All your burette readings (initial and final), as well as the size of your pipette, must be recorded but on no account of experimental procedure is required. All calculations must be done in your answer book.
A is solution of trioxonitrate (V) acid, B is a solution containing 6.90 g of potassium trioxocarbonate (IV) per dm\(^3\)
(a) Put A into the buret and titrate it against 20.0 cm\(^3\) or 25.0 cm\(^3\) portions of B using methy orange or screened methyl orange as indicater. Record the volume of your pipette. Tabulate your burette readings and calculate the average volume A used. The equation for the reaction is K\(_2\)CO\(_{3(aq)}\) + 2HNO\(_{3(aq)}\) \(\to\) 2KNO\(_{3(aq)}\) + CO\(_{2(g)}\) + H\(_2\)O\(_{(l)}\)
(b) From your results and the information provided calculate;
(i) concentration of solution B in mol dm\(^{-3}\)
(ii) number of potassium ions in 1.00 dm\(^3\) of B [C = 12.0, O = 16.0, K = 39.0, Avogadro constant = 6.02 x 10\(^{23}\) mol \(^{-1}\)]
Credit will be given for strict adherence to instructions, for observations precisely recorded and for accurate inferences. All tests observations and inferences must be clearly entered in your answer book. in ink, at the time they are made.
C is a mixture of two simple salts. Carry out the following exercises on C. Record your observations and identify any gases evolved. Sate the conclusion you draw from the result of each test.
(a) Put all of C into a beaker of boiling tube and add about 10cm\(^3\) of distilled water. Stir well and filter. Keep the residue and keep the residue and the filtrate. Test the filtrate with litmus
(b) Add about 1 cm\(^3\) of dilute hydrochloric acid to the residue in a test tube and warm gently Divide the reaction mixture into two portions.
(c)(i) To the first portion from (b) add saturated sodium trioxocarbonate (V) solution in excess.
(d) To about 2cm\(^3\) of the filtrate from (a) add a few drops of barium chloride solution followed by excess dilute hydrochloric acid.
(a) Name one laboratory equipment used for
(i) keeping salts dry:
(ii) converting vapour to liquid during distillation
(ii) bubbling a gas into a liquid
(b) (i) What technique would you use to purify a sample of sodium chloride contaminated with ammonium chloride?
(ii) Given sodium hydroxide solution, outline the procedure you would use to determine whether or not all the ammonium chloride in (b)(i) above had been removed.
(c) State what is observed on carrying out each of the following exercises.
(i) Adding few drops of methyl orange indicator to lime juice:
(ii) Adding few drops of concentrated HNO\(_3\) to acidified FeSO\(_4\) solution
(iii) Exposing a fresh precipitate of silver chloride to sunlight for 30 minutes
(iv) Adding zinc dust to dilute CuCl\(_2\) solution;
(v) Adding dilute H\(_2\)SO\(_4\), to Pb(NO\(_3\))\(_2\) solution
(a) State how you would carry out the following procedures in the laboratory:
(i) Remove the sediment in sample of water;
(ii) Soften temporarily hard water without heating it,
(iii) Obtain pure water from muddy water;
(iv) Remove oxygen and moisture from a sample of air
(b)(i) What type of salts are alums?
(ii) State the function of alum in water treatment plants.
(iii) State and explain how rain water that hac passed through limestone deposits will react with soap solution.
(c)(i) Write an equation for the laboratory preparation of chlorine
(ii) List the products of the reaction of chlorine with hot concentrated sodium hydroxide solution
(iii) What is observed when moist blue litmus paper comes in contact with chlorine?
(iv) Calculate the volume of chlorine at s.t.p. that would be required to react completely with 3.70g of dry slaked lime according to the following equation:
Ca(OH)\(_{2(s)}\) + Cl\(_{2(g)}\) –> CaOCl\(_{2}\). H\(_2\)O\(_{(s)}\) [H = 1, O = 16, Ca = 40, 1 mole of gas occupies 22.4 dm\(^3\) at s.t.p.]
(d)(i) State what is observed on warming ammonium trioxonitrate (V) with sodium hydroxide solution
(ii) Explain why ammonium trioxocarbonate (IV) leaves no residue on being heated.
(a)(i) Give the names of two allotropes of sulphur.
(ii) State and explain what is observed when hydrogen sulphide is bubbled through acidified potassium tetraoxomanganate (VII) solution
(iii) List one product of the reaction of sulphur (IV) oxide with hydrogen sulphide
(b)(i) What are the raw materials for the manufacture of tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid by the contact process?
(ii) Write an equation for the reaction that requires a catalyst in the contact process and state the catalyst used.
(iii) State the observation and the product formed when concentrated H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) reacts with each of the following:
I. Copper turnings Ii. A cube of sugar
(c)(i) Give three uses of sodium trioxocarbonate (IV).
(ii) What name is given to reactions of the following type?:
exposure to air
Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\) + 10H\(_2\)O\(_{(s)}\) \(\to\) Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\); H\(_2\)O\(_{(S)}\) + 9H\(_2\)O
(iii) Calculate the solubility of Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\) at 25°C, if 20 cm\(^3\) of its saturated solution at that temperature gave 1.75g of the anhydrous salt. [C = 12, O = 16, Na = 23].
(a) What is meant by each of the following terms?:
(i) Esterification
(ii) Saponification
(b)(i) Give the general molecular formula of alkynes
(ii) Write the molecular formula and empirical formula of ethylethanoate.
(iii) Draw the structure of 1, 1, 2, 2-tetrabromoethane
(iv) Write an equation for the reaction of ethanol with sodium
(c) Consider the following reaction schemes:
I II
Petroleum —> Petroleum Fractions. Higher Petroleum Fractions —> Petrol + X

(i) State type of process/reaction involved in each of the stages labelled I to IV.
(ii) Identify X and Y
(iii) Give the IUPAC name of the product obtained in stage III.
(iv) What are the reaction conditions for stage IV?
(d) Explain why palm wine: (i) froths or foams (ii) tastes sour after some days.
(a)(i) List two properties of iron that are characteristic of transition metals
(ii) Using equations only, show the processes involved in the extraction of iron and the removal of impurities in the blast furnace.
(iii) The following reaction occurs when a piece of iron is exposed to moist air for some days:
4Fe\(_{(s)}\) + 3O\(_{2(g)}\) + xH\(_2\)O\(_{(l)}\) —> 2Fe\(_2\)O\(_3\)\(_{(s)}\) State three methods by which this reaction can be prevented
(iv) What is the oxidation number of iiron in the product in (iii) above?
(b)(i) Arrange the following metals in the order of increasing reactivity. Hence, state which of them is/are extracted by electrolysis Au, Zn, Mg, Na, Sn, Ca
(ii) Why is zinc said to be amphoteric?
(c)(i) Define oxidation in term of electron transfer
(ii) Determine how many moles of electrons are transferred when 4825 coulombs of electricity are passed through an electrolytic cell. [1F = 96500C]
(iii) Calculate the number of copper (II) ions that will be discharged by 0.250F. [Avogadro constant = 6.02 x 10\(^{23}\)
a)(i) State Graham’s law of diffusion.
(ii) Calculate the vapour density of a triatomic gas X if its relative: atomic mass is 16.
(iii) Equal volumes of gases Y and Z are maintained at the same temperature and pressure. If the mass of a molecule of Y is twice that of Z state and explain which of the molecules has the, greater average velocity.
(b) The graph below is the ratio curve for the following reaction carried out in an open vessel.
MgCO\(_{3(s)}\) + 2HCI\(_{(aq)}\) \(\to\) MgCl\(_{2(aq)}\) + CO\(_{2(g)}\) + H\(_2\)\(_{(l)}\).
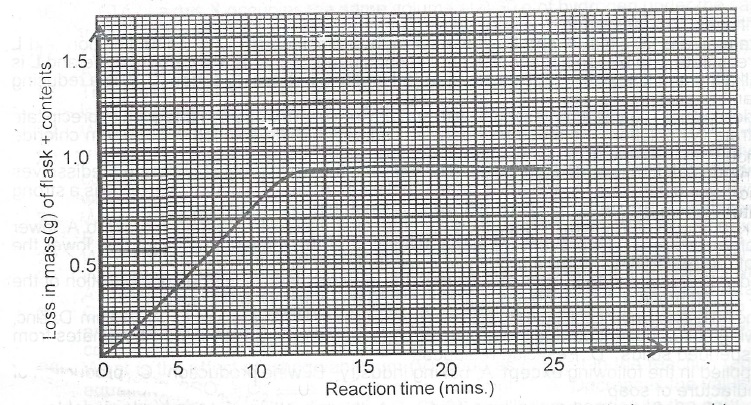
(i) For how long did reaction occur?
(ii) Why was there a loss in mass?
(iii) State whether reaction rate was fastest at the beginning, the middle or towards the end of the reaction. Give reason for our answer.
(iv) List three reaction conditions that can affect the slope of the curve
(c) Consider the following reaction at equilibrium: PCI\(_{5(g)}\) \(\rightleftharpoons\) PCI\(_{3(g)}\)); \(\Delta\)H = +95 kJmol\(^{-}\)
(i) Write an expression for the equilibrium constant K.
(ii) Predict the effect of the following on the equilibrium position.
I. Increased pressure
II. Increased temperature
III. Removal of chlorine Sketch an energy profile diagram for the forward reaction.
(a)(i) List three properties of elements which increase generally across a period in the Periodic Table,
(ii) Give two differences between a chemical reaction and a nuclear reaction.
(b) Use the information provided in the table below to answer Questions (i) – (vii).
|
Atom of Element |
P | Q | R | S | T |
|
Mass Number |
16 | 40 | 35 | 18 | 20 |
|
Atomic Number |
8 | 20 | 17 | 8 | 10 |
Which of the atoms in the table above:
(i) are isotopes of the same element?;
(ii) contains 18 neutrons?;
(iii) is chemically unreactive?;
(iv) readily forms an ion with two positive charges?
(v) attain an octet structure by accepting one electron?;
(vi) forms ionic bond with R?;
(vii) belongs to the s-block in the Periodic Table?
(c) Describe in outline how each of the following conversions can be carried out in the laboratory. Write appropriate equations for the reactions involved in each case
(i) CuCO\(_3\) to Cu
(ii) MgO to MgSO\(_4\).
P,Q,R and S are metals in the same group in the Periodic Table but in periods 3,4, 5 and 6 respectively which of them loses electrons least readily?
- A. P
- B. C
- C. R
- D. S
Given that the electronic configuration of an element X is 1s22s22p63s 23p4, it can be deduced that X
- A. belongs to group VI in the Periodic Table
- B. belongs to periodic Table
- C. contains 3 unpaired electrons in the ground state
- D. has atomic number 27
What is the mass number of an element if its atom contains 10 protons, 10 electrons and 12 neutrons?
- A. 32
- B. 22
- C. 20
- D. 10
Allotropes of an element differ in their
- A. physical properties
- B. chemical properties
- C. mass numbers
- D. electronic configuration
A plastic which cannot be softened by heat is described as
- A. thermosetting
- B. non-biodegradable
- C. thermoplastic
- D. malleable
Biotechnology is applied in the following except
- A. baking industry
- B. wine production
- C. production of antibiotics
- D. manufacture of soap
If 20 cm3 of distilled water is added to 80 cm3 of 0.50 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid, the concentration of the acid will change to
- A. 20 mol dm-3
- B. 0.40 mol dm-3
- C. 2.00 mol dm-3
- D. 5.00 mol dm -3
Which of the following on burning in air contributes to acid rain?
- A. Sulphur
- B. Magnesium
- C. Aluminium
- D. Zinc
When sodium hydroxide solution is added to a solution of zinc salt, the white precipitate formed re-dissolves in excess sodium hydroxide because
- A. sodium is more reactive than zinc
- B. sodium hydroxide is a strong alkali
- C. zinc hydroxide is amphoteric
- D. zinc hydroxide is unstable
A colourless, odourless liquid T, gives effervescence with sodium trioxocarbonate (IV) and a white precipitate with silver trioxonitrate (V) solution T is most probably
- A. sodium chloride solution
- B. barium chloride solution
- C. dilute trioxonitrate (V) acid
- D. dilute hydrochloric acid
Two-organic substances are labelled K and L if K gave a blue-black colour with iodine solution and L gave a deep red precipitate with Million’s reagent, it can be concluded that
- A. K is a carbohydrate and L is a protein
- B. K is alkaline and L is acidic
- C. K is unsaturated and L is a reducing sugar
- D. K is a reducing agent and L is an amino acid
Which of the following needs to be hydrolyzed before it shows reducing property?
- A. Glucose
- B. Maltose
- C. Sucrose
- D. Fructose


