a. Complete the table below.
|
Organism |
Mode of feeding |
Feature of mouthpart that adapts organism to mode of feeding |
[6 marks]
b. List five parts of the alimentary canal of an earthworm. [5 marks]
c. State six ways by which water could be polluted by agricultural practices. [6 marks]
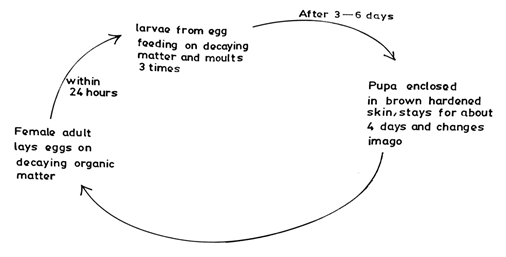
d. Describe briefly the life cycle of a housefly. [5 marks]
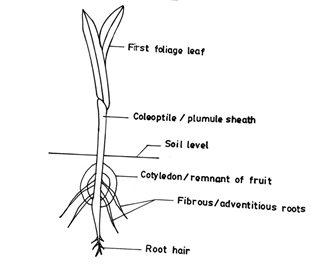
e. Make a diagram, 6 cm – 8 cm long of the hypogeal germination in a mature maize seedling and label fully. [8 marks]
Explanation
a. Table
|
Organism |
Mode of feeding |
Feature of mouthpart that adapts organism to mode of feeding |
|
Adult mosquito |
Fluid feeding/piercing/sucking |
|
|
Weevil |
Chewing/boring |
Possession of pointed short and strong rostrum |
|
Cockroach |
Biting/chewing |
Well developed mandibles/strong sharp mandibles |
b. Parts of alimentary canal of earthworm
- Mouth;
- Pharynx;
- Oesophagus/gullet;
- Crop;
- Gizzard
- Intestine;
- Anus.
c. Ways by which water could be polluted by agricultural practices
- Farmers add excess fertilizers/organic material to soil which may cause water pollution;
- The inorganic/artificial fertilizers that contain high concentrations of nitrates and phosphates, dissolves in rain water and washed into nearby streams and rivers;
- Nitrates and phosphates accelerate the growth of algae/eutrophication;
- The death/decay of algae in rivers and streams increase the population of bacteria rapidly;
- And cause oxygen level to decrease drastically;
- Killing aquatic organisms;
- Use of chemicals/dynamite for fishing which pollutes water
- Dumping of cleared vegetation on water bodies;
- Slash-burn methods of farming which might wash ash to nearby rivers/water bodies;
- Pesticides/insecticides also sprayed on crops are usually non-biodegradable;
- They are washed into nearby rivers/streams/water bodies;
- Accumulate in the bodies of aquatic organisms;
- And are passed along the food chain;
- The concentration of pesticides/insecticides can reach toxic level in the bodies of the final consumers in the higher trophic levels is causing these organisms to die;
d. (i) Life cycle of a Housefly
- The female housefly lays eggs on decomposing matter/rubbish;
- The eggs hatch into larvae/maggot;
- In a few hours;
- They crawl unto food;
- Which if solid will be digested by enzymes to liquid;
- The larvae have twelve segments on the body;
- The body then contracts;
- The skin hardens and turns brown to enclose the pupa;
- After about four days, the pupa changes into the adult/imago;
- Inside the puparium/brown skin cover;
- The adult fly then emerges;
- And flies away.
OR
e. Diagram of a mature maize seedling