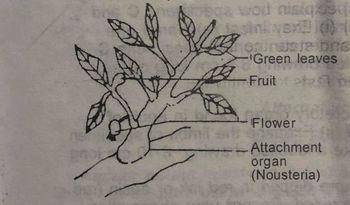
(a) identify specimen D without giving reason (b) (i) State two observable features of specimen D which indicate its mode of nutrition (b) (ii) What is the mode of nutrition cf specimen D? (c) Make a labelled drawing to show features of biological importance of the specimen (d) (i) Examine and identify without reasons specimens E and F
You are provided with specimens A, B and C (a) identify specimens A, B and C without reason.
(b) Make a labelled drawing 6-8 cm long of the longitudinal section of specimen A to illustrate its essential features
(c) (i) Suggest the possible means of pollination of specimen A (ii) Give three reasons for your answer
(d) (i) Name one agent of dispersal each for specimen B and C (ii) Give one reason each for your answer.
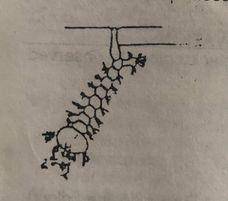
(a) Name the organism represented in the diagram above (b) Name the structure labelled x (c) Into what stage would the organism develop?
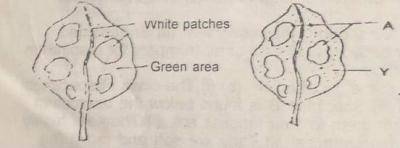
The diagram above illustrates a leaf before and after an experiment stated below. The leaf shown in diagram I was detached from a potted plant which had been exposed to sunlight for 4-5 hours while diagram ll shows the same leaf after the test for starch.
(7) (a) Name the type of leaf used for this experiment (b) Why is this type of leaf most suitable for the experiment? (c) State one precaution that should be taken in carrying out this experiment (d) What would be the colours of the parts labelled X and Y after the test for starch? (e) Suggest the aim of this experiment.
List (a) two plant characteristics (b) two animal characteristics found in Euglena.
(a) Name the vessel that carries blood from the wall of the small intestine to the liver (b) State two similarities in structure between the transport systems in plants and animals.
(a) (i) State one function of plastids to plants (i) Name one plastid found in plants (b) State one function each of (i) mitochondrion (ii) chromosome
(a) What would you observe if a filament of spirogyra is immersed in 0. 1 m sodium chloride solution for about one hour?
(b) Name the process which occurred during the immersion of the spirogyra filament in 0.1 m sodium chloride solution.
(a) List three functions of the kidney.
(b) Make a labelled diagram of the mammalian kidney tubule (nephron)
(c) Describe how the kidney carries out two of the functions listed in (a).
(a) Describe how the floral parts of a named flower are adapted to wind-pollination.
(b) Explain how each of the following behaviours in animals affects the reproduction process: (i) territoriality. (ii) display; (iii) seasonal migration.
(a) Describe an experiment to demonstrate the influence of auxins on the growth of plant shoot.
(b) List three uses of auxins in agriculture.
(c) Describe briefly the mechanism of transmission of impulses through a nerve fibre.
(a) List five morphological features that are characteristic of plant found in each of the following habitats:-(i) tropical rainforest. (ii) savanna. In each case, state function of the features listed in (a) to the plant.
(b) Explain the term: ecological succession
(c) By means of a diagram only, outline the carbon cycle to show the relative importance of the cycle to life in general.
Which of the following processes will not introduce carbondioxide into the atmosphere?
- A. Breathing
- B. Photosynthesis
- C. Respiration
- D. Putrefaction
- E. Burning
The large intercellular air spaces which penetrate the tissues of most hyrophytes provide a pathway through
which
- A. carbondioxide absorbed by leaves can diffuse to the roots
- B. oxygen produced in the leaves can diffuse to the submerged parts
- C. salts absorbed by roots can reach other parts of the plant
- D. plant hormones are transported to various parts
- E. manufactured food is translocated
Which of the following is an example of reproductive adaptation?
- A. Succulent stems of cactus plant
- B. Changing colour of chameleon
- C. Possession of spines by desert plants
- D. Neck colouration in Agama lizard
- E. Leaf-shedding in trees
The theory that new organs or characteristics develop in organisms when there is a need for them was
postulated by
- A. Charles Darwin
- B. Jean Lamarck
- C. Gregor Mendel
- D. Wallace
- E. Louis Pasteur
Which of the following is not true about a bacterial colony growing on an agar plate?
- A. They are visible without the aid of the microscope
- B. Bacterial cells found in one colony often belong to one species
- C. Different colonies have different colours
- D. Only one species of bacterial colony can grow on a culture at any time
- E. Colonies growing on an agar plate under the same conditions must belong to one species


