Study specimens L and M and answer questions 4(a) to 4(e). (a) Classify each of specimens L and M into its: (i) Phylum L: ________ M: _______(ii) Class L:_______ M:_______ (b)(i) State three observable features of members of the class of specimen L. (ii) Name three other classes of the phylum to which specimen L belongs. (c)(i) State two ways each by which specimens L and M are of economic importance. L: _______ M: ________ (ii) State five ways by which specimen L can be controlled. (d)(i) State five observable differences between specimens L and M.

(ii) State four observable similarities between specimens L and M. (e) Name one habitat each of specimens L and M. L:_______ M:_______
Beakers D, E, F and G contain seeds that have been sown for seven days. Carefully remove one seed/seedling from each of the beakers labelled D, E, F and place each on the corresponding white tile labelled D, E, F and G. Study them and answer questions 2(a) to 2(c). (a) Observe the soils and seed/seedling then record the observation and result on the table below.

(b)(i) Name one condition for germination that was likely absent in the beakers labelled E, F and G
E: _________ F: _________ G: _________
(ii) Give two reasons for the result in beaker D.
(c) Make a drawing 8cm to 10cm long of one sees/seedling obtained from the beaker labelled D and label fully.
Study specimen A, B and C and answer questiions 1(a) to 1(c). (a)(i) Name the part of the body where specimens A, B and C would be found in a mammal. A: _________ B: _________ C: __________
(ii) State one function each of specimens A, B and C. A: ________ B: _________ C: _________
(b)(i) Make a drawing , 6cm to 8cm long of the anterior view of specimen C and label fully. (ii) State one function each of four of the parts labelled in 1(b)(i).
(c)(i) Mention the total number of each of specimens A, B and C in adult humans . A: _________ B: _________ C: _________ (ii) Name two other vertebrae in humans.
(a) Complete the table below by naming the nutrient cycle that involves each of the given processes and give three other processes involved in the nutrient cycle.

(b)(i) What is irritability?
(ii) Complete the table below by stating the type of response elicited by each of the given actions.

(c) Name three animals each that exhibit: (i) territoriality (ii) seasonal migration (iii) display
(a) Complete the table below by naming five wildlife animals in West Africa and one body part each that makes them endangered because of the activities of humans.

(b) State three effects each of the following factors on conservation of natural resources: (i) poor economy of a nation (ii) poaching
(c) State four roles played by the Government in conservation of natural resources
(a) Complete the table below by placing each of the following organisms under the appropriate heading: Algae, Bacteria, Dog, Water lettuce, Tadpole, Cat, Lemna, Waterleaf, Mucor, Mushroom

(b)(i) Name four products of decomposition (ii) Mention three roles of decomposers on a refuse dump
(c) List three materials found in a refuse dump which would not be affected by the action of decomposers.
(a) What is dentition in animals?
(b) Describe briefly the generalised structure of a tooth in animals.
(c) List three food substances that plants manufacture from glucose.
(d) Make a diagram, 6 cm to 8 cm long of an experimental set-up to show that oxygen is produced during photosynthesis.
A sample of human blood was put in a test tube and allowed to spin in a centrifuge. The components of the blood sample were clearly separated.
(a) List the four main components of blood that would be in the test tube.
(b) Name the component of the blood that: (i) would form the top layer in the test tube, (ii) destroys pathogens; (iii) is biconcave in shape (iv) would be relatively low in a haemophilic condition (v) is produced in the bone marrow: (vi) is a thrombocyte; (vii) is nucleated.
(c) Mention three chemical substances transported by the blood component named in 1(b)(i).
(d) List four diseases associated with blood.
(e) Explain briefly why a disease of the blood could be dangerous.
Which of the following statements is not Lamarck’s postulate on evolution?
- A. great changes in the environment result in corresponding changes in species
- B. frequently used organs become well developed while the ones not used become vestigial
- C. well developed acquired characters are inheritable
- D. survivors in a competitive community must have inherited useful traits
Natural selection arises as a result of?
- A. gene mutation
- B. change of habitat
- C. reduction in population
- D. climate change
Which of the following organisms exhibits division of labour?
- A. butterfly
- B. cockroach
- C. termite
- D. housefly
A woman with Rhesus negative blood group was advised not to marry a man with Rhesus positive blood group because
- A. it will hinder her from having blood transfusion from her husband
- B. it will result in sickness and probably death of the offspring
- C. her children may all resemble her husband
- D. it may affect her childbearing ability
In humans, pointed eyebrows (B) is a dominant trait over smooth eyebrows (b). A student and the mother have smooth eyebrows while the father has pointed eyebrows. What is the genotype of the father?
- A. BB
- B. Bb
- C. bb
- D. BBbb
Which of the following statements about sickle cell anaemia is correct?
- A. it is caused by sex-linked genes
- B. it is more common in males than in females
- C. two sickle cell carrier parents may have a sickling child
- D. it is caused by recessive genes
Plants suitable for experiments in genetics must not
- A. produce numerous seeds within a short time
- B. have a small number of chromosomes
- C. have a relatively short life cycle
- D. produce one generation in a large period
A mixture of blood with antigen A and blood containing antibody a will?
- A. lead to agglutination
- B. facilitate dissolution of clot
- C. have no effect on blood composition
- D. change the blood group
Which of the following statements about mitosis is not correct?
- A. chiasmata are not formed
- B. Bi-valents are not formed
- C. It does not lead to variation
- D. Four daughter cells are produced
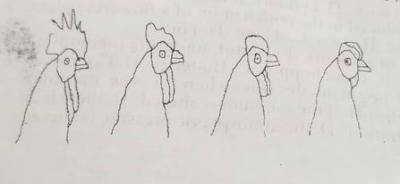
The diagrams above are illustrations of types of comb found in domestic fowl. Study them and answer this question.
Which factor is most likely responsible for the various types of comb?
- A. environment
- B. genetics
- C. physiology
- D. morphology
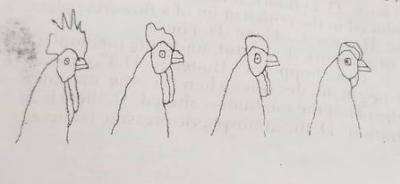
The diagrams above are illustrations of types of comb found in domestic fowl. Study them and answer this question.
The types of comb show ?
- A. variation
- B. inheritance
- C. cell theory
- D. courtship behaviour
Which of the following resources cannot be conserved?
- A. forest
- B. water
- C. soil
- D. garbage
Which of the following practices is a wildlife conservation method?
- A. use of cover crops
- B. crop rotation
- C. mulching
- D. discouraging poaching


