(a) List four characters which can be transmitted from parent to offspring in man.
(b) State two differences between mitosis and meiosis.
(c) Explain briefly the importance of meiosis and fertilization in the reproduction of organisms.
(d) In a monohybrid cross between a pure breeding plant that produces blue flowers and a pure breeding plant that produces white flowers, the F1 generation produced only blue flowers. By means of labelled cross diagrams, state the type of flowers you would expect if the Fl generation is (i) self-pollinated; (ii) cross-pollinated with a pure breeding plant that produces white flowers. Give reasons for your answers in (d) (i) and (ii).
Explanation
(a) Characters which can be transmitted from parents to offspring in man are:
(i) Tongue rolling
(ii) Sickle cell anaemia
(iii) Colour blindness
(iv) Height (Tallness or shortness)
(v) Haemophilia
(vi) Colour of skin
(vii) Colour of hair
(viii) ColoOr of eyes
(ix) Shape (wrinkle or round).
(b) Two differences between mitosis and meiosis are:
| Mitosis | Meiosis |
|
(1) End of mitosis results in two daughter cells formed from one parent cell. |
-End of meiosis results in formation of one gamete. |
(c)(i) Meiosis has contributed a lot in the development of quality organisms by bringing together good characters from both parents into an offspring. Mostly used in animal husbandry and crops improvement, Meiosis also involves exchange of materials which bring about variation in the offspring.
(ii) Fertilization is the first stage in the formation of a new organism. Without fertilization, it would be impossible to produce new organisms through sexual reproduction. Hence, it has erased the possibility of most organisms going into extinction because most offspring resemble their parents.

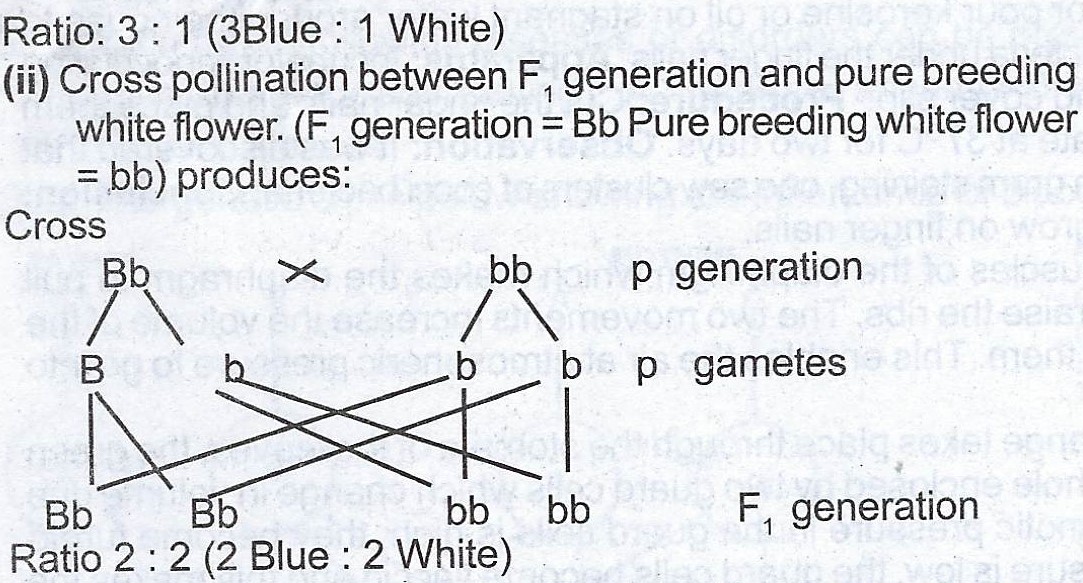
Reasons for the answer in (d)(i):
In F1 generation, all the numbers produced are heterozygous (dominant recessive) blue. When self pollinated, the F2 generation produced three blue offsprings which are homozygous blue, two heterozygous blue and one white.
Reason for (d)(ii):
Two of the offsprings produced are heterozygous blue and two homozygous recessive white (2:2) or (50:50). This result is due to F1 parents
which are heterozygous blue and the pure breeding white flowers which are homozygous recessive white.

