(a) Copy and complete the table below
| Disease | one effect | one remedy |
| kidney stones | ||
| Nephritis | ||
| Diuresis |
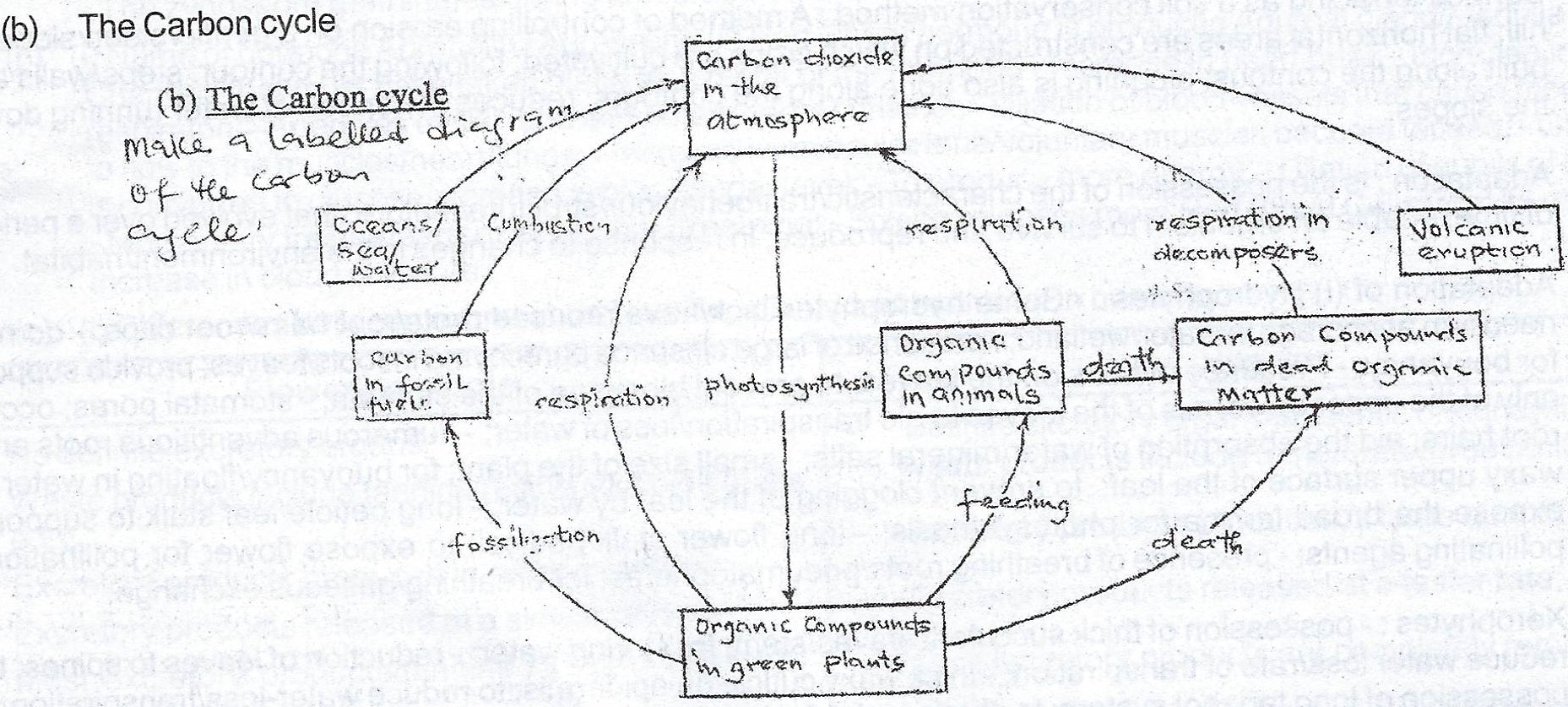
(b) Make a labelled diagram of the carbon cycle.
(c)(i) What is Estuarine habitat?
(ii) Construct a food chain typical of an Estuarine habitat.
(d)(i) Name two diseases that can attack plant crops.
(ii) State three ways of controlling plant diseases.
(e) State four functions of a public health authority
(f) State four ways of maintaining food hygiene in the community.
Explanation
(a) Kidney diseases
| Diseases | One effect | One remedy |
| kidney stones | Abdominal pains; decreased frequency of urination, pains during urination; presence of blood in the urine; increased blood pressure. | Drink plenty of water kidney transplant; avoid foods rich in calcium/red meat/meat; consult a physician. |
| Nephritis | Oedema/swelling of feet and ankle; high blood pressure; blood in urine/dizziness/back pain/fatigue/general weakness; inflammation of the kidney tubules | consult a physician; kidney transplant; dialysis/all food items must be washed/cooked properly; drinking water boiled/filtered/sterilized |
| Diuresis | Thirst/dehydration occurs; high blood pressure may occur; loss of appetite;weakness; fatigue; nausea; loss of serum electrolyte. | Consult a physician; avoid fans/air conditions in cold weather, avoid excessive drinking of alcohol |
(c) (i) Estuarine habitat; is the place point where a river enters to ocean/sea, into which the tides flow; fresh water mix with salt water; to form brackish water.
(ii) food chain typical of an estuarine; phytoplanktons - branacles => fish => brid OR Detritus => worm => molluse => bird OR Detritus => shrimp => fish => bird
(d)(i) Pests that can attack plant crops :
Stem borer
army worms
weevils
black tea-thrips
aphids
root mealybugs
variegated grasshopper
beetle; rodents
squirrel
locust
birds
mites
cotton stainer
any correctly named examples.
NOTE : Spelling must be correct to score.
(ii) Ways of controlling plant diseases
- Chemical control/ use of fungicides/ nematicides/ bactericides/ pesticides
- Biological control/ use of predators and parasites of insects/ pests to keep them in check
- Breeding resistant varieties of crop
- Planting genetically modified crops that can resist viruses/ bacteria transmitted by pests
- Destruction of infested crops by burying/ deep burial/pruning of affected parts
- Destruction of alternate host
- Adopt good management/ crop rotation.
(e). Functions of a public health authority
- ensures cleanliness of public places/markets/schools/playgrounds
- concerned with the proper disposal of refuse
- provides maternity clinics/health centres/nursing homes/family planning
- provides child welfare services
- provides medical inspection of schools
- registers birth/death
- prevents controls infectious diseases/ administers vaccination/ immunization/ inoculation
- informs World Health Organization of the outbreak of infectious diseases
- ensures adequate provision of clean water to the public
- provides ambulance services
- provides quarantine services for plants/ animals/ humans
- gives health certificate to travelers
- provides public health education/awareness of diseases
- inspects and certifies health of animals and cleanliness of slaughter house/ abattoir.
(f). Ways of maintaining food hygiene : -
- proper harvesting/ storage methods must be ensured to prevent damage to food items
- food items must be properly washed/ cleaned to prevent contamination
- food items must be properly cooked at appropriate temperatures
- kitchen/cooking areas must be kept clean always/free from germs
- perishable food items must be properly preserved/ refrigerated
- proper personal hygiene must be observed by those handling food
- cooking utensils must be properly washed/ cleaned before and after use
- cooked/prepared food must be covered at all time
- proper disposal of unused/leftover food.

