Study specimens L, M and N carefully and use them to answer questions 4(a) to 4(c).
(a)(i) State the habitats of specimens L, M and N.
(ii) State the modes of nutrition of specimens L. M and N.
(iii) Explain how each of specimens Land M are adapted to their modes of feeding.
(b)(i) Describe briefly the relationship that exists among specimens L, M and N.
(ii) State two ways in which specimen M is of economic importance.
(iii) State one way in which specimen M can be controlled.
(c) Make a drawing 8cm – 10cm long of specimen M and label fully.
(a) Study specimens E and F carefully and use them to answer questions 2(a)(i) to 2(a)(ii).
(i) State the Class to which each of specimens E and F belong.
(ii) List four observable features each of specimens E and F.
(iii) State how each of the observed features in 2(a)(i) adapt each of specimens E and F to their habitats.
(b) Study specimen G and use it to answer questions 2(b)(i) to 2(b)(ii).
(i) Classify specimen G into its phylum and class.
(ii) State four observable features of specimen C.
(iii) Name one habitat of specimen C.
Observe specimens A, B, C and D closely and use them to answer questions 1(a) to 1(e).
(a)(i) Specimen A Into its division and class.
(ii) State three observable features of specimen A which are characteristics of the class mentioned in 1(a)(i) above.
(b) State the relationship between specimen A and: (i) specimen B; (ii) specimen C; (iii) specimen D.
(c)(i) From. your observations of specimens B and C, what type of plant is specimen A? (ii) Suggest the agent of pollination ot specimen B.
(iii) State two reasons for the answer in 1(c)(i) above.
(d) Classify specimen D fully according to origin and structure.
(e) Make a drawing 8 cm 10 cm long of specimen C and label fully.
(a) State five reasons why animals move from place to place.
(b) State one function each of the following structures found in plants:
(i) epidermis
(ii) phloem
(iii) sclerenchyma.
(c) Give two examples each of the following types of organisms:
(i) parasitic plants
(ii) saprophytes.
(d) State two adaptive features of plants which inhabit salt water swamp.
(e) State two factors each which result in
(i) increase
(ii) decrease, in population density.
(f) Mention four ways in which modern agricultural activities may threaten the survival of species.
(g) State three reasons why mitosis is important to living organisms
(h) State three causes of food spoilage.
(a)(i) Explain the term co-ordinance.
(ii) Calculate the number of individuals with co-dominant blood group.
(iii) What is the total number of individuals in the table that are able to donate blood to an accident victim with blood group B?
(b) A man whose blood group is heterozygous A is married to a
woman whose blood group is AB. With the aid of a genetic diagram, suggest the possible blood groups of their children.
A survey to determine blood groups was carried out on 250 people living in a community. The results are represented in the table below.
| Blood group | Percentage |
| A | 8.0 |
| B | 14.0 |
| AB | 32.8 |
| O | 45.2 |
(a) Explain briefly the following ecological terms:
(i) biosphere
(ii) habitat
(b) Describe the mode of nutrition in a named carnivorous plant.
(c) State three reasons why the dispersal of fruits and seeds are important.
(d) State six methods of conserving soil.
(a) Define the following in
(i) elimination
(ii) excretion
(iii) secretion.
(b) Describe the digestion of boiled fish in the gut of humans
(c) Make a diagram 8cm – 10am long of a longitudinal section of a villus and label fully.
(a) (i) List three characteristics of living organisms.
(ii) Explain briefly the characteristics listed in (a)(i) above.
(b) In a tabular form, state four differences between plants and animals.
(c)(i) Name one organism that exhibits both plant and animal features.
(ii) State four animal features and two plant features possessed by the organism named in (c)(i) above.
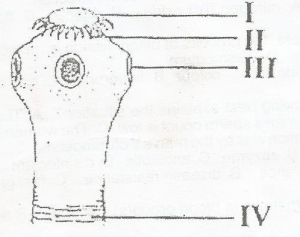
In the diagram, the young proglottid is represented by
- A. iii
- B. iv
- C. i
- D. ii
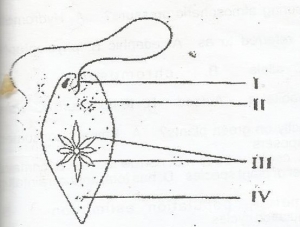
In the diagram, the part responsible for photosynthesis is labelled
- A. iii
- B. iv
- C. i
- D. ii
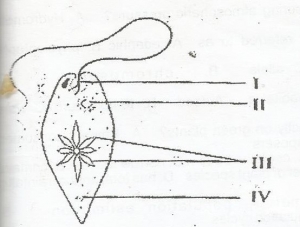
In the diagram, the part labelled II is the
- A. nucleus
- B. eyespot
- C. basal granule
- D. contractile
Lamarck’s theory of evolution is based on the fact that
- A. organisms acquire genes from their parents
- B. organisms pass on acquired characters to their offspring
- C. characteristics of organisms are determined by the creator
- D. characteristics of organisms are the sum of their parents characters
Which of the following organisms is not a social insect?
- A. Termites
- B. Ants
- C. Grasshoppers
- D. Bees
The main reason for nuptial flight in termites is to
- A. escape unfavourable conditions
- B. search for food
- C. form new colonies
- D. communicate with one another
In dihybrid inheritance, Mendel considered
- A. a pair of contrasting characters
- B. two pairs of contrasting characters
- C. three pairs of contrasting characters
- D. four pairs of contrasting characters
Which of the following diseases can be inherited?
- A. pneumonia
- B. AIDS
- C. sickle cell anaemia
- D. goitre
The F1 generation of a cross between a red cock and white hen were all red because the gene for the
- A. white colour did not segregate
- B. red colour was dominant
- C. white colour was dominant
- D. red colour was recessive
A small stem from a hibiscus plant was placed in a nutrieent medium, and it developed into a new plant. The new plant was reproduced
- A. asexually with different genotype from the parent plant
- B. sexually with a different genotype from the parent plant
- C. asexually with the same genotype as the parent plant
- D. sexually with the same genotype as the parent plant
Which of the following statements about chromosomes is correct?
- A. All the chromosomes of a species are the same in shape
- B. the bear number present in a species is constant
- C. they are neatly arranged in the eytoplasm
- D. They bear ribosomes on their outer membranes
Which of the following traits is not a morphological variation in humans?
- A. Ability to taste PTC
- B. Colour
- C. Fingerprints
- D. Size
Differences in characteristics that exist among individuals of the same species is referred to as
- A. genetics
- B. dominance
- C. hybird
- D. variation


