All your burette readings (initial and final), as well as the size of your pipette, must be recorded but no account of experimental procedure is required. All calculations must be done in your answer book.
A is a solution containing 14.0gdm\(^{-3}\) of potassium hydrogen tetraoxosulphate (VI). B is a solution of sodium hydroxide.
(a) Put A into the burette and titrate with 20.0cm\(^{-3}\) or 25.0 cm\(^{-3}\) portion of B using methyl orange, as Indicator. Record the volume of your pipette. Tabulate your burette readings and calculate the average volume of A used.
(b) From your results and the information provided, calculate the:
(i) concentration of A in mol dm\(^{3}\)
(ii) concentration of B in g dm\(^3\)
(iii) volume of A (in dm\(^{-3}\)) that would produce one mole of Sodium tetraoxosulphate (VI) in solution. The equation for the reaction is:
2KHSO\(_{4(aq)}\) + 2NaOH\(_{(aq}\) \(\to\) K\(_2\)SO\(_{4(aq)}\) + NaSO\(_{4(aq)}\) + 2H\(_2\)O\(_{(l)}\) [H = 1; O = 16, Na = 23, KHSO\(_4\) = 136gmol\(^{-2}\)]
Credit will be given for strict adherence to instructions, for observations precisely recorded, and for accurate inferences. All tests, observations, and inferences must be clearly entered in your answer book, In ink, a the time they are made.
C is a mixture of two simple salts. Carry out the following exercises on C. Record your observations and identify any gases evolved. State the conclusion you draw from the result of each test.
(a) Add about 10cm\(^3\) of distilled water to all of C in a boiling tube. Shake the mixture and filter: Keep both the filtrate and the residue.
(b) Divide the filtrate into two portions.
(i) To the first portion, add about 2cm\(^3\) of barium chloride solution, followed by dilute hydrochloric acid in excess. Warm the mixture and identify any gas evolved.
(ii) To the second portion, add few drops of acidified potassium tetraoxomanganate (VIl) solution and shake.
(C) Put the residue in a test tube and add about 3cm\(^3\) of dilute hydrochloric acid Warm gently and identify any gas evolved. Keep the mixture.
(d) Divide the clear solution from (c) above into two portions
(i) To the first portion, add sodium hydroxide solution in drops and then in excess.
(ii) To the second, add aqueous ammonia in drops and then in excess.
(a) A soluble chloride X reacted with a liquid Y on heating, to give gas Z which turned moist blue litmus paper red and fumed in moist air.
(i) Identity Y and Z
(ii) Give one chemical test to confirm that X is a chloride
(b)(i) State one laboratory use of calcium chloride.
(ii) Name one laboratory technique suitable for separating a mixture of iron filings and ammonium chloride without applying heat.
(iii) State the action of solutions of the following salts on litmus respectively: K\(_2\)CO\(_3\); NaNO\(_3\), AICl\(_3\), (NH\(_4\))\(_2\)SO\(_4\).
(a)(i) What is an electrolyte?
(ii) Classify each of the following as strong electrolyte/weak, electrolyte/non-electrolyte. Potassium chloride; sodium ethanoate, aqueous ammonia; cane sugar
(b)(i) Write half-cell equations for the reactions in the Daniel cell .
(ii) Why is the Daniel cell classified as an electrochemical cell?
(iii) Give two other examples of electrochemical cell.
(c) Explain the following observations.
(i) Graphite conducts electricity, unlike most non-metals
(ii) In the electrolysis of copper (II) tetraoxosulphate (VI) solution, the blue colour fades with platinum electrodes while the colour intensity is unaffected with copper electrodes (equations required)
(iii) A solution of dry hydrogen chloride in methylbenzene (toluene) does not conduct electricity whereas hydrochloric acid does.
(a)(i) Define heat of neutralization
(ii) Give the reason why copper (II) chloride can be prepared by neutralization, unlike lead (II) chloride.
(b)(i) Describe in outline, the manufacture of trioxonitrate (V) acid by the catalytic oxidation of ammonia, giving equations where appropriate.
(ii) What are the products obtained when sodium tioxonitrate (V) is heated strongly?
(c) When powdered magnesium is heated to redness in a stream of nitrogen, magnesium nitride (Mg\(_3\)N\(_2\)) is formed.
(i) Write an equation for the reaction
(ii) Hence, calculate the amount (in mole) of magnesium nitride that can be obtained from 3.0g of magnesium [Mg = 24].
(a)(i) What type of reaction is involved in each of the conversion processes indicated as I to V below?
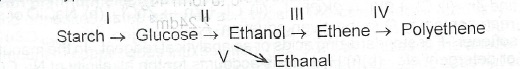
(ii) Name one isomer of glucose
(iii) Explain why palmwine becomes sour on prolonged exposure to air.
(b)(i) List the reagents and the reaction condition necessary for ethanoic acid to form an alkanoate.
(ii) Give two uses of alkanoates
(c)(i) What is the lUPAC name of the following compound?
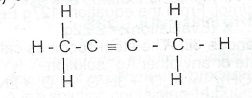
(ii) Outline one chemical test to distinguish between methane and the compound in (c)(i) above.
(iii) Write an equation for the combustion of ethene in excess oxygen.
(a)(i) List the quantum number that are assigned to an electron in an atom.
(ii) What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy the 3d orbital?
(b) An element represented as P has the following electronic configuration: 1s\(^2\)2s\(^2\)2p\(^6\)2s\(^2\)
(i) Write the electronic configuration of the ion of P.
(ii) Without identifying P, write the likely formula of its chloride.
(iii) State with reason, whether P will be a good oxidizing or reducing agent.
(c)(i) What is electron affinity?
(ii) Explain briefly why ammonia can precipitate in dative bonding.
(d)(i) If an element in Group IV loses an alpha particle, to which group would the product belong?
(ii) Two equally toxic substances X and Y which decay to non-toxic products, were absorbed through the skin. If their half-lives are 8 minutes and 2 months respectively, which of them constitutes the greater health hazard? Explain your answer
(a) If a steel spoon were to be plated with silver, state what would be suitable for use as the;
(i) anode. (ii) cathode; (iii) electrolyte
(b)(i) Write an equation for one of the reactions involved in the purification of bauxite.
(ii) Give the reason why the carbon anodes are changed at intervals during the electrolysis of pure alumina solution in molten cryolite.
Xg of a pure sample of iron (II) sulphide reacted completely with excess dilute hydrochloric acid to give 3.20g of iron (II) chloride according to the following equation: FeS\(_{(s)}\) + 2HCI\(_{(aq)}\) —> FeCl\(_{2(aq)}\) + H\(_2\)S\(_{(g)}\).
(a) Mention one method apart from heating by which the reaction can be made to proceed faster
(b) Calculate the value of X. [CI = 35.5, Fe = 56; FeS = 88g mol\(^{-1}\)]
(a) List two uses of sodium trioxocarbonate (IV).
(b) Sodium trioxocarbonate (IV) solution is alkaline.
(i) What phenomenon is responsible for this observation?
(ii) Name the product obtained on passing carbon (IV) oxide into saturated sodium trioxocarbonate (IV) solution.
(a) Write an equation for the reaction of chlorine with
(i) potassium iodide solution;
(ii) zinc on heating
(b) Identify the product Q in the following reaction: Cl\(_2\) + 2NaOH \(\to\) NaCl + H\(_2\)O + Q.
(a)(i) What is meant by the activation energy of a reaction?
(ii) State the effect of a catalyst on activation energy.
(b) What substance serves as a catalyst in each of the following?
(I) Hydrogenation of oils
(ii) Biochemical reactions.
(a)(i) What is the general formula for alkanoic acids?
(ii) State two chemical properties of ethanoic acid.
(b) Which of propene, butane and pentane
(i) will decolorize acidified KMnO\(_4\) solution?
(ii) can be easily polymerized?
(iii) is an isomer of methylpropane?
(iv) can be obtained from an alkanol by dehydration?
(a) What is the IUPAC name of Fe\(_2\)(SO\(_4\))\(_3\)?
(b)(i) Write an equation to represent the reaction of hydrogen sulphide with iron (III) chloride solution.
(ii) Mention one change observed during the reaction in (b)(i) above.
(a)(i) Arrange the following elements in the order of increasing reactivity. Iron, Lead, Magnessium, Aluminium.
(ii) Which of the following elements in (a)(i) above reacts with sodium hydroxide to give hydrogen?
(b) What property of tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid does each of the following reactions illustrate?
(I) S + 2H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) —> 3SO\(_4\) + 2H\(_2\)O
(ii) MgO + H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) —> MgSO\(_4\) + H\(_2\)O
(iii) C\(_{12}\)H\(_{22}\)C\(_{11}\) + H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) —> 12C + H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) + 11H\(_2\)O
(a) State two postulates of the kinetic theory of gases.
(b) Write two chemical properties that are common to both carbon (IV) oxide and sulphur (IV) oxide.
Copy and complete the following table
| Element | Number of Neutrons | Electronic Configuration | Group in the periodic Table |
| \(^{23}_{11}Na\) | — | 1s\(^{2}\)2s\(^{2}\)2p\(^{6}\)3s\(^{1}\) | 1 |
| \(^4_2He\) | 2 | —- | — |
| —- | 7 | 1s\(^{2}\)2s\(^{2}\)2p\(^{2}\) |
—- |
Which of the following compounds is used as a gaseous fuel?
- A. CH 3-COO-CH2-CH3
- B. CH 3-CH 2-CH 2-CH 3
- C. CHCI 3
- D. CH 3-CH2-COOH
- E. CH3-C=CH
A positive reaction to Fehling’s test indicates the presence of
- A. strach
- B. reducing sugars
- C. oxidizing agents
- D. alkanoic acids
- E. alkanols
The products of the reaction between CH3CH 2COOH and CH3OH are H 2
O and
- A. CH 3CH2COOCH3
- B. CH3CH 2COOCH 2CH 3
- C. CH3CH2CH2COOH
- D. CH3CH2CH2OH
- E. CH3COOH
When alkanols react with sodium, the ga evolved is
- A. hydrogen
- B. oxygen
- C. methane
- D. ethyne
- E. carbon (IV) oxide


