Specimens I and J are cross-sections of two plants whose cut ends were dipped in red ink or eosin (red dye) for at least 6 hours (a) Observe specimen I with the hand lens provided. Record your observation about the colouring of the tissues by the red ink or eosin.
(a) ldentify specimens E, F, G and H without reason (b) Name one excretory organ found in each o specimens E, F, G and H (c) (i) State the habitats of specimens E and H (i) Examine the limbs of specimen H. List two ways by which specimen H is adapted to the habitat (ii) Make a labelled drawing 8-10 cm long of specimen E
Study specimens A,B, C and D carefully (a) ldentify specimens A and B without reason (b) Name the organism responsible for the damage observed on specimens A and B (c) List two ways by which each of specimens A and B can be properly stored (d) (i) ldentify specimens C and D without reason (i) List one animal or crop each that can be attacked by specimens C and D (ii) Explain how specimens C and D affect the crop or animal they infest (e) Name one way each by which a farmer can control specimens C and D (f) Make a labelled drawing 6-8 cm long of the dorsal view of specimen D.
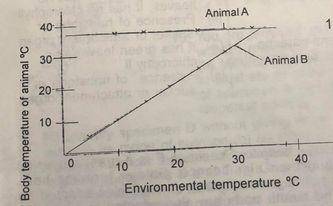
The graph below illustrates the changes in the body temperature of two animal A and B at different environmental temperatures. Study the graph carefully and use it to answer questions (a) to (c) (a) From the graph of the environmental to deductions on the effect of the environmental temperature on the body temperature of the animals indicated as (i) A (i) B (b) Suggest one way by which the animal indicated as B can maintain its body temperature or prevent its body from over-heating (c) Give one example each of an animal whose body temperature can be similarly affected by environmental temperatures cs (i) Animal A (ii) Animal B
List two diseases that may be spread as a result of poor irrigation system.
6. Mention the process by which food can be synthesized in an ecosystem where tnere is no sunlight.
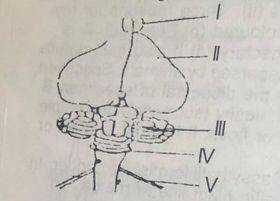
5. (a) Name the parts labelled | – IV (b) Which number indicates a part of the peripheral nervous system?
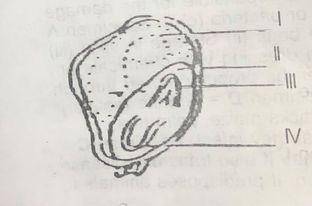
3. (a) Name the parts labelled | – IV (b) In which of the labelled parts is food stored?
2. (a) Name two supporting tissues found in plants (b) Give one function of the Golgi body in the cell.
1. (a) List three features which are essential for cross-pollination to take place (b) State three characteristics
(a) Explain briefly how the process of meiotic division contributes to variation in a population
(b) State Mendel’s first and second laws of inheritance.
(c) A pure breeding brown coloured rat BB was crossed with a pure breeding white rat bb. By means of diagram only, show the genotypes of the offspring up to the second filial generation.
(a) Describe the process of succession in an abandoned farm land.
(b) List seven ways by which micro-organisms can -be controlled to maintain good health.
(a) (i) Give two reasons why termites are described as social insects.
(ii) Name four castes found in the termite nest, stating one of each castes.
(b) Describe five behavioural adaptations of termites which enable them to survive in their environment.
(a) Describe briefly the process involved in the breakdown of glucose in the cell of living organisms to produce energy (AT P)
(b) State two conditions under which glycogen can be converted to glucose to produce energy.
(c) Describe an experiment to demonstrate that oxygen is released by green plants during photosynthesis.
Which of the following statements is not associated with the theory of natural selection?
- A. There is a struggle for existence
- B. There is competition among the offsprings
- C. The weaker offsprings are eliminated
- D. Food and other needs are abundant
- E. Nature selects those that survive to reproduce their kind
What is the significance of the bee dance to other bees?
- A. Warning signal
- B. Presence of food
- C. Mating signal by the male
- D. Soaring the enemies away
- E. Time for nuptial flight
The process by which plants and animals are modified in structure, physiology and behaviour in order to survive is known as
- A. evolution
- B. adaptation
- C. succession
- D. aggregation
- E. hibernation
Which of the following statements about the modifications of pentadactyl fore-limb is not correct?
- A. Wings are modified for flying in birds
- B. Flippers are modified for grasping in sharks
- C. Legs are modified for walking and running in antelopes
- D. Arms are adapted for grasping and holding in human beings
- E. Flippers are modified for swimming in whales


