Give one example each of (a) protective colouration (b) structural adaptation in animals for temperature regulation 4.
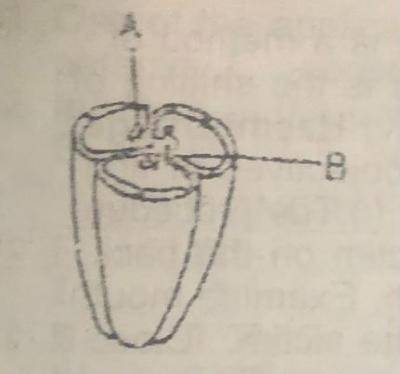
The diagram below represents the transverse section of a fruit (a) State the kind of placentation found in the fruit (b) Name one fruit that has this kind of placentation

(a) Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D
(b) What is the significance of the relative size of B and C?
(c) Name the structures in: (i) Amoeba (ii) earthworm. Which are equivalent in function to the structure illustrated in the diagram

The set-up in diagrams I and II illustrate breathing mechanisms in mammals
(a) Name the structures in mammals that are equivalent in function to the parts labelled (i) glass tube (ii) bell jar (iii) balloons (iv) rubber sheets (v)A (vi) B.
(b) Name the processes illustrated by diagrams (i) I (i)
(c) In which of the bell jars is the pressure lower?
(a) Explain briefly the following types of fertilization in animals; (i) external fertilization (ii) internal fertilization
(b) Name two groups of animal each that exhibit the types of fertilization in (a)
(c)(i) If the placenta in a pregnant woman is detached from the uterine wall, give three effect this will have on the foetus
(ii) Name three other features in the uterus of a pregnant woman that are useful for the development of the foetus
(d) Explain briefly how the activities of organisms bring bout dynamic equilibrium in the habitat.
(e) State four problems that organisms in the intertidal zone of a marine habitat could encounter.
(f) Explain briefly the reasons that the following factors are necessary for germination; (i) moisture (ii) viable seeds
(g) Explain briefly the reason light energy is considered a limiting factor in the production of foods by autotrophs.
(a) Explain briefly; (i) independent assortment of genes (ii) the reason blood group O in humans can only exist in homozygous form while blood groups A and B can exist both in homozygous and heterozygous forms.
(b) Complete the table below by naming the classes of vertebrates in their evolutionary trend and giving one example each of the classes.
| Classes of vertebrate | One example |
(a) Complete the table below;
| Disease | Causative organism | Vector | Control |
| Cholera | |||
| Trypanosome | |||
| Female Anopheles mosquito | |||
| Ringworm | None |
(b) Explain briefly the biological basis of preserving foods using each of the following methods;
(i) salting (ii) irradiation (iii) smoking
(a)(i) What is a deficiency disease?
(ii) Complete the table below by naming five nutrient deficiency diseases in humans and stating one remedy for each of the diseases.
(b) Outline a chemical test for (i) Starch in a tuber of yam (ii) Glucose in orange fruit
| Nutrient deficiency disease | Remedy |
(a) Explain briefly how the human ear carries out its function of balancing.
(b) (i) make a drawing 8 cm – 10 cm long of the structure of the human ear and label fully.
(ii) Describe briefly the structure of the middle ear in humans.
Which of the following statements best explains the reason why termites swarm at night?
- A. Light is not necessary for swarming
- B. They avoid day-flying birds
- C. Light destroys their wings
- D. They can only see in the dark
Who proposed the theory of evolution by natural selection
- A. Darwin
- B. Lamark
- C. Aristotle
- D. Linnaeus
Replication of DNA molecules is catalysed by an enzyme called
- A. polymerase
- B. ptyalin
- C. pepsin
- D. amylase
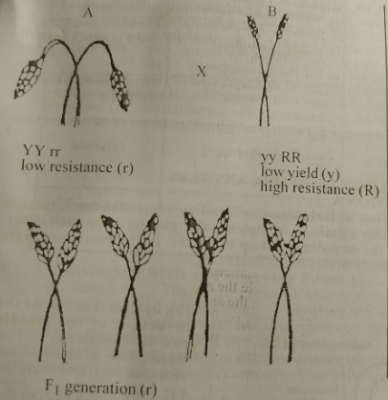
The diagram above is an illustration of a cross between plants A and B of the same species. Study it to answer the question below
The process that gave rise to the F1 generation is
- A. self fertilization
- B. cross fertilization
- C. out-breeding
- D. test cross
The diagram below is an illustration of a cross between plants A and B of the same species. Study it and answer the question below;
If the F1 generation are plants with high yield and resistance, the genotype of the F1 generation plants would be
- A. YYRR
- B. YyRr
- C. yyRr
- D. yyrr
Which of the following diseases can be inherited?
- A. Pneumonia
- B. Whooping cough
- C. Sickle cell anemia
- D. Malaria
Which of the following statements about chromosomes is correct?
- A. All the chromosomes of a species are the same shape
- B. The number present in a specie is constant
- C. They are neatly arranged in a cytoplasm
- D. They bear ribosomes on their outer membranes
Measurements of height and weight of students in a class show
- A. discontinuous variation
- B. continuous variation
- C. shortness is more prevalent
- D. fatness is less prevalent
Variation which exhibits a wide range from one extreme to the other is
- A. phenotypic variation
- B. discontinuous variation
- C. continuous variation
- D. genotypic variation
A child that can receive blood donation from anybody belongs to the blood group
- A. O
- B. A
- C. B
- D. AB
Which of the following substances is not a conservable natural resource?
- A. Mineral
- B. Air
- C. Soil
- D. Water


