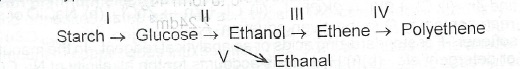
(a)(i) What type of reaction is involved in each of the conversion processes indicated as I to V below?
(ii) Name one isomer of glucose
(iii) Explain why palmwine becomes sour on prolonged exposure to air.
(b)(i) List the reagents and the reaction condition necessary for ethanoic acid to form an alkanoate.
(ii) Give two uses of alkanoates
(c)(i) What is the lUPAC name of the following compound?
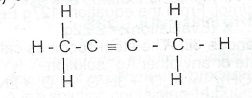
(ii) Outline one chemical test to distinguish between methane and the compound in (c)(i) above.
(iii) Write an equation for the combustion of ethene in excess oxygen.
Explanation
(a)(i) Reaction I is hydrolysis: Reaction II is fermentation or decomposition; Reaction Ill is dehydration; Reaction IV is polymerization; Reaction V is oxidation
(ii) Isomers of glucose are fructose, galactose
(iii) Palm wine turns sour on exposure to air because it contains ethanol which undergoes bacterial/ atmospheric oxidation on exposure to air to produce ethanoic acid which is responsible for the sour taste.
(b)(i) Conditions for converting CH\(_3\)COOH to an alkanoate:
- Presence of an alkanol
- Presence of conc. H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) or conc. HCI or dry HCI
- Heat/temperature (of about 40°C — 110°C) or refluxing (high temperature) up to 150°C
(ii) Use of Alkanoates: In the manufacture of perfumes, flavours, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, etc. as well as in the food, paint or soap industry.
(c)(i) The IUPAC name of the compound with the given structure.
(ii) To distinguish between but-2-yne and methane; pass each gas in turn into bromine water or tetraoxochlomethanee or acidified KNnO\(_{4(aq)}\). Decolorizatioln indicates But-2-yne. No visible reaction indicates methane.
(iii) Equation for the combination of ethene in excess of oxygen. C\(_2\)H\(_4\) + 3O\(_2\) ---> 2H\(_2\)O + 2CO\(_2\)

