(a) (i) What is a gene?
(ii) Differentiate between the terms genotype and phenotype
(b) Explain the following terms:
(i) hybrid
(ii) pure breeding
(iii) nucleotide.
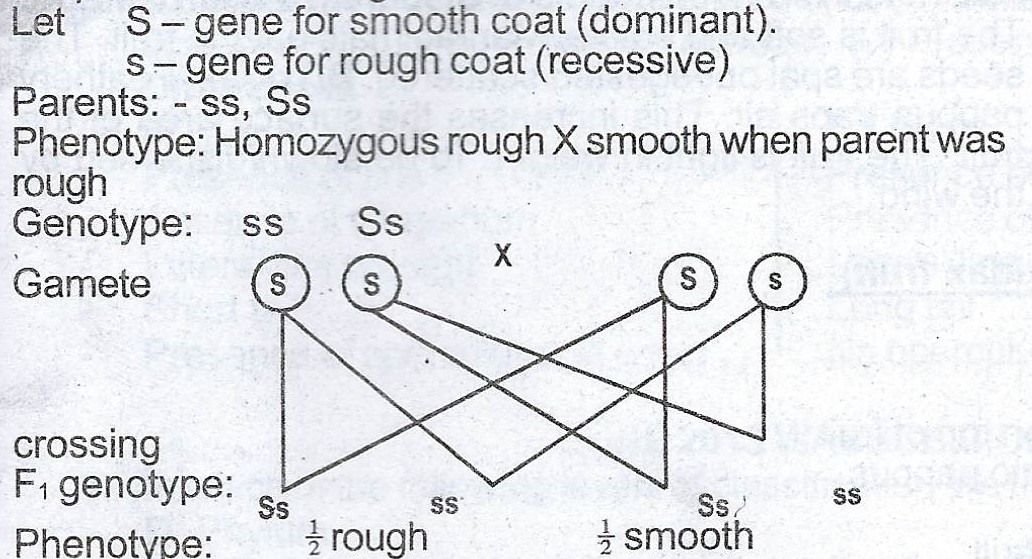
(c) In garden pea seeds, smooth seed coat is dominant over rough seed coat. With the aid of a genetic diagram, determine the result expected if a homozygous rough pea is crossed with a smooth seed coat plant whose parents were rough coated.
Explanation
(a)(i) What is a gene? Genes are units of heredity located in the chromosomes which are responsible for the coding of a particular protein to transfer trait or character from parents to offspring.
(ii) Differentiate between the terms genotype and phenotype: Genotype is the genetic make-up of genes in an organism that is independent of the environment while a phenotype is all observable features, appearance of the organism that is determined by the environment and the genotype.
(b) Explain the following terms:
(i) Hybrid: Offspring produced from a cross between two parents with contrasting characters.
(ii) Pure-breeding: A process of producing a particular genotype over many generations.
(iii) Nucleotides: The basic building block of a nucleic acid consisting of a ribose, deoxyribose. protein, a phosphate group and a nitrogen base.
(c) In a garden, pea seeds, smooth seed coat is dominant over rough feed coat. With the aid of a genetic diagram, determine the result expected if a homozygous rough pea is crossed with a smooth seed coat plant whose parents were rough coated.