Answer all the questions in this section.
Study specimen S, T, U, V and Wand answer questions 4 (a) to 4(e).
(a) (i) Name the habitats of each of specimens S, U and W.
(ii) Name the class to which each of specimens S, U and W belong.
(b) State: (i) Four observable similarities between specimens S and U. (ii) five observable differences between specimens S and U.
(c)(i) identify the sex of specimen U. (i) State two reasons for the answer in 4 (c)(i).
(d)State four observable features that adapt specimen S to its habitat.
(e) Construct a food chain using at least three of the given specimens.
Study specimens H, K, L and M and answer questions 2 (a) to 2 (e).
(a) Name the location of each of the specimens H, K and M in the body of a mammal.
(b)(i) Name the fluid in specimen L (ii) State two functions of the fluid named in 2 (b) (i). (iii) Which of the other specimens is specimen L associated with?
(c)(i) State two observable differences between specimens H and K. (i) State two observable features of specimen K that adapt it to its function.
State one biological importance each of specimens K and M.
(d) Make a drawing 8 cm -10 cm long, of specimen M and label fully.
(a)(i) Cut a pieces of specimen A, place it on the white tile. Add a few drops of iodine solution. Record the observation and result in a tabular form.
(ii) Squeeze a few drops of specimen E on another clean white tile provided, add a few dre Record the observation and result in a tabular form.
(b)(i) State two observables differences between specimens A and B. (ii) Suggest two factors that are likely to be responsible for the state of specimen B.
(iii) With the aid of hand lens/magnifying lens, observe.specimen B. and name an organism that is likely growing on it. (iv) State the mode of feeding of the organism on specimen B (c) ) Make a drawing 6cm-8 cm long, of specimen C and label fully. one function each of any three parts labeled.
(a) State two difference between tactic and nastic movements in plants.
(b) Give two examples each of organisms that show:
(i) tactic movement
(ii) nastic movement
(c) (i) State three ways of caring for the mammalian skin.
(ii) List three stimuli to which the mammalian skin is sensitive.
(d) State five effects of high temperature on a terrestrial habitat.
(e) (i) What is courtship behaviour in animals?
(ii) List three courtship behaviours in animals.
(f) Name three organisms that carry out holozoic mode of nutrition.
(g) Explain briefly how fingerprinting can be used to detect crime.
(a) (i) Explain the term agglutination as used in blood transfusion.
(ii) The table below represents blood transfusion between blood donors and recipients.
| Donor | Recipient | ||||
| A | B | AB | O | ||
| A | |||||
| B | |||||
| AB | |||||
| O | + | ||||
(b) Explain how each of the following organisms are adapted for obtaining food.
(i) Mosquito larva
(ii) Dodder plant
(iii) Grasshopper
(a) (i) What is a habitat?
(ii) Explain briefly three roles of a decomposer in an ecosystem.
(b) Explain briefly energy flow in a freshwater habitat.
(c) (i) State three harmful effects or microorganisms to plants
(ii) State six beneficial effects of microorganism to humans.
(a) In sequence, name the organs that constitute the alimentary canal of humans
(b) State: (i) three structural differences; (ii) three structural similarities; between the alimentary canal of a bird and human.
(c) Explain briefly how the dentition of herbivores is adapted for feeding
(d) State two roles of the pancreas in digestion
(a) (i) List three forms in which living cells exist
(ii) Give one example each of the forms listed in 1 (a)(a)
(b) Make a diagram, 6 cm — 10 cm long, of a typical plant cell and label fully
(c) (i) In a tabular form, state three differences between a plant cell and animal cell.
(ii) State three similarities between a plant cell and animal cell.
An organism at the start of a food chain which provides the total input energy into an ecosystem is the
- A. sun
- B. producer
- C. consumer
- D. decomposer
The capillarity of a soil refers to
- A. the particle size of soil
- B. how easily water passes through soil
- C. how well water rises up in soil
- D. proportion of water a soil holds
The major problem experience by organisms living in small water bodies is
- A. drying up
- B. oxygen deficiency
- C. scarcity of food
- D. wave action

Study the diagram above and answer the question.
A decrease in the number of 11 will result in
- A. an increase in urine production
- B. an increase in energy production
- C. a decreased population
- D. decreased immunity
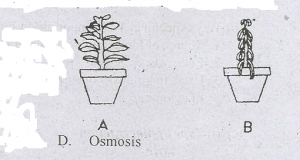
Plant A was seen to appear as Plant B after seven hours
Study the above diagrams carefully and answer the questions.
The environmental factors responsible for the condition in plant B are
- A. low humidity and low temperature
- B. high humidity and low temperature
- C. low humidity and high temperature
- D. high humidity and high temperature
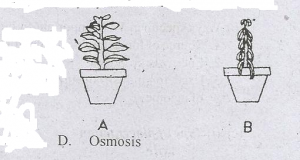
Plant A was seen to appear as Plant B after seven hours
Study the above diagrams carefully and answer the questions.
The term that can be used to describe what happened to Plant A after seven hours is
- A. wilting
- B. competition
- C. transpiration
- D. Osmosis
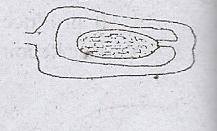
The type of placentation illustrated in the diagram above is
- A. marginal
- B. perietal
- C. axile
- D. basal
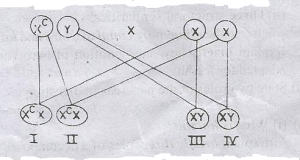
The illustration above represents a cross between a colour blind male and normal female.
Study it carefully and answer the questions.
Which of the genotypes are carriers of colour blindness?
- A. 1 and 11 only
- B. 1 and 111 only
- C. 11 and 111 only
- D. 1, 11 and 111 only
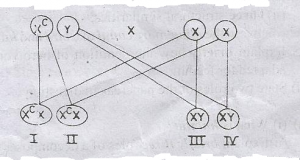
The illustration above represents a cross between a colour blind male and normal female.
Study it carefully and answer the questions.
What is the genotype ratio of carrier females to normal males in the cross?
- A. 1:1
- B. 2:3
- C. 3:4
- D. 4:1
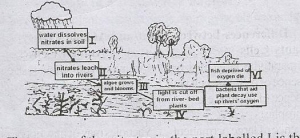
Use the diagram above that shows the effect of nitrates on water bodies Study it carefully and answer questions.
Another cause that could lead to the phenomenon in the diagram is
- A. exhaust from cars
- B. oil spillage
- C. dumping of sewage
- D. excess rainfall
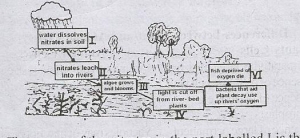
Use the diagram above that shows the effect of nitrates on water bodies Study it carefully and answer questions.
The phenomenon in the diagram is termed
- A. denitrification
- B. conservation
- C. eutrophication
- D. global warming
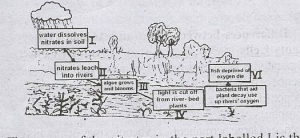
Use the diagram above that shows the effect of nitrates on water bodies Study it carefully and answer questions.
The source of the nitrates in the diagram is termed
- A. root nodules of legumes
- B. cloud
- C. fertilizers
- D. organic matter
The inability of an organism to adapt to its habitat can lead to
- A. dormancy
- B. adaptation
- C. extinction
- D. survival


