(a) (i) List three forms in which living cells exist
(ii) Give one example each of the forms listed in 1 (a)(a)
(b) Make a diagram, 6 cm — 10 cm long, of a typical plant cell and label fully
(c) (i) In a tabular form, state three differences between a plant cell and animal cell.
(ii) State three similarities between a plant cell and animal cell.
Explanation
(a) (i) Forms in which living cells exist
- Single/free-living
- Colony/colonial
- Filamentous/filament
- Part of a living organism.
(ii) Example
- Single/free-living -Amoeba/Chlamydomonas/Paramecium/Euglena
- Colony/colonial -Eudorina/Pandorinallolvox/Sponges
- Filamentous/filament - Spirogyra/Chladophora/Ulothrix/Zygnema/Oedogonium
- Part of living organism - cheek cell/onion cell/epidermal cell/parenchyma cell.
(b) Diagram of a typical plant cell
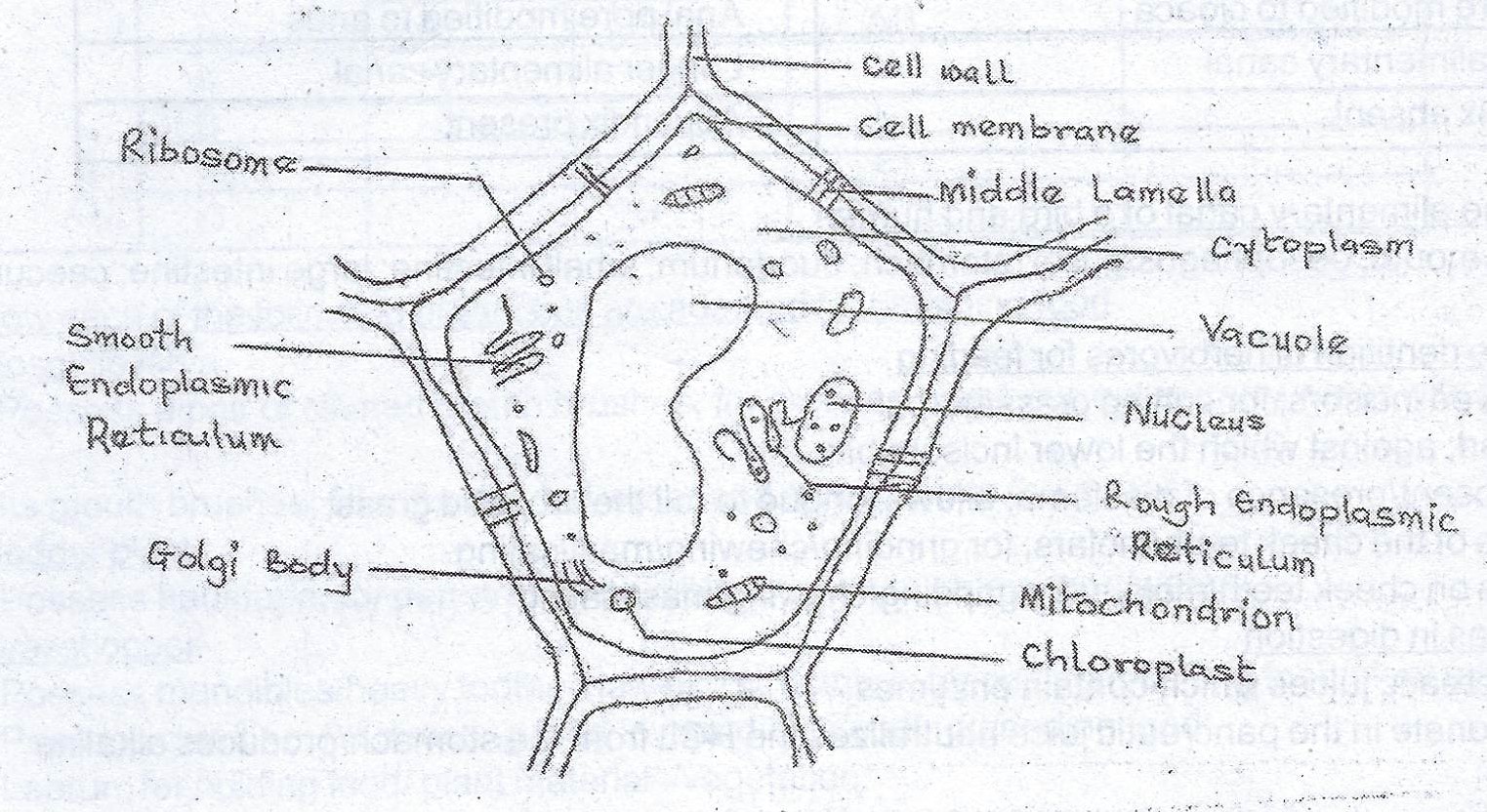
(c) (i) Differences between a plant cell and an animal cell
| plant cell | Animal |
| Has cellulose cell wall / rigid | Lacks cellulose cell wall |
| Has one large central vocoule | has numerous/vocoule |
| has chloroplast | lacks chloroplast |
| Contains starch granules in its cytoplasm | contains glycogen granules in it cytoplasm |
| Usually larger in size | Usually smaller in size |
| Does not have lysosome | has lysosome |
| Does not have centrioles / centrosome | Has centrioles / centrosome |
| Has a regular / defined cell shape | has an irregular / indefinite cell shape |
| cytoplasm less dense | cytoplasm more dense |
| stores lipid as oil | stores lipid as fat |
(ii) Similarities in plant cell and animal cell;
They both have cytoplasm; nucleus; vacuole; mitochondrion; Golgi body; (smooth/rough) endoplasmic reticulum; cell membrane/plasma membrane; ribosomes

