(a) What is meant by each of the following terms?:
(i) Esterification
(ii) Saponification
(b)(i) Give the general molecular formula of alkynes
(ii) Write the molecular formula and empirical formula of ethylethanoate.
(iii) Draw the structure of 1, 1, 2, 2-tetrabromoethane
(iv) Write an equation for the reaction of ethanol with sodium
(c) Consider the following reaction schemes:
I II
Petroleum —> Petroleum Fractions. Higher Petroleum Fractions —> Petrol + X

(i) State type of process/reaction involved in each of the stages labelled I to IV.
(ii) Identify X and Y
(iii) Give the IUPAC name of the product obtained in stage III.
(iv) What are the reaction conditions for stage IV?
(d) Explain why palm wine: (i) froths or foams (ii) tastes sour after some days.
Explanation
(a)(i) Esterification is the reaction between alkanols and alkanoic acids to form alkanoates in the presence of mineral acids
(ii) Saponification is the reaction between caustic soda/sodium hydroxide/alkalis and fats or oils to produce salts or fatty acids/soap.
(b)(i) The general molecular formula of alkynes is C\(_n\)H\(_{2n-2}\)
(ii) The molecular formula of ethylethanoate is C\(_4\)H\(_8\)O\(_2\) and its empirical formula is C\(_2\)H\(_4\)O.
(iii) The structure of 1, 1, 2, 2 - tetrabromoethane is
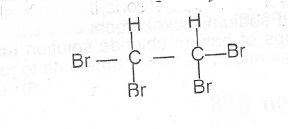
2C\(_2\)H\(_5\)OH + 2Na \(\to\) 2C\(_2\)H\(_5\)ONa + H\(_2\)
(c)(i) Stage (i) is fractional distillation;
Stage (ii) is cracking;
Stage (iii) is Chlorination or halogenation or Addition:
Stage (iv) is polymerisation
(ii) X is ethene / C\(_2\)H\(_4\). Y is chlorine molecule / CI\(_2\)
(iii) IUPAC name of the structure below is 1, 2, dichloroethane
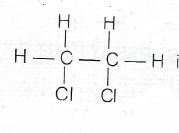
(iv) The reaction conditions for the polymerisation of ethene (stage iv) are high temperature (150°C to 300°C). High pressure (any pressure 500 to 1500 atmosphere) presence of a trace of oxygen or peroxides.
(d)(i) Palm wine Froths or foams because of the process of fermentation. The CO\(_2\) bubbles produced, cause the mixture to foam.
(ii) Palm wine tastes sour after some days because it has been oxidized to ethanoic acid by bacteria Atmospheric oxygen.

