A is a solution containing 0.050 mol. dm of tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid. B is a solution of anhydrous trioxocarbonate (IV).
(a) Put A into the burette and titrate with 20cm\(^3\) or 25cm\(^3\) portions of B using methyl orange as an indicator. Record the volume of your pipette. Tabulate your burette readings and calculate the average volume of A used
(b) From your results and the information provided, calculate the:
(i) Concentration of solution B in mol. dm\(^{-3}\)
(ii) mass of sodium tetraoxosulphate (VI) that would be formed in solution of 1dm\(^3\) of solution B were neutralized by solution A
(iii) volume of carbon (IV) oxide at s.t.p. that would be liberated in (b)(ii) above. The equation for the reaction is: N\(_2\)CO\(_{3(aq)}\) + H\(_2\)SO\(_{4(aq)}\) \(\to\) Na\(_2\)SO\(_{4(aq)}\) + H\(_2\)O\(_{(l)}\) + CO\(_{2(g)}\) [O = 16; Na = 23, S = 32; molar volume of gases of s.t.p. = 22.4dm\(^3\)
C and D are samples of two different simple salts. Carry out the following exercises on them. Record your observations and identify any gases evolved. State the conclusion you draw from the result of each test.
a) Heat about one-half of C in a dry test tube until no further change is observed. Allow to cool.
(b)(i) To the cooled residue from (a) above, add about 5cm\(^3\) of dilute hydrochloric acid and warm.
(ii) To about 2cm\(^3\) of the clear solution from (b)(i) above add aqueous ammonia in drops until it is in excess.
(c) Put all of D in a boiling tube and add about 10cm\(^3\) of distilled water. Shake thoroughly and divide into two portions.
(d)(i) To the first portion from (c) above, add about 2cm\(^3\) of barium chloride solution, followed by dilute hydrochloric acid in excess. Warm the mixture.
(ii) To the second portion from (c) above, add 2 or 3 of acidified potassium tetraoxomanganate (VII) solution and shake.
(a) Draw a labelled sketch of the laboratory set-up for dissolving hydrogen chloride acid.
(ii) Give one chemical test to distinguish between hydrochloric acid and ethanoic acid
(b) Outline a suitable laboratory procedure for obtaining a fairly pure sample of sodium chloride crystals from a solution of it that is contaminated with some methyl orange:
(c) Name one substance used in the laboratory for:
(i) drying ammonia gas,
(ii) testing for the presence of water;
(iii) converting copper (I) oxide to copper.
(a) (i) Define heat of combustion.
(ii) What name is given to the container used for determining tne reaction?
(b) The heat of combustion of carbon in excess air is – 3935 kJ.
(i) Sketch an energy profile diagram for the reaction.
(ii) Calculate the heat change when 60 g of carbon undergoes complete combustion to produce carbon (IV) oxide. (C = 12)
(iii) Explain why the value of the heat of neutralization of strong acids by strong bases is constant.
(c) Give reason for the following:
(i) rusting of iron is regarded as a slow combustion process;
(ii) iron filings rust much more faster than iron nails when exposed to the same atmospheric condition;
(iii) iron is better protected from corrosion by plating it with.zinc than with tin
(a)(i) Determine the maximum number of electrons that can occupy the principal energy level M of an atom.
(ii) Show the changes in the electronic structures of atoms of sodium and fluorine (\(^{23}_{11}\)Na: \(^{19}_{9}F\)) when they combine to form sodium fluoride.
(iii) State: three properties that sodium fluoride would have, based a-n the bond type present in the compound.
(b) Write equations to show when:
(i) sodium metal burns in limited supply of oxygen;
(ii) water is added to the product in (b)(i) above
(c) Describe a suitable laboratory procedure for comparing the conductance of 1 mol dm\(^{-3}\) aqueous solutions of sodium hydroxide and ethanoic acid.
(a)(i) What is meant by hydrocarbons?
(ii) A hydrocarbon consists of 92.3% carbon. If it’s vapour density is 39, determine its molecular formula. (H = 1; C = 12)
(b)(i) Outline a suitable laboratory procedure for obtaining ethanol from cassava tubers
(ii) List two laboratory reagents used for oxidizing ethanol to ethanoic acid.
(c) What name is given to each of the following processes?:
(i) Conversion of alkanols to alkanoates;
(ii) Breakdown of proteins to amino acids;
(iii) Conversion of oils to fats
(iv) Alkaline hydrolysis of fats and oils.
(a)(i) Draw a labelled diagram for the laboratory preparation of a dry sample of chlorine
(ii) Give one chemical test for chlorine.
(b) Write equations to represent the reaction of chlorine gas with: (i) iron (II) chloride solution;
(ii) potassium iodide solution;
(iii) hot concentrated sodium hydroxide solution.
(c) State what is observed on:
(i) bubbling hydrogen chloride gas into an solution of lead (II) trioxonitrate (V);
(ii) heating the mixture from (c)(i) above to boiling and aging it to cool.
(d) A solution of bismuth chloride was prepared by adding the oxychloride which is a white powder to concentrated hydrochloric acid. The following equilibrium was set up: BiOCI\(_{(s)}\) + 2HCI\(_{(aq)}\) \(\rightleftharpoons\) BiCl\(_{3(aq)}\) + H\(_2\)O\(_{(q)}\). State what would be observed if some water is added to the system. Explain your answer
Potassium trioxochlorate (V) undergoes thermal decomposition according to the fotpowing equation: 2KCIO\(_3\) \(\to\) 2KCI + 3O\(_2\)
(a) What substance could be used in the laboratory to in ease the rate of the reaction
(ii) absorb the oxygen produced
(b) Give the reason why an aqueous solution of silver trioxonitrate (V) gives a white precipitate with KCI but not with KClO\(_3\).
(a) State whether entropy increases or decreases during each of the following processes
(i) condensation of steam;
(ii) melting of wax;
(iii) dissolution of sugar in water;
(iv) abscas on charcoal.
(b) What deduction can be made in each case given that the value of the free energy change for a particular reaction is:
(i) zero;
ii) negative
When ethane – 1,2-dioic acid is heated with concentrated tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid, a reaction represented by the following equation occurs:
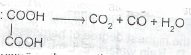
(a) State the type of process involved in the reaction
(b) What is the basicity of ethane-1, s-dioic acid?
(c) List three differences in the chemical properties of the two oxides of carbon produced during the reaction
(a) Write an equation to show the action of strong heat on:
(i) potassium trioxonitrate (V):
(ii) sucrose.
(b) State two observations in respect of the reaction between granulated zinc and dilute tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid.
(a) When MgSO\(_4\).XH\(_2\)O crystals were exposed to the atmosphere for several days, three was a loss in mass
(i) What name is given to this phenomenon?
(ii) Give another example of a compound that exhibits this phenomenon
(b) If 0.50 mole of MgSO\(_4\).XH\(_2\)O has a mass of 123g. calculate the value of X. (H = 1, O = 16, Mg = 24, S = 32)
(a) Define oxidation in terms of electron transfer.
(b) Consider the following: Cu\(_{(s)}\) + 2Ag\(^{+}_{(Ag)}\) \(\to\) Cu\(^{2+}_{(aq)}\) + 2Ag\(_{(s)}\)
(i) State the species that is reduced
(ii) Write half-cell equation for each of the species.
(a) Give one example each of a naturally occurring substance that;
(i) conforms to the general formula C(_x\)(H\(_2\)O)\(_y\);
(ii) contains the carboxyl group as its functional group.
(b) Name the process for obtaining: (i) paraffin oil from crude oil; (ii) benzene from ethyne.
A shortened form of the Periodic Table is shown below. Use it to answer questions (a) and (b)
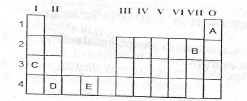
(a) Which of the elements represented as A to E in the table, above is:
(i) transition metal;
(ii) an alkaline earth meta
(iii) the least reactive;
(iv) the most electronegative?
(b)(i) What type of bond would exist in a compound formed when element D reacts with oxygen?
(ii) Write the formula of the compound formed in (b)(i) above.
(1)(a) State Avogadro’s law
(b) Which of the state of matter contains particles that are: (i) readily used
(ii) held firmly together by some forces of cohesion;
(iii) involved in rapid random motion?
(a) State two differences in the chemical properties of metals and non-metals.
(b) List two general methods of extract metals from their ores.
What is the molar mass of an alkyne with the formula Cx H 14? (H = 1, C = 12)
- A. 86g
- B. 92g
- C. 98g
- D. 110g
- E. 112g
The following compounds contain the same type of bonds except
- A. sodium chloride
- B. hydrogen chloride
- C. magnesium chloride
- D. potassium chloride
- E. lithium chloride
When magnesium ribbon burns in air, the products are
- A. magnesium nitride and magnesium oxide
- B. magnesium nitride and carbon (ll) oxide
- C. magnesium oxide and steam
- D. magnesium nitride and soot
- E. magnesium oxide and carbon (ll) oxide
Destructive distillation of coal means
- A. heating coal in plentiful supply of air
- B. burning coal in air to produce water and carbon (IV) oxide
- C. heating coal in the absence of air
- D. heating coal in limited supply of air
- E. separating coal into various allotropes of carbon


