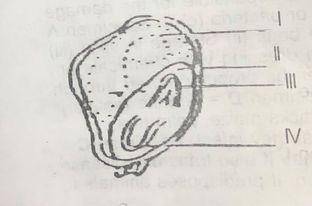
3. (a) Name the parts labelled | – IV (b) In which of the labelled parts is food stored?
2. (a) Name two supporting tissues found in plants (b) Give one function of the Golgi body in the cell.
1. (a) List three features which are essential for cross-pollination to take place (b) State three characteristics
Specimen G is a paste made from a food material. Carry out the following tests to identify the food substances contained in specimen G. Wash the test tube after each use to ensure that the next sample is not contaminated. All tests and observations should be recorded in a table as shown below.
| Test | observation | inference |
(a) (i) Pour 5 cm/(^3/) of specimen G into a test tube and add three drops of sodium hydroxide solution. Shake two test tube. Record your observation. Then add three drops of copper (ii) tetraoxosulphate (VI) solution (CuSO/(_4/)). Shake the test tube. Record your observations and inference (b) Pour 5 cm/(^3/) of specimen G into a test tube and three drops of Sudan IIl. Shake the mixture. Record your observation and inference (d) To another 5 cm/(^3/) of specimen G add four drops of Fehling’s solution. Shake the test tube. Warm the mixture. Record your observation and inference
(a) identify specimen D without giving reason (b) (i) State two observable features of specimen D which indicate its mode of nutrition (b) (ii) What is the mode of nutrition cf specimen D? (c) Make a labelled drawing to show features of biological importance of the specimen (d) (i) Examine and identify without reasons specimens E and F
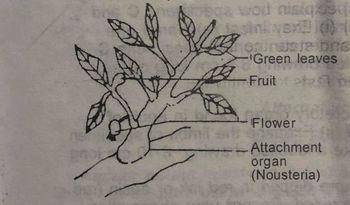
You are provided with specimens A, B and C (a) identify specimens A, B and C without reason.
(b) Make a labelled drawing 6-8 cm long of the longitudinal section of specimen A to illustrate its essential features
(c) (i) Suggest the possible means of pollination of specimen A (ii) Give three reasons for your answer
(d) (i) Name one agent of dispersal each for specimen B and C (ii) Give one reason each for your answer.
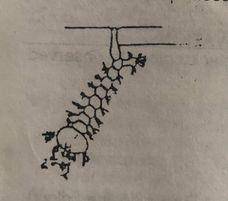
(a) Name the organism represented in the diagram above (b) Name the structure labelled x (c) Into what stage would the organism develop?
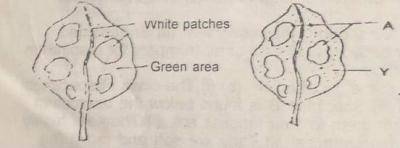
The diagram above illustrates a leaf before and after an experiment stated below. The leaf shown in diagram I was detached from a potted plant which had been exposed to sunlight for 4-5 hours while diagram ll shows the same leaf after the test for starch.
(7) (a) Name the type of leaf used for this experiment (b) Why is this type of leaf most suitable for the experiment? (c) State one precaution that should be taken in carrying out this experiment (d) What would be the colours of the parts labelled X and Y after the test for starch? (e) Suggest the aim of this experiment.
List (a) two plant characteristics (b) two animal characteristics found in Euglena.
(a) Name the vessel that carries blood from the wall of the small intestine to the liver (b) State two similarities in structure between the transport systems in plants and animals.
(a) (i) State one function of plastids to plants (i) Name one plastid found in plants (b) State one function each of (i) mitochondrion (ii) chromosome
(a) What would you observe if a filament of spirogyra is immersed in 0. 1 m sodium chloride solution for about one hour?
(b) Name the process which occurred during the immersion of the spirogyra filament in 0.1 m sodium chloride solution.
In the following experiments wash the test tube and the measuring cylinder before each use. You are provided with Solution A (a) Place three drops of solution A on a white tile and add one drop of iodine solution. Record your observation (b) Put 10cm³ of solution A in a beaker and add a few drops of dilute tetraoxosulphate (vi) acid (H\(_2\)SO\(_4\),) in a test tube and boil fora few minutes. Then add a few drops of sodium hydroxide solution and allów the mixture to cool. Divide the mixture into two equal portions
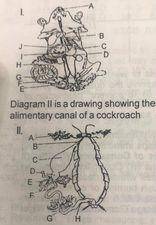
Diagram 1 is a drawing showing the alimentary canal of a mammal. Study the diagram carefully (a) Name the structure labelled A to J (b) What are the functions of the parts labelled A, C and H?
(C) Name the parts labelled A to H (d) State the functions of the parts labelled D and E (e) State two features common diagram I and D in diagram II (f) identify and name the parts in diagrams I and ll that perform similar functions
(a) identify specimens A and B (b) (i) Name the group or class of animals to which each specimen belongs (ii) State the location of specimen B in the organism (c) State two characteristic features common to specimens A and Band which adapt them to their functions (d) What is the function of specimen A in the organism? (e) Suggest the habitats of the animals to which each of the specimens belongs (f) Make a labelled drawing 6 to 7cm long of specimen B to illustrate its essential features.
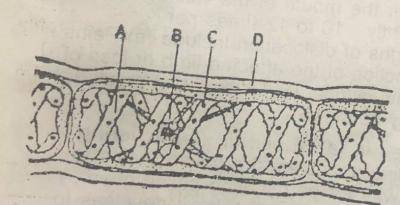
Study the diagram below (a) (i) ldentify the organism illustrated in the diagram (i) Give two reasons for your answer
(b) (i) Name the parts labelled A to D (ii) State the function of one of the labelled parts
State two ways in which agricultural practices can affect an ecological system.

