1.Define the following terms: (i) Accommodation (ii) Metamorphosis
2. Why is the wall of the left ventricle of the heart thicker than that of the right ventricle?
3. Why is sugar contained in the urine of a person with diabetes mellitus?
4.Which hormone controls water reabsorption in the kidney?
5. Explain the significance of hemoglobin in respiration
Study the diagram below and use it to answer Question 6

6. (a) What is the aim of the experiment illustrated in the diagram above?
(b) Name the liquid labeled I. (c) Name two materials that can be used as living tissue (d) (i) What would happen to the level of solution inside the living tissue in both A and B if the set-up is allowed to stand for about three hours? (ii) Give a reason for your.answer (c) What is the function of set-up B?
7. (a) What is pest? (b) List three plant pests and name the plant attacked by each
Use the diagram below to answer Question 8

8 (a) identify the organism represented in the diagram
(b) List three features that adapt the organism to its environment.
9. (a) (i) identify specimens A and B without giving reasons. (ii) What are the possible habitats of specimens A and B? (b) Remove the wings of specimen A and make a large labeled drawing 12cm to 15 long of it. (C) In a tabular form, give three differences between specimens A and B (d) Give two economic importance of specimen A and one of specimen B
10. (a) What types of leaves are specimens C,D and E?
(b) () identity the leaf arrangement in specimen D. (ii) What type of venation is exhibited in specimen C?
(c) Observe specimens C and E with a hand-lens. Which one has more stomata? (d) (i) State the likely habitat of the plants from which specimen C was obtained.
(ii) Of what importance are specimens C, D and E to the plant? [1mark] (e) Making use of the hand lens, identify specimens F, G and H
(f) State their modes of nutrition? (g) State two Observable differences between specimens F andG|.
11. (a) identify specimens I,J and K stating organism from which each has been obtained.
(b) List two functions of each of the specimens. (C) Arrange tne specimens in order of evolutionary advancement.
(a) Define the term ” Conservation”.
(b) State three reasons for conservation.
(c) List four methods of conserving each of the following: (i) water (ii) wildlife (iii) forest.
(d) Mention three forest or game reserves in Nigeria.
(a) Make a labelled diagram of the female reproductive organ of a
(i) flowering plan
(ii) mammal (man) .
(b) State the functions of any two of the labelled parts in (a) (i) and (ii).
(c) Compare reproduction in mammals, amphibians and birds with respect to
(i) number of eggs produced
(ii) method of fertilization
(iii) parental care.
(a) Explain the following terms:
(i) first aid
(ii) artificial respiration
(iii) dislocation
(iv) haemorrhage
(b) (i) State three objectives of first aid.
(ii) Explain the procedure for administering the mouth-to-mouth method of artificial respiration.
(c) (i) State three signs of dislocation.
(ii) Name two ways of stopping bleeding from an open wound.
(a) Describe an experiment to compare the water-holding capacity of sandy, loamy and clayey soils.
(b) List three factors that may affect the water-holding capacity of soils.
(c) (i) State the characteristics of sandy and loamy soils.
(ii) What type of vegetation does each support?
Which of the following behavioural patterns describes adaptive colouration?
- A. Counter shadding
- B. Hibernation
- C. Aestivation
- D. Aggregation
- E. Migration
Bees communicate with one another to obtain information about the direction of food source through
- A. complicated set of dances
- B. smell
- C. contract notes
- D. observation
- E. sounds
Which of the following characteristics distinguishes the soldier termite from other members of the caste?
- A. Wingless, strong mandibles and large head
- B. Small head, small thorax and large abdomen
- C. Small head, Wingless, and small thorax
- D. Small head, winged and small thorax
- E. Small mandibles, small head and wingless.
In an inter-species competition, the less successful species usually
- A. reproduce faster
- B. become more active
- C. become domant
- D. occupy more space
- E. become eliminated
In which of the following is the knowledge of genetics not applicable?
- A. Development of high-yielding varieties
- B. Preservation of seeds
- C. Development of early maturing varieties
- D. Development of early maturing seed
In man haemophilia is recessive and sex linked, The
probability of carrier mother and a normal father having a haemophilic male is
- A. 1/4
- B. 1/8
- C. 2/3
- D. 1/2
- E. 1
Which of the following is not a morphological variation
- A. Shape of nose
- B. Colour of skin
- C. Colour of eyes
- D. Ear lobe
- E. Tongue rolling
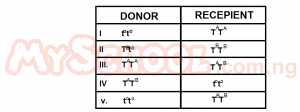
In which of the underlisted blood groupings is agglutination likely to occur during transfusion?
- A. I
- B. II
- C. III
- D. IV
- E. V
One of the use of variation is in
- A. determining the size and weight of an individual
- B. determining paternity
- C. conservation of wildlife
- D. controlling of disease vector
- E. sex determination
Which of the following farm practices can cause loss of soil fertility?
- A. Mulching
- B. Compost application
- C. Use of fertilizers
- D. Terracing
- E. intensive cropping
In palm-wine, yeast acts as a
- A. carrier
- B. culturing agent
- C. preservative
- D. catalyst
- E. sweetening agent
The farming practice by which an exhausted farm land is left for a number of years before cultivation is
known as
- A. crop rotation
- B. continuous cropping
- C. monocropping
- D. bush fallowing
- E. mixed cropping
Crops grown mainly to feed animals are called
- A. forage crops
- B. here crops
- C. wood crops
- D. oil crops
- E. spices
Which of the following factors may not cause over-crowding?
- A. Limited space
- B. Scarcity of food
- C. Reduced birth rate
- D. Lose immigration conditions
- E. Increased birth rate
A habitat with low rainfall, very low humidity, exposed soil with little plant cover, few trees and shrubs is
likely to be
- A. a rain forest
- B. a mangrove forest
- C. a desert
- D. a swamp
- E. an estuarine
Which of the following factors does not affect the distribution of organisms in an aquatic habitat?
- A. Turbidity
- B. Depth of water
- C. Humidity
- D. Temperature
- E. Availability of nutrient


