Catalytic hydrogenation of benzene produces
The correct answer is: C
Explanation
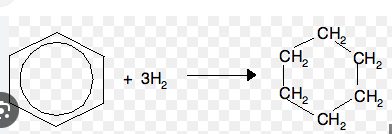
Hydrogenation of benzene involves the addition of 3 molecules of H\(_2\) = 6 Hydrogen atoms in all.
To do this, the three double bonds present in the Benzene (C\(_6\)H\(_6\)) will be opened so that the 6 Hydrogen molecules can attach to the Carbon atoms each, resulting into C\(_6\)H\(_{12}\) (in a cyclic form, hence the name cyclo). Recall, Saturated Hydrocarbon with 6C atoms is called Hexane, hence the name is cyclohexane.
There is an explanation video available .


