State what you would see on;
(i) bubbling SO\(_2\) into acidified KMnO\(_4\) solution
(ii) mixing zinc dust with CuSO\(_4\) solution
(iii) adding concentrated HNO\(_3\) to freshly prepared FeSO\(_4\) solution.
(b) List two substances in case which, if added to dilute H\(_2\)SO\(_4\), would give you
(i) H\(_{2(g)}\)
(ii) ZnSO\(_{4(aq)}\)
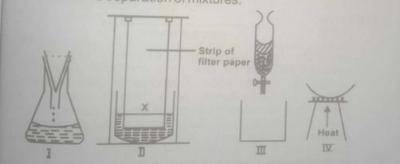
(c) The diagram labeled I to IV ABOVE illustrate different laboratory set-ups used in the separation of mixtures.
(i) Name the separation technique illustrated by each diagram
(ii) Which of the set-ups is used for concentrating dilute salt solutions, for the purpose of crystallization?
(iii) Which of the set-ups is used in obtaining clear water from muddy water?
(iv) Mention the set-up you would use to separate a polar solvent from a non-polar solvent
(v) State the modification you would make to the set-up labelled IV in order to use it for separating a mixture of NaCl and NH\(_4\)CI
Credit will be given for strict adherence to instructions, for observations precisely recorded, and for accurate interference. All tests, Observations and inferences must be clearly entered in your answer book, in ink at the time they are made. C and D are aqueous solutions of simple salt and an inorganic compound respectively. Carry out the following exercises on C and D. Record your observations and identify the gasses evolved. State the conclusion and draw from the result in the test and add sodium hydroxide in excess.
(b)(i) Test D with litmus paper
(ii) Put about 5cm\(^3\) of D in a test tube and add sodium hydroxide solution in drops and then in excess
(iii) Add about 1cm\(^3\) of the soap solution provided to about 10 cm\(^3\) of D mixture. Repeat the test using distilled water in place D
All your burette readings (initial and final), as well as the size of your pipette, must be recorded but no account of experimental procedure is required. All calculations must be done in your answer book. A is a solution of HCl containing 7.30g dm\(^{-3}\), B is a solution of X\(_2\)CO\(_{3}\) containing 10.6 gdm\(^{-3}\)
(i) Put A into your burette and titrate readings against 20.0 cm\(^3\) or 25.0cm\(^3\) portions of B using methyl orange as indicator. Tabulate your burette reading and calculate the average volume of A used. The equation for the reaction involved in the titration is ;
X\(_2\)CO\(_{3(aq)}\) + 2HCl\(_{(aq)}\) \(\to\) 2XCl\(_{(aq)}\) + H\(_2\)O\(_{(l)}\) + CO\(_{2(g)}\)
(ii) From your results and the information provided above, calculate the (i) concentration or A in mol dm\(^{3-}\)
(a) State the role of each of the following substances in the treatment of river water for town supply (i) Sand bed. (ii) Alum (iii) Chlorine
(b)(i) Give three major uses of H\(_2\)SO\(_4\)
(ii) Explain the following observation: A strip of blue litmus paper dropped into concentrated H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) becomes charred whereas in dilute H\(_2\)SO\(_4\), it turns red and is not charred.
(iii) Write an equation to show how concentrated H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) reacts with zinc.
(c)(i) List two gaseous pollutants that can be generated by burning coal.
(ii) Explain why coal burns more easily when it is broken into pieces than when it is in lump form.
(ii) What gas is responsible for most of the explosions in coal mines?
(iv) Name: the non-volatile residue left behind after the destructive distlillation of coal
(d)(i) What is meant by allotropy?
(ii) Name two crystalline allotropes of carbon
(iii) Name two elements apart from carbon, which exhibit allotropy
(iv) It is now known that carbon has an allotropic form called fullerene, containing molecules of formula C\(_{60}\). Calculate the mass of one mole of these molecules [C = 12]
(a) Mention one oxide in each case, which
(i) used in bleaching
(ii) is a redish-brown gas
(iii) reacts with NaOH and also with HCI;
(iv) dissolves in water to give a solution with pH greater than 7;
(v) oxidizes hot, concentrated HCI to chlorine
(b)(i) State three methods that can be used to removo hardness in a sample of water that contains calcium hydrogentrioxocarbonate (IV).
(ii) Explain with the aid of appropriate equation, why it is not advisable to build a house with limestone in an environment polluted by sulphur (IV) oxide.
(c)(i) List two compounds of potassium which yield oxygen when heated strongly
(ii) Calculate the amount (in moles) of gas which occupies 250 cm\(^3\) at s.t.p. [1 mole of gas occupies 22.4 dm\(^3\) at s.t.p]
(iii) If 250 cm\(^3\) of a gas at s.t.p. is heated to 27°C at constant pressure, calculate its new volume.
(iv) Explain in terms of the collision theory what happens as a gas is heated at constant pressure.
(a)Give two reasons why aluminium is preferred to copper for making overhead electric cables.
(ii) Describe briefly the electrolytic extraction of aluminium from purified bauxite.
(b) The diagram below represents an electrolytic cell used for the purification of copper.
(i) Which of the electrodes I and II increases in mass during the electrolysis? Give reasons for your answers
(ii) State with reason the site of oxidation
(iii) Identify III and explain why its colour does not change in intensity during the electrolysis.
(c) Calculate the current in amperes that will deposit 8.00 g of calcium from used CaCl\(_2\) in 1 hour 15 minutes. [Ca = 40.0; 1 Faraday = 96500C]
(a) i) An organic compound X contains 40% carbon, 6.67% hydrogen, the rest being oxygen. If X has a relative molecular mass of 60, determine its
(i) empirical formula (ii) molecular formula. [H = 1 ; C = 12; O = 16]
(b) An alkanoic acid Y has a relative molecular mass of 74.
(i) State the functional group of Y
(ii) What t of reaction is involved when Y is converted to an alkanoate?
(iii) Determine the structural formula of Y.
(iv) Write an equation for the reaction between Y and sodium
(v) If X in (a) above boils at 118°C and belongs to the same homologous series as Y, state with reason, whether the boiling point of Y will be equal to, higher or lower than 118°C.
(c)(i) What is fermentation?
(ii) Write an equation for the fermentation of glucose.
(iii) What must be added to glucose solution to make it ferment?
(iv) Explain why a tightly corked grass bottle filled to the brim with fresh palm wine shatters on standing.
(a) (i) State three characteristic properties of transition metals.
(ii) What is the oxidation state of manganese In each of the following species? (1) MnCl\(_2\) (II) MnO\(_2\) (III) MnO\(_4^{-}\)
(iii) Explain why manganese conducts electricity in the solid state but manganese chloride conducts only when molten or in solution.
(b)(i) The collision theory suggests that for two particles to react, they must collide. What two factors determine whether or not the collision would lead to formation of products?
(ii) Use an energy profile diagram to illustrate what is meant by the enthalpy change (\(\Delta\)H) and the activation energy (E\(_A\)) of a reaction.
(c) When few drops of aqueous KSCN are added to a solution of iron (III) salt the following equilibrium is set up:
Fe\(^{3}_{(aq)}\) + 3SCN\(^{-}_{(aq)}\) \(\rightleftharpoons\) Fe(SCN)\(_{3(aq)}\)
yellow colourless deep red
The equilibrium mixture has a pale red colour.
(i) Explain what would happen if more KSCN\(_{(aq)}\) were added to the equilibrium mixture.
(ii) Which of the ions in the equilibrium mixture forms an insoluble hydroxide with NaOH\(_{(aq)}\)? Write an equation for the reaction
(iii) State two changes observed on adding NaOH\(_{(aq)}\) to the equilibrium mixture.
(a) The electronic configuration of five elements represented by the letters P, Q, R, S and T are indicated below.
P – 1s\(_2\)2s\(_2\)2p\(_2\)
Q 1s\(_2\)2s\(_2\)2p\(_4\)
R 1s\(_2\)2s\(_2\)2p\(_6\)
S – 1s\(_2\)2s\(_2\)2p\(_6\)3s\(_2\)
T – 1s\(_2\)2s\(_2\)2p\(_6\)3s\(_2\)3p\(_5\)
without identifying the elements, state which of them
(i) belongs to group VI in the periodic table;
(ii) is strongly metallic in character;
(iii) readily ionizes by gaining one electron;
(iv) contains two unpaired electrons in the ground state atom
(v) readily loses two electrons during chemical bonding
(vi) Does not paricipates in chemical reactions?
(vii) is an s-block element.
(b)(i) Copy and complete the table below as appropriate
| Particle | Number of Protons | Number of Electrons | Number of Neutrons |
| \(^1_1H\) | 1 | 1 | |
| \(^{27}_{13}\)Al\(^{3+}\) | |||
| \(^{16}_{8}O^{2+}\) | 8 |
(ii) Give the reason why atomic radius increases down a group in the periodic table but decreases from left to right in a period.
(c)(i) What is meant by the half-life of a radioactive element?
(ii) The nuclide \(^{210}_{84}PO\) loses an alpha 4° particle to form lead. Write an equation for the reaction.
(d) State the type of chemical bonding which accounts for each of the following observations:
(i) Chlorine exists as discrete molecules
(ii) Sodium chloride dissolves readily in water;
(iii) CuSO\(_{4(aq)}\) forms a deep blue complex ion with excess NH\(_{3(aq)}\)
Which of the following processes will pollute water?
- A. Exposure of a body of water ultraviolet rays
- B. Discharge of industrial effluents effluents into water ways
- C. Passage of river water through a send bed
- D. Addition of a measured quantity of chlorine to water
What are the two gases associated with the formation of acid rain?
- A. CO2 and HCI
- B. CO2 and N2
- C. CO2 and NO2
- D. HCI ans SO2
When a sample of water was boiled, it lathered more readily with soap. it can be concluded that the sample most likely contained
- A. magnesium tetraoxosulphate (VI)
- B. suspended solids
- C. Organic impurities
- D. calcium hydrogentrioxocarbonate (IV)
What is the main impurity in haematite?
- A. CaSiO3
- B. CaCO3
- C. SiO3
- D. Fe2O3
Which of the following compound is used for removing impurities from bauxite?
- A. NaOH
- B. CaCO3
- C. Na3AIF6
- D. H2SO4
What volume of 0.20 mol dm -3 NaOH solution would yield 5.0 g of NaOH on evaporation to dryness? [NaOH = 40g mol-1]
- A. 400 cm3
- B. 625 cm3
- C. 1000 cm3
- D. 1600 cm 3
When excess ethene is shaken with acidified KMnO4 solution, the product obtained is
- A. ethane
- B. ethanal
- C. ethane - 1, 2 - diol
- D. ethanoic acid
What process does the following equation represent ? n(C\(_{6}\)H\(_{10}\)O\(_{5}\)) + nH\(_{2}\)O → nC\(_{6}\)H\(_{12}\)O\(_{6}\) ?
- A. Polymerization of glucose
- B. Hydrolysis of starch
- C. Fermentation of sugar
- D. Dehydration of carbohydates
The reaction of vegetable oil with a solution of wood ash is
- A. saponification
- B. neutralization
- C. hydrogenation
- D. esterification
What is the organic product of the reaction of C2H 5OH with excess acidified K 2Cr 2O7(aq)?
- A. CH3COOH
- B. C2H5OC2H5
- C. HCOOCH 3
- D. C2H5CHO
Which of the following substances could be responsible for the banana taste of a food flavour?
- A. Methylbenzene
- B. Butanol
- C. Ethanol
- D. Pentylethanoate
Wine containing 8% to 17% ethanol can be converted to gin containing about 40% ethanol by
- A. evaporation
- B. distilation
- C. fermentation
- D. oxidation


