C is a mixture of an organic and an inorganic salt. The test recorded in the table below were performed as indicated,
(a)Copy and complete the table as appropriate.
| Test | Observation | Inference |
| (i) C + water mixed thoroughly and filtered | Partially soluble, colourless filtrate, white residue | |
|
(ii) Portion of filtrate from (i) + NH\(_{3(aq)}\) in drops, then in excess |
White precipitate which dissolves in excess to give a colourless solution | |
| (iii) Portion of filtrate from (i) + NH\(_3\) in drops, then in excess | White precipitate insoluble in excess | |
| (iv) Portion of filtrate from (i) + conc. HCl + heat | White precipitate which dissolves on warming and reappears on cooling | |
| (v) Portion of filtrate from (i) + conc. H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) + gentle warming | Brown fumes produced on warming | |
| (vi) Residue from (i) + iodine solution | Blue-black colouration | |
| (vii) Residue from (i) + Fehling’s solution + heat | ||
| (vii) Residue from (i) + dil HCl solution + heat + Fehling’s solution |
(b) From the information provided and your inference, identify the compounds of C
(c) Describe the action of heat on a solid sample of the inorganic component Write an equation for the reaction.
(d) State what would be observed if an aqueous suspension of the organic component were heated to boiling
A is a solution containing 0.50 mole of barium chloride per dm\(^3\). Solution B contains 1.0 mole of tricxocarbonate (IV) salt per dm\(^3\)
(a) State what would be observed and give the confirmatory test for any gases evolved if the following tests were performed
(i) mixing 2cm\(^3\) each of solutions A and B in a test tube
(ii) adding excess dilute hydrochloric acid to the mixture from (a)(i) above
(b) 10cm\(^3\) of solution A were measured into each of seven boiling tubes of uniform bore and various quantities of solution B were added respectively to the boiling tubes, The tubes were immersed in hot water. After the reaction, the height of the product in each of the tubes was measured. The results were as tabulated below.
| Test tube | I | II | III | IV | V | VI | VII |
| Volume of sodium B added (cm\(^3\)) | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 |
| Height of the product (to the nearest m) | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
(i) Plot a graph of the height of the product against the volume of solution B added to each test tube. Explain the shape of the graph
(ii) Calculate the amount (in mole) of the trioxocarbonate (IV) salt contained in the volume of solution B added to tube lV
(iii) Calculate the amount (in mole) of barium chloride contained in 10cm\(^3\) of solution A. Hence, determine the mole ratio of barium chloride and the trioxocarbonate (IV) Salt in the reaction
(a) Name the apparatus used in the laboratory to (i) Convert vapour into liquid during distillation
(ii) determine the volumetric composition of water
(ii) produce an intermittent supply of any gas which can be evolved by the action of a liquid on a solid without heating.
(b) Give the reason for the following;
(i) the edge of the lid of a desiccator should be greased
(ii) a standard solution of sodium hydroxide is not prepared by weighing out accurately a given mass of the solid and making it up to the required volume.
iii) after the reduction of copper (II) oxide by a a stream of hydrogen gas passed overs the heated oxide in a combustion tube, it is necessary to continue passing the gas over the residue until the residue cools.
(c) An acid-base indicator turns orange in an acidic solution, green in a neutral solution and blue in an alkaline solution. The table shows the results obtained when a few drops of the indicator were added to samples of some liquids.
| Liquid | Colour of the indicator in the liquid |
|
Glucose solution Rainwater Lime water Vinegar Stomach powder solution |
Green Pale orange Blue Orange Pale blue |
(i) Arrange the liquids in increasing order of their expected pH values.
(ii) Explain why the colour of the indicator in the sample of rainwater is pale orange whereas in pure water it is green.
(iii) A given crystalline solid is suspected to be either sodium chloride or ammonium tetraoxosulphate (VI). Describe how you would use the indicator to identify the solid.
(iv) State with reason whether or not phenolphthalein indicator can be used to distinguish between the samples of glucose solution and vinegar.
(v) What would be the colour of methyl orange indicator in the lime water sample?
(a) State two factors which can affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
(b) 0.72g of magnesium was added to different volumes of 2 mol. per dm\(^3\) hydrochloric acid. The volume of liberated was as measured at room temperature and pressure. The result of the experiment was as tabulated
| vol. of 2 mol. per dm\(^3\) HCl used (cm\(^3\) | Vol. of H\(_2\) evolved in cm\(^3\) (to the nearest 10cm\(^3\)) |
|
5 15 25 35 45 |
120 360 550 600 600 |
Use the data in the table to plot a graph of the volume of hydrogen liberated against the volume of acid used.
(c) From the graph in (b) above, determine the volume of: (i) hydrogen that would be produced if 50 cm\(^3\) of the acid were added to 0.72g of magnesium.
(ii) the acid which must be added to 0.72 g of magnesium to produce 480 cm\(^3\) of hydrogen;
(iii) the acid needed exactly to dissolve 0.72 g of magnesium completely.
(d) Explain your answer to (c)(iii).
(e) From your answers to (c) above, deduce the: (i) volume of the acid which will dissolve 1 mole of magnesium completely. (Mg = 24)
(ii) volume of hydrogen that would be liberated if 1 mole of magnesium dissolves completely in the acid;
(iii) equation for the reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid. Show clearly how you arrived at you answers
(a) Give three differences between electrovalent compounds and covalent compounds
(b) List two physical properties of metals which can be accounted for by their structure
(c) Thorium (Th) metal undergoes a reaction represented by the following equation:
\(^{234}_{90}Th \to X + ^{234}_{91}Pa\)
(i) State the type of process involved in the reaction
(ii) Balance the equation equation and hence identify X.
(iii) Name one equipment which can be used to detect X.
(iv) Sketch a curveto show the mass of given quantity of thorium will change over a long period of time.
(d) Y is a moderately reactive divalent found naturally in the combined state as the trioxocarbonate (IV) salt, YCO\(_3\) is decomposed by strong heat, state the steps you would use in extracting Y from the ore. Write equation to show the chemical processes involved.
(a) Name one gaseous hydrocarbon which is
(i) used for welding.
(ii) a major raw material for the plastic industry.
(b) Write the structural formula of the hydrocarbon in (a)(i) above. Name the process by which it can be converted to neoprene rubber.
(c) Potatoes contain a high proportion of carbohydrate.
(i) Give the main product formed when potatoes are dehydrated completely
(ii) Describe how you would convert potatoes to ethanol. State the reactions involved the process and write equation for the final stage of the conversion.
(iii) Draw a labelled diagram of the apparatus you would use to obtain a sample of fairly pure ethanol from the product formed in (c)(ii) above. What is the name given to the technique?
(a)(i) Give two uses of chlorine.
(ii) State the action of chlorine on moist blue litmus paper
(b) Draw a labelled diagram for the laboratory preparation of a dry sample of chlorine
(c) State the type of reaction involved between chlorine and (i) aqueous iron (II) chloride;
(ii) propane. Write an equation for each reaction and name the product formed in (c)(ii).
(d) Consider the reactions the following equations: Cl\(_{2(g)}\) + 2Br\(^-_{(aq)}\) \(\to\) 2Cl\(^-_{(aq)}\) + Br\(_{2(g)}\)
F\(_{2(g)}\) + 2Cl\(^-_{(aq)}\) —> 2F\(^-_{(aq)}\) + Cl\(_{2(g)}\)
From the equations, arrange bromine, chlorine and fluorine in increasing order of oxidizing ability. Give the reason for your answer.
The set-up shown in the diagram below was used to separate a drop of universal indicator into the constituent dyes using ethyl ethanoate as the solvent.
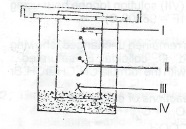
(a) What name is given to the separate strated in the diagram?
(b) State: (i) how many components are resolved in the separation;
(ii) the material normally used in laborary as the adsorbent medium;
(iii) which of the labels the point of application of the indicator.
Sketch a curve to show how the solubility of a gas varies with increasing temperature
Give one oxide in each case which;
(a) can act as a reducing agent
(b) can be used as a refrigerant
(c) is the anhydride of a strong acid;
(d) is yellow when hot and white then hot and white when cold;
(f) is usad as a pigment in paints.
(a) Name the industrial process by which ethene is obtained from petroleum fractions
(b) Give the I. U. P.A.C name of the isomer whose structure is shown below.
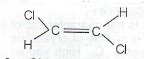
(c) Illustrate with an equation, one reaction in which benzene behaves as:
(i) unsaturated hydrocarbon
(ii) a saturated hydrocarbon
(a) Give two reasons why fused alumina is mixed with cryolite in the electrolytic extraction of aluminium.
(b) Write an equation for the reaction of sodium hydroxide with bauxite.
(a) Give the products of electrolysis of dilute copper (II) tetraoxosulphate(VI) solution using the following materials as electrodes:
(i) carbon rod;
(ii) copper rods
(b) For each of the process in (a) above;
(i) write the anodic half reaction;
(ii) state how electrolysis affects the pH of electrolyte
Methane is obtained when a powdered mixture of anhydrous sodium ethanoate and soda-lime is heated in a hard glass test tube.
(a) Write an equation for the reaction.
b) Explain briefly why soda-lime is preferred to sodium hydroxide for the preparation.
A colourless and odourless gas X burns in oxygen with a pale blue flame.
(a) Suggest two gases which X could be.
(b) Give one chemical test that could be used to confirm which of the two gases X is.
(a)State three characteristics of a catalyst.
(b) Mention one manufacturing process in which each of the following metals is used as a catalyst:
(i) iron;
(ii) nickel;
(iii) platinum
(c) Give one example of an organic catalyst.
State the atoms represented as shown below:

(a) State the relationship between the two atoms.
(b) What is the difference between them?
(c) Give two examples of elements which exhibit the phenomenon illustrated above.
Which of the following is suitable for determining different isotopes present in an element which exhibits isotopy?
- A. Sensitive weighing balance
- B. Cathoda ray tube
- C. Mass spectrometer
- D. Geiger muller counter
- E. Eudiometer
Hydrogen is used for the following except
- A. manufacturing of ammonia
- B. synthesis of hydrochloric acid
- C. extinguishing fire
- D. conversion of coal to petrol
- E. manufacture of margarine
In solution, aminoethanoic acid (glycine) can be represented as NH+3 CH2COO. This implies that it
- A. is soluble in all inorganic liquids
- B. can function as a weak acid or a weak base
- C. does not form salt with mineral acids
- D. is highly acidic
- E. cannot form esters with alkanols
river contaminated by alkali waste will have a pH of about.
- A. 1
- B. 3
- C. 5
- D. 7
- E. 9


