Study carefully specimens J, K and L and use them to answer questions 4(a) to 4(d).
(a)(i) State the class of each of specimens J, K and L
(ii) State three reasons each for placing each of specimens J, K and L in their classes.
(b) State two structural adaptations possessed by each of specimens K and L for escaping predators.
(c) Make a drawing, 8 – 10cm long of the lateral view of specimen J.
(d) State: (i) two similarities; (ii) two observable differences between specimens J and L.
Study carefully specimens C, D and E and use them to answer questions 2(a) to 2(c).
(a) (i) State the mode of nutrition of specimen D.
(ii) State one way by which each of specimens C, D and E is of economic importance.
(b)(i) Classify specimens C, D and E into their phyla and classes.
(ii) List three observable characteristic features of each of the classes to which specimens C, D and E belong.
(iii) In a tabular form, state two observable differences between C and D.
(C) List four observable features of specimen E that are sensory in nature.
(a) Study carefully specimens A and B and use them to answer questions 1(a) to 1(c).
(a)(i) Name the types of fruit in specimens A and B with reasons.
(ii) Make a drawing, 8-10cm long of the lateral view of specimen B and label fully.
(b) Describe the modes of dispersal of specimens A and B.
(c) In a tabular form, state five differences between specimens A and B.
(a) (i) Describe epigeal germination of a seed.
(ii) In a tabular form, state three differences between epige germination and hypogeal germination.
(b)(i) What is seed dormancy?
(ii) State three ways b which dormancy in seeds can be broken.
(c) State six advantages of using contraceptives in puma populations.
(a) Explain the following terms:
(i) disease
(ii) symptoms of diseases.
(b)(i) List two physical and two chemical barriers that prevent pathogens from penetrating the body of an organism.
(ii) Explain how vaccination protects the body from contracting infectious diseases.
(c) Distinguish between an antibody and a antigen.
(d) Name the causative agents of:
(i) Malaria
(ii) Cholera
(iii) AIDS.
(a) (i) What is a gene?
(ii) Differentiate between the terms genotype and phenotype
(b) Explain the following terms:
(i) hybrid
(ii) pure breeding
(iii) nucleotide.
(c) In garden pea seeds, smooth seed coat is dominant over rough seed coat. With the aid of a genetic diagram, determine the result expected if a homozygous rough pea is crossed with a smooth seed coat plant whose parents were rough coated.
(a) Explain briefly the following terms:
(i) conservation
(ii) endangered species.
(b) State: (i) five reasons why conservation of forests is important;
(ii) four ways by which forest reserves can be conserved.
(c)(i) What is the importance of decomposers in the ecosystem?
(ii) Name one plant and one animal decomposer.
(a) Describe briefly the role of the stomach in digestion.
(b) (i) Name three parts of plants in which food can be stored.
(ii) Give one example in each case.
(c) Explain briefly how the level of sugar in the mammalian blood can be regulated.
(a) Explain briefly four factors that affect the diffusion of substances.
(b) Explain the following terms:
(i) active transport
(ii) transpiration.
(c) State four ways by which plants can reduce high rate of transpiration.
(d) State the features of red blood cells and how these features adapt the cell to perform its functions.

In the diagram, the function of the part labelled 2 is to?
- A. produce egg cells
- B. protect sperms during fertilization
- C. secrete hormones during coitus
- D. protect the developing embryo
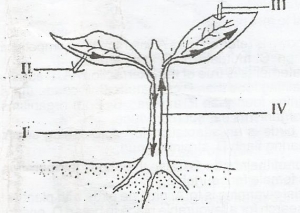
In the diagram, the arrow labelled II represents the
- A. release of oxygen
- B. intake of carbon (IV) oxide
- C. movement of photosynthates
- D. movement of nutrients
Which of the following sequences is the correct evolutionary trend in plants?
- A. Algae → liverworts → mosses → ferns
- B. Liverworts → mosses → ferns → algae
- C. mosses → algae → ferns → liverworts
- D. Ferns → Liverworts → mosses → algae
Bees are of great importance to the farmer because they
- A. provide him with honey
- B. pollinate flowers
- C. sting crop pests to death
- D. destroy flowers by sucking nectar from them
What name is given to a sudden change in a gene or chromosome?
- A. Allele
- B. Genotype
- C. Mutation
- D. Phenotype
Two yellow-flowered hybrid plants each carrying a recessive factor for flowers with green colour were crossed.
Which of the following ratios shows the correct proportion of offspring that have green flowers?
- A. 2 in 2
- B. 1 in 3
- C. 1 in 4
- D. 1 in 5
In a case of complete dominance, what is the phenotypic ratio of the cross Bb X Bb; where B =black and b = white?
- A. 1 black : 1 grey : 2 whites
- B. 1 black : 3 whites
- C. 1 black : 2 blues : 1 white
- D. 3 blacks : 1 white
In the structure of DNA, which of the following statements is true?
- A. The double helix are held together by covalent bonds
- B. Nucleotide is made up of ribose, phosphate and an organic nitrogen compound
- C. Guanine is the opposite of cytosine
- D. Adenine is the opposite of cytosine
Two plants with red flowers were back crossed, which of the following results indicate that the plants are heterozygous
red flowers, where red flowers are dominant?
- A. 75% red and 25% white
- B. 50% red and 50% white
- C. 100% white
- D. 100% red
Which of the following diseases is transmittable through genes?
- A. HIV /AIDS
- B. Sickle cell anaemia
- C. Diabetes
- D. Presbyopia
The classes of fingerprints in man are
- A. whorl, alternate, opposite and compound
- B. compound, loop, whorl! and alternate
- C. whorl, arch, compound and loop
- D. arch, simple, compound and opposite
Which of the following statements is true about the ABO blood group system?
- A. Antigens are located on the surface of white blood cells
- B. Antibodies are located in the blood plasma
- C. Antibodies are located on the surface of red blood cells
- D. Antigens are located in the blood plasma


