Study specimens T, V and W carefully and use them to answer questions 4(a) to 4(d)
(a) Classify Specimen T,V and W according to the following criteria: (i) Agricultural classification: (ii) Life cycle.
(b) State two ways in which specimen W is important to human nutrition.
(c) With a scalpel or knife, make a cross Section of specimen T.
(ii) What type of placentation is observed in the cut section of specimen T? Name one example of a fruit with similar placentation as observed in the cut section of specimen T.
Make a drawing 10 cm – 12 cm long of the transverse section and label fully.
(d) Make a transverse section of Specimen V and state: (i) Three Observable differences;
(ii) Three observable similarities; between the transverse section of specimen T and V.
Study specimen Xi and Xii and use them to answer question 4 (e) (i) to 4 (e) (ii)
(e) Carefully remove the bark of specimen Xi to expose the naked part.
(i) State two observable differences between Specimen Xi and Xii.
(ii) If Xi and Xii are planted, what difference will be noticed after a month? State one reason for the answer in 4 (e)(ii)
Observe Specimen Q, under a microscope and specimen R Carefully, Use them to answer questions 3 (a) to 3 (e).
(a)(i) State the phylum to which each of specimen Q and R belong. (ii) State one reason each for the answers stated in 3 (a) (i).
(iii) What is the symmetry of specimen Q and R?
(b)(i) State two observable feature each of specimen Q and R. (ii) State one function each of the features mention in 3 (b) (i).
(c) (i) Name the sex of specimen R. (ii) Give one reason for the answer given in 3 (C) (i).
(d) In tabular form, state four observable differences between specimen Q and R,
(e) Make a drawing 10 cm-12 cm long of the lateral view of specimen Rand label fully.
Study Specimen G and H carefully them to answer question 2 (a) to 2(c).
(a) (i) Name the phylum of specimens G and H.
(ii) State two reasons for the answer given in 2 (a)(i).
(b) Name the structures on specimen G and H that are used for defense.
(c)(i) State two habitat of each of specimen G and H. (i) State two ways in which each of specimen G and H are of economic importance.
Study specimen M, N and P carefully and use them to answer question 2 (d) and 2 (e).
(d) (i) Name the class of organisms to which each of the specimen M, N and P are associated. (ii) State one function common to the specimen named in 2 (d)(i).
(iii) In a tabular form, State four observable difference between specimen M and P.
(e) Explain three features of biological importance in Specimen M.
Study Specimens A and B carefully and use them to answer question 1 (a) to 1 (e).
(a) Classify Specimen p no its division and class.
(b) (i) State the types of leaf arrangements in specimens A and B.
(ii) Name the leaf shape of specimens A and B.
(c)(i) State the type of leaf margin in specimen A. (ii) State the types of venation found in the leaves of specimens A and B.
(d)(i) List three observable similarities found in specimen A and E. (ii) In a tabular form, state four observable differences between specimens A and B.
(e) Make a drawing 8-10 cm long of the leaf of specimen A and label fully.
(a) Copy and complete the table below
| Disease | one effect | one remedy |
| kidney stones | ||
| Nephritis | ||
| Diuresis |
(b) Make a labelled diagram of the carbon cycle.
(c)(i) What is Estuarine habitat?
(ii) Construct a food chain typical of an Estuarine habitat.
(d)(i) Name two diseases that can attack plant crops.
(ii) State three ways of controlling plant diseases.
(e) State four functions of a public health authority
(f) State four ways of maintaining food hygiene in the community.
(a) Explain the following terms:
(i) test cross
(ii) monohybrid cross.
(b) In a mango plant the, the allele for bean-shaped seed is r and is recessive to round-shaped seed R. With the aid of a genetic diagram, determine the genotypes of the offspring if:
(i) a homozygous bean-shaped parent with a homozygous round shaped parent;
(ii) a heterozygous bean-shaped parent is crossed with a heterozygous round shaped parent.
(a)(i) What is sewage?
(ii) State five effects of releasing untreated sewage into a stagnant water body.
(b) Explain surface terracing as a soil conservation method.
(c) Explain the term adaptation.
(d) Explain two ways each by which the following organisms adapt to their habitats:
(i) hydrophytes
(ii) xerophytes.
(a) Explain how the leaf of a flowering plant is adapted for photosynthesis.
(b) Describe briefly the mode of feeding in tapeworm.
(c) Name one mineral element each needed for the proper functioning of :
(i) bones (ii) red blood cells
(iii) thyroid gland.
(d)(i) State three benefits of including roughages in the diet of humans.
(ii) State three reasons why proteins are important to humans.
(a) Explain briefly sexual reproduction in Rhizopus.
(b) A student suddenly stepped on a big snake, he cried for help and ran away.
(i) Name the hormone produced in the body for the reaction.
(ii) In which part of the human body is the hormone named in (b) (i) produced?
(iii) State five changes that must have taken place as a result of the hormone named in (a) (i).
(c) (i) In tabular form, state three differences between excretion in flowering plants and excretion in humans,
(ii) List two organelles found in plant cell that are responsible for the excretion of metabolic wastes.
Which of the following statements about protoplasm of a cell is not correct? It
- A. comprises of the nucleus
- B. consists of the cytoplasm
- C. comprises of the cell organelles
- D. consists the nucleus only
The following organisms have structures for movement except
- A. Amoeba
- B. Spirogyra
- C. Volvox
- D. Paramecium
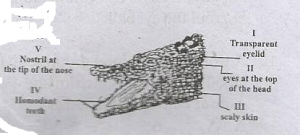
The diagram above is illustration of a crocodile. Use it to answer this question.
Two characteristic features of the class to which the crocodile belongs are labelled
- A. I and II
- B. III and IV
- C. II and IV
- D. II and V
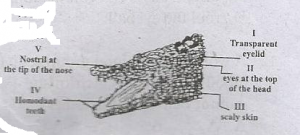
The diagram above is illustration of a crocodile. Use it to answer this question.
Two characteristic features of the class to which the crocodile belongs are labelled
- A. I and II
- B. III and IV
- C. II and IV
- D. II and V
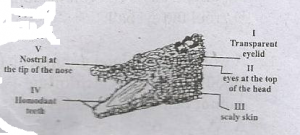
The diagram above is illustration of a crocodile. Use it to answer this question.
Which of the labelled parts enable the animal to stay under water most of the time?
- A. I, IV and V
- B. I, II and V
- C. I, III and IV
- D. III, IV and V
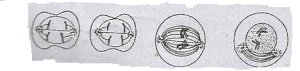
The following diagram above show the sequence of events in early cell division. Study the diagram and answer the question.
In which of the following cells is this divisin likely to take plce?
- A. Sperm cell
- B. Blood cell
- C. Muscle cell
- D. Uterine cell

The diagram above illustrates a part of the mammalian skeleton . use it to answer this this question
The function of the part lebelled I is to
- A. provide support to the spinal cord
- B. provide surface for attachment of the muscle
- C. carry the spinal cord
- D. articulate with adjacent vertebrae

The diagram above illustrates a part of the mammalian skeleton . use it to answer this this question
The part of the skeleton illustrated in the diagram is the
- A. atlas vertebrae
- B. axis vertebrae
- C. cervical vertebrae
- D. thoraeic vertebrae
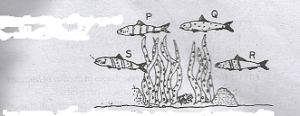
The variety P,Q,R and S Outlive the others because the
- A. variety is the most beautiful
- B. variety does not have markings
- C. markings of the variety are similar to those of the environment
- D. predator does not like eating the variety
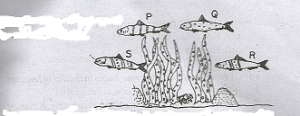
In explaining the term camouflage, to a class, the diagram above show four varieties, P, Q, R, and S of the same species of fish living amongst water plants in a river were used
Which of the varieties is most likely to outlive the others?
- A. P
- B. Q
- C. R
- D. S
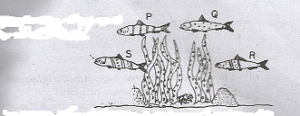
In explaining the term camouflage, to a class, the diagram above show four varieties, P, Q, R, and S of the same species of fish living amongst water plants in a river were used
Which of the varieties is likely to decrease most in number if a predatory fish is introduced into the river?
- A. P
- B. Q
- C. R
- D. S
Which of the following statements about sex-linked characters is not true?
- A. They are usually borne on the X = chromosome
- B. They are more common in males
- C. Males are usually carriers
- D. They are not usually carried on the Y chromosomes


