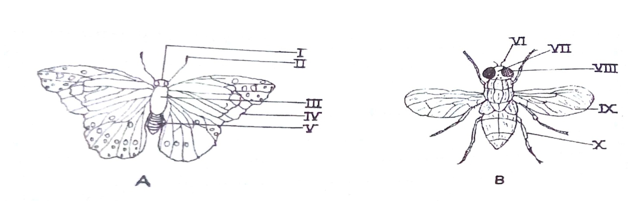
. Study specimens A and B and answer questions 1(a) to 1(c).
(a)(i) Name the habitat of each of specimens A and B. (ii) Name the adult stages into which each of specimens A and B would develop.
(iii) Name the phylum and class common to the adult stages into which each of specimens A and B.
(b) State three observable features of biological significance in: (i) specimen A (ii) specimens B.
(c)(i) State four observable structural differences between specimens A and B.
(ii) State three observable similarities between specimens A and B.
2. Study specimens C, D and E and answer questions 2(a) to 2(c).
(a)(i) Name the organism from which each of specimens C, D and E are obtained.
(ii) State the function common to specimens C, D and E.
(iii) State three observable features which adapts specimen C to its function.
(b)(i) State three observable structural similarities between specimens C and D.
(ii) State three observable structural differences between specimens C and D.
(c) Make a drawing 6cm – 8cm long of specimen C and label fully.
(3) Study specimens K and L and answer questions 3(a) to 3(c).
(a)(i) Name the floral parts of specimen K. (ii) Indicate the number of the floral parts in each whorl of specimen K.
(b)(i) Name the sex of specimen K. (ii) Give one reason for your answer in 3(b)(i).
(c)(i) What is the symmetry of specimen K?. (ii) Give one reason for your answer in 3(c)(i).
(d) Name one pollinating agent of each of specimens K and L.
(e) State four observable structural differences between specimens K and L.
(f) Make a drawing 8cm – 10cm long of specimen K and label fully.
(a) Name five vertebrae in mammals with their corresponding locations in the table below.
(b) State one function each of the following parts in a dicotyledonous leaf: (i) palisade; (ii) vascular bundle; (iii) epidermis.
(c)State one function each of the following parts in the stem of a flowering plant: (i) sieve tube; (ii) cortex; (iii) pith.
(d) In a tabular form, state:
(i) two external structural differences between the stem and root of a maize seeding.
(ii) two internal structural differences between the stem and root of a maize seeding
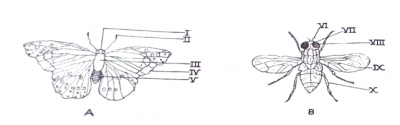
The diagrams below are illustrations of two organisms. Study them and answer question 3 (a) to (f)
(a)(i) Identify organisms A and B.
(ii) Name the parts labeled I to X.
(b) State one function each of the parts labeled VI, VIII, IX and X.
(c) Name the specific habitats of organisms A and B.
(d) State three structural adaptations of organism A to its mode of life.
(e)(i)State three structural similarities between organisms A and B.
(ii) State three structural differences between organisms A and B.
(f)(i) Name the class of organisms A and B.
(ii) State three reasons for the answer in (f) (i).
(g)State one biological importance of organism A.
Diagrams D, E and F are illustrations of tools used for ecological studies. Study them and answer questions (a) to (c).
(a)(i) Identify diagrams D, E and F.
- Name the parts labeled I to VIII.
- State one function each of the parts labeled I, III, IV, V and VII.
(b) State one use each of the tools labeled D, E and F.
(c) Describe briefly the use of each of the tools labeled D, E and F.
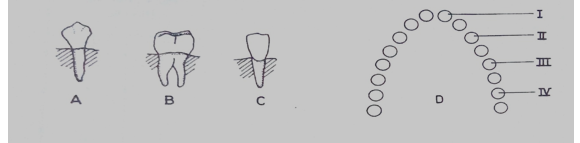
Diagrams A, B and C are illustrations of different types of teeth in humans. Diagram D is a representation of the arrangement of teeth in the lower jaw of a human.
Study them and answer questions (a) to (f).
(a) (i) Name the type of teeth in diagrams A, B, and C.
(ii) Which of the teeth would be found in positions I, II and IV?
(iii)State one function each of the teeth illustrated in diagrams A, B and C.
(iv) State one reason each for the answers in (a) (iii).
(b)If the tooth labeled B is decayed, list two factors that may be responsible.
(c)What is the total number of each of the teeth labeled A, B and C in the dentition of an adult human?
(d)Which of the teeth would be absent in a rabbit?
(e)(i) Name the tooth that would be found in position III of diagram D.
(ii) In which of the parts labeled I, II, III and IV would a tooth not be found in an infant?
(f) State five ways of caring for the teeth in humans.
(a)(i) Identify organisms A and B. [2 marks]
(ii) Name the parts labeled I to X. [5 marks]
(b) State one function each of the parts labeled VI, VIII, IX and X. [4 marks]
(c) Name the specific habitats of organisms A and B. [2 marks]
(d) State three structural adaptations of organism A to its mode of life. [6 marks]
(e)(i)State three structural similarities between organisms A and B [3 marks]
(ii) State three structural differences between organisms A and B. [3 marks]
(f)(i) Name the class of organisms A and B. [1 marks]
(ii) State three reasons for the answer in 3 (f) (i). [3 marks]
(g)State one biological importance of organism A. [1 marks]
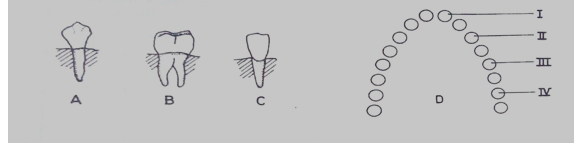
Diagrams A, B and C are illustrations of different types of teeth in humans. Diagram D is a representation of the arrangement of teeth in the lower jaw of a human.
Study them and answer questions (a) to (f).
(a) (i) Name the type of teeth in diagrams A, B, and C.
(ii) Which of the teeth would be found in positions I, II and IV?
(iii)State one function each of the teeth illustrated in diagrams A, B and C.
(iv) State one reason each for the answers in (a) (iii).
(b)If the tooth labeled B is decayed, list two factors that may be responsible.
(c)What is the total number of each of the teeth labeled A, B and C in the dentition of an adult human?
(d)Which of the teeth would be absent in a rabbit?
(e)(i) Name the tooth that would be found in position III of diagram D.
(ii) In which of the parts labeled I, II, III and IV would a tooth not be found in an infant?
(f) State five ways of caring for the teeth in humans.
(a) State five processes involved in the water cycle.
(b) Name one instrument used for measuring each of the following physical factors:
- pH;
- light intensity;
- turbidity;
- temperature.
(c) Explain briefly the contributions of the following scientists to the formulation of the cell theory:
- Robert Hooke;
- Theodore Schwann.
(d) What is meant by each of the following terms:
- Nastism
- Taxism
(e) Make a diagram, 6 cm – 8 cm long of the human tongue illustrating the four areas of taste.
(f)(i) List four ways through which microorganisms enter the human body.
(ii) State three harmful effects of microorganisms to humans.
(a)(i) State Mendel’s laws of inheritance.
(ii) State five applications of genetics in medicine.
(iii) State three disadvantages of inbreeding.
(b)(i) What is evolution?
(ii) Distinguish between convergent evolution and divergent evolution.
(a) Explain briefly the following terms:
- ecosystem;
- abiotic environment.
(b) List three ecological factors each which are specific to:
- aquatic habitats;
- terrestrial habitats.
(c) State briefly the relationship between green grass and a rabbit in a given habitat.
(d) Draw a typical pyramid of energy using four feeding levels.
(a)Describe briefly the process involved in the conversion of food to chyme in the stomach of a mammal.
(b)Complete the table below by stating one enzyme, digestive juice, food acted upon and
end-product in the corresponding spaces.
| One Enzyme |
One juice |
One food acted upon |
One end-product |
|
Pepsin (i) ———– Lipase |
(ii)————— (iii)————— (iv)————— |
(v) ——————– (vi) ——————- (vii) ——————- |
(viii)——————- Maltose (ix)———————– |
(c) Describe an experiment to show that carbon dioxide is necessary for photosynthesis.
(a) State two roles each of the following compounds in respiration:
(i) glucose;
(ii) oxygen.
(b) List two types of cellular respiration
(c) Name the structures of gaseous exchange in the following organisms:
| S/N | ORGANISM | STRUCTURE OF GASEOUS EXCHANGE |
| 1 | Ameoba | |
| 2 | Tilapia | |
| 3 | Adult Toad | |
| 4 | Grasshopper |
(d) Make a diagram, 6 cm to 8 cm long of an open stoma in a leaf and label fully.
(a)(1) Explain briefly chemosynthesis as a mode of nutrition.
(ii) Give two examples of organism that carry out chemosynthesis.
(b) List three gases in the atmosphere with their percentage composition.
| Gases in the atmosphere | Percentage composition |
(c) (i) State four characteristics of a salt marsh habitat.
(ii) Explain briefly how plants are modified for anchorage in a salt marsh habitat.
(d) (i) List four bacterial disease associated with poor food hygiene.
(ii) State three effects of poor food hygiene.
(e) A person was involved in a car accident and became unconscious due to excessive blood loss. Explain briefly how the blood lost could be restored.
(f) State three differences between tillage and bush burning as farming practices.
| Tillage | Bush burning |
a. Explain briefly the following terms:
i. gene;
ii. Hybrid;
iii. Trait.
(b) Two heterozygous yellow flowers are crossed. Using a genetic diagram, state the phenotypic and genotypic ratios of the first filial generation.
(c) State four transmitted characters in plants.
(a). Explain briefly the following terms:
(i) Renewable natural resources
(ii) Non -renewable natural resources;
(b) Give two examples each of:
(i) Renewable natural resources
(ii) Non -renewable natural resources
(c) State five ways of conserving forests
(d) State four effects of adding animal manure to garden soil.
(e) Give the possible genotypes in humans;
(a). Name the gases involved in the photosynthesis of a plant.
(b) State one role each of the gases named in 2 (a).
(c) (i) What is a variegated leaf?
(ii)Which part of the variegated leaf would test positive when treated with iodine solution?
(iii) State two reason for the answer in 2(c) (ii).
(iv) Name one mineral element required by plants for the formation of the part that would test positive in 2(c)(ii).
(d) The table below indicates different methods by which organism obtain food. Place the following organism under the heading in the table below: Human, Mushroom, Venus flytrap, Waterleaf plant, Tapeworm, Elephant grass, Housefly, Lichen, Spirogyra, Rhizopus.
| Holozoic | Parasitic | Symbiotic | Saprophytic | Autotrophic |
(a) Explain briefly how the structure of each of the following cells relate to their functions:
(i) Sperm cell
(ii) Palisade cell.
(b) Make a drawing, 8cm to -10cm long of the front view of the female reproductive system in humans and label fully.
(c) State two differences between reproduction in mammals and in amphibians.
(d) State two methods of birth control in humans.
Which of the following is not a social insect?
- A. termite
- B. housefly
- C. honeybee
- D. ant
In evolution, fossils are naturally preserved in
- A. rocks
- B. water
- C. chemicals
- D. trees
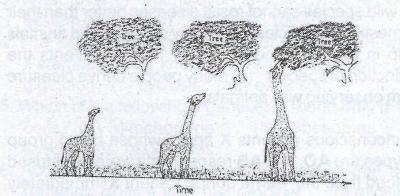
The theory supports
- A. natural selection
- B. struggle for survival
- C. independent assortment
- D. the use and disuse of body parts
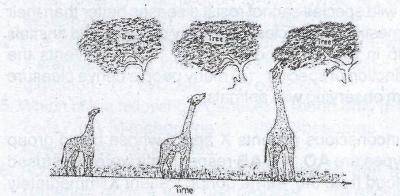
The diagram above is an illustration of one of the theories of evolution. Who proposed the theory in the illustration?
- A. Louis Pasteur
- B. Gregor Mendel
- C. Robert Hooke
- D. Jean Lamarck