(a)(i) Give one laboratory use of activated charcoal
(ii) A piece of phosphorus and some magnesium ribbon were burnt in two separate jars of oxygen. Water was then added to dissolve the product. State the action of litmus on each of the resulting solutions
(b) Give one chemical test to distinguish between CH\(_3\)CH\(_2\)OH and CH\(_3\)COOH.
(c) Describe how you would dilute accurately a solution containing 0.10 mole of the solute per dm\(^3\) of solution to 0.010M.
Credit will be given for strict adherence to the instructions, for observations precisely recorded, and for accurate inferences. All tests, Observations, and inferences must be clearly entered in your answer book, in ink, at the time they are made. Carry out the following exercises on sample C.
Record your observations and identify any gases evolved
(a) Put all of C into a test tube and add about 5cm\(^3\) of water. Shake the mixture and filter. Keep both the residue and the filtrate
(b) Divide the filtrate into two portions;
(i) To the first portion, add a few drops of dilute trioxonitrate (V) acid followed by about 1cm\(^3\) of silver trioxonitrate (V) solution
(ii) Add excess aqueous ammonia to the mixture in (i) above
(iii) To the second portion, add about 2cm\(^3\) of dilute sodium hydroxide solution and warm gently
(c) Add about 2cm\(^3\) of dilute hydrochloric acid to the residue from (a) above and warm gently. Filter if necessary and divide the resulting solutio into two portions.
(i) To the first portion add dilute sodium hydroxide solution in drops until it is in excess
(ii) To the second portion, add aqueus ammonia in drops until it is in excess.
All your burette readings (initial and final) as well as the size size of your pipette, must be recorded but no account of experimental procedure is required. All calculations must be done in your answer book.
Xg of pure potassium trioxocarbonate (IV) was treated with 1dm\(^3\) of 0. 25M tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid to obtain solution A which contains excess acid. B is a solution containing 2.8g of potassium hydroxIde per 250cm\(^3\) solution.
(a) Put A into the burette and titrate with 20cm\(^3\) or 25cm\(^3\) portions of B. using methyl orange as indicator. Record the volume of your pipette. Tabulate your burette readings and calculate the average volume of acid used.
(b) From your results and the information given. Calculate the;
(i) concentration of the excess acid in A in mol dm\(^3\)
(iii) value of X. The equation for the reaction between the excess acid the potassium hydroxide is H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) + 2KOH \(\to\) K\(_2\)SO\(_4\) [H = 1. C = 12, O = 16. S = 32, K = 39]
(a)(i) Define oxidation in terms of electron transfer.
(ii) Write balanced equations for the half reactions for the following changes in acidic solution: Mn0\(^-_4\) + Fe\(^{2+}\) —> Mn\(^{2+}\) + Fe\(^{3+}\)
(b)(i) Distinguish between an electrolytic celI and an electrochemical cell.
(ii) Sketch a cell for the electrolysis of molten magnesium chloride. Lable the anode and the cathode and indicate the direction of electron flow. Give the electrode reactions.
(iii) Give one reason why a platinum anode is not suitable for the eloctrolysis in (b)(i) above.
(c) Calculate the mass of lead that would be deposited from a solution of lead (II) trioxonitrate by the same quantity of electrically depositing 1.35g of copper. (Cu = 63.5, Pb = 207)
(a)(i) Define the term addition polymerization
(ii) What type of organic compounds undergo addition polymerization
(iii) List two factors which affect the strength of polymers
(b) The diagram below shows some reaction pathways involving ethanol

(i) Write the name and structural of the organic product X
(ii) State the reagent for the conversation indicated as step A.
(iii) What type of reaction will ethanol undergo CH\(_3\)CH\(_2\)COOH during the process of conversation indicated as step B?
(c)(i) Write three balanced equation for the complete combustion of ethanol in :date the volume of oxygen required at s.t.p for the complete combustion of ethanol. (H = 1, C = 12, O = 16, molar volume of gases at s.t.p. = 22.4 dm\(^3\))
(d)( i} State two substances produced when coal is heated in the absence of air
(ii) What name is given to the process in (d)(i) above?
(iii) State the importance of the non-volatile residue of the process named in (d)(iii) to the iron and steel industry.
Consider the reaction represented by the equation: 2SO\(_{2(g)}\) + O\(_{2(g)}\) 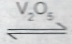 2SO\(_{3(g)}\). \(\Delta\)H = 188KJ.
2SO\(_{3(g)}\). \(\Delta\)H = 188KJ.
(a) Write an expression for the equilibrium constant
(b) Sketch an energy diagram for the forward reaction, showing the profile for the catalyzed and non-catalyzed systems.
(c) state the reason, the effect of the following on the position of equilibrium of the system:
(i) increase in temperature
(ii) increase in pressure;
(iii) removal of some of the SO\(_3\) produced;
(iv) presence of V\(_2\)O\(_5\)
(d)(i) Write equations to show how the sulphur(VI) oxide is converted to tetraoxosulphate(VI) acid in the contact process
(ii) Give two uses of tetraoxosulphate(VI) acid.
(a)(i) List two physical properties used as criteria for purity of substances
(ii) describe how you would prepare a pure, dry sample of sodium chloride crystals by a neutralization reaction, using bench reagents.
(iii) Give two other general methods for preparing soluble salts.
(b) Explain the following observations:
(i) a sheet of iron placed in dilute copper (II) tetraoxosulphate (VI) solution reddish brown;
(ii) the white gelatinous precipitate formed when a few drops of sodium hydroxide solution are added to a solution of aluminium salt dissolves in excess alkali;
(iii) the pale green prepared iron(II) chloride solution changes to brown on bubbling chlorine gas through it.
(iv) Write a balanced equation for the reaction of dilute hydrochloric acid with marble. List two industrial process in which limestone is used as a raw material.
Liquefied air is mainly a mixture of nitrogen and oxygen which can be separated into its components by fractional distillation (Boiling point of nitrogen is 196°C, Boiling point of oxygen is 174°C)
(a) Name the fraction which distills over first. Give the reason for your answer.
(b) Give another industrial application of fractional distillation as a separation technique.
(a) Name the type of solid structure possessed by:
(i) diamond;
(ii) iodine;
(iii) sodium chloride.
(b) Give:
(i) one alloy of tin:
(ii) a common reducing agent which is a compound of tin.
(a) Arrange the first three members of the halogen family in their increasing order of electronegativity. Give the reason for your answer.
(b) State and explain what happens when chlorine reacts with starch iodide paper.
Benzene contains six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms.
(a)(i) Draw two stable structures of benzene to show how these atoms are arranged.
(ii) What is the concept behind these structures?
(b) Give (i) two uses of benzene. (ii) one industrial source of benzene.
(a) Give the formula indicating the relationship between entropy, free energy and enthalpy changes of a system.
(b) For each of the following, state whether entropy change is positive, negative or zero.
(i) H\(_2\)O\(_{(g)}\) -> H\(_2\)O\(_{(g)}\)
(ii) Cl\(_{2(g)}\) —> 2CI\(_{(g)}\)
(iii) HCI\(_{(g)}\) -> HCl\(_{(g)}\)
(a) Give one reason why a collision between reactants may not produce new species.
(b) Explain, illustrating with appropriate equation(s), why an aqueous solution of aluminium chloride is acidic.
(a) Balance the nuclear equation below and hence identify Y.
\(^{238}_{94}U \to ^{234}_{92}Th + Y\)
(b) In a tabular form, state two of the observations in the cathode ray experiment and the corresponding deductions.
A hydrocarbon X which decolorizes bromine water but has no action on ammoniacal silver trioxonitrate (V) solution was found to have a molar mass of 58 g mol\(^{-1}\)
(a) Deduce the molecular formula of X. (H = 1, C = 12)
(b) Write the structures of two isomers of X.
(a) Give two reasons why carbon(IV) oxide is used for extinguishing fire
(b) Explain briefly the water softening action of cation exchane resins.
(a) Write the electronic configuration of an element with atomic number 15, indicating the distribution of electrons in the energy sub-levels
(b) Give the formula and the colour of the complex formed between ammonia and copper (II) ions
Petrol can be obtained from diesel by
- A. distillation
- B. cracking
- C. catalysis
- D. polymerization
- E. dehydrogenation
The following metals are extracted by the electrolytic method except
- A. potassium
- B. calcium
- C. sodium
- D. tin
- E. magnesium
Which of the following compounds crystallizes without water of crystallization?
- A. Na2CO3
- B. CuSO4
- C. MgSO4
- D. NaCI
- E. FeSO4
The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide is represented by the equation: 2H2O(l) + O2(g) what mass of hydrogen peroxide would be required to produce 22.4dm3 of oxygen at s.t.p? (H = 1, O = 16, molar volume of a gas at s.t.p. = 22.4dm3)
- A. 18 g
- B. 34 g
- C. 36 g
- D. 64 g
- E. 68 g


