All your burette readings (initial and final), as well as the size of your pipette, must be recorded but no account of experimental procedure is required. All calculations must be done in your answer book.
A is a solution of H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) containing 4.9 gdm-3, B is a solution containing X g dm\(^{-3}\) of Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\).
(a) Put A into the burette and titrate it against 20.0 cm\(^3\) or 25.0 cm\(^3\) portions of B using methyl orange as an indicator. Record the volume of your pipette. Tabulate your burette readings and calculate the average volume of A used. The equation for the reaction involved in the titration is; H\(_2\)SO\(_{4(aq)}\) + Na\(_2\)CO\(_{3(aq)}\) \(\to\) Na\(_{2}\)SO\(_{4(aq)}\) + H\(_2\)O\(_{(l)}\) + CO\(_{2(g)}\)
(b) From your results and information provided above, calculate the:
(i) Concentration of A In mol dm\(^{-3}\)
(ii) concentration of B in mol dm\(^{-3}\)
(iii) mass of salt formed when 500 cm\(^3\) of B is Completely neutralized by A.
(v) volume of carbon (IV) oxide liberated in (b) (ii) above at s.t.p. [O = 16, Na = 23, S = 32, 1 mole or a gas occupies 22.4 dm\(^3\) at s.t.p.]
Credit will be given for strict adherence to instructions, for observations precisely recorded, and for accurate inferences. All tests, observations, and inferences must be clearly entered in your answer book, in ink, at the time they are made.
C Is an inorganic salt. D is an organic compound. Carry out the following exercises on C and D. Record your observations and identify any gases evolved. State the conclusion you draw from the result of each test.
(a) (i) Put C in a test tube and add about 10 cm\(^3\) of distilled water. Stir well.
(ii) Divide the resulting solution into two portions. To the first portion add sodium hydroxide solution in drops and then in excess.
(iii) To the second portion add dilute trioxonitrate (V) acid. Then add silver trioxonitrate (V) solution followed by aqueous ammonia in excess. tube and odd about 2- 5 cm\(^3\) of ‘Xn’.
(ii) Identify the functional group present in D.
(a) State what would be observed when:
(i) Chlorine is passed through a freshly prepared solution of FeCl\(_2\).
(ii) SO\(_2\) is bubbled into a solution of FeCl\(_3\);
(iii) A few drops of water Is added to sodium hydroxide pellets in a test tube;
(iv) Dilute H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) is added to CaCO\(_{3(s)}\)
(b) Three test tubes contain solutions of SO\(_3^{2-}\), CO\(^{2-}_3\) and SO\(_4^{2-}\) respectively. Describe one chemical method that you would use to identify the solution containing SO\(_4^{2-}\)
(c)(i) Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the separation of a mixture of petrol and water
(ii) Which of the following will dissolve faster? 10g of NaOH pellets in 100 cm\(^3\) of water; 10g of NaOH powder in 50 cm\(^3\) of water. Give the reason for your answer.
(i) Name two amorphous forms of carbon
(ii) State the reason why graphite is a lubricant but diamond is not.
(iii) Draw and label a diagram for the laboratory preparation of a dry sample of carbon (IV) oxide.
(b)(i) Give one example of the following: I. Soil pollutant; II. Water pollutant; III. Air pollutant.
(ii) State the major use of sulphur (IV) oxide in a chemical industry.
(c)(i) Explain in terms of the kinetic theory why petrol is volatile
(ii) State two criteria for determining the purity of a substance.
(iii) Mention one use of each of the following gases: I. Krypton; II. Argon
(d)(i) When zinc metal was added to aqueous copper (I) tetraoxosulphate (VI), the solution turned colourless. I. Name the compound in the colourless solution. II. Write the ionic equation for the reaction. Ill. State what would be observed when a few drops of sodium hydroxide solution is added to a portion of the colourless solution.
(ii) Calculate the volume of CO\(_2\) produced when 5.3g of Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\) reacted with excess HNO\(_{3(aq)}\) + Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\) + 2HNO\(_{3(aq)}\) \(\to\) 2NaNO\(_{3(aq)}\) + CO\(_{2(g)}\) + H\(_2\)O\(_{(l)}\) [H = 1, C = 12, N = 14, O = 16, Na = 23, 1 mole of a gas occupies 22.4 dm\(^3\) at s.t.p.]
(a)(i) State the two types of hardness in water.
(ii) Name a salt that causes each type of hardness.
(ii) Write a balanced equation for the removal of each type of hardness.
(iv) State one effect of hard water on soap.
(b)(i) State whether the pH of each of the following is less than, equal to, or greater than 7.
I. Glucose solution II. Chlroine water III. Lime water IV. Sour milk
(ii) Give the difference between the following compounds: I. an acidic oxide and an amphoteric oxide; II. concentrated acid and a dilute acid; Ill. a normal salt and an acid salt
(c)(i) Iron reacts with H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) according to the equation: Fe\(_{(s)}\) + H\(_2\)SO\(_{4(aq)}\) —> FeSO\(_{4(aq)}\) + H\(_{2(g)}\)
Calculate the mass of FeSO\(_4\) that would be produced by 0.5 mole of Fe. [H = 1, S = 32, Fe = 56]
(ii) List two allotropes of sulphur
(d)(i) State what would La observed when a damp starch-iodide paper is dropped into a gas jar of chloride
(ii) Explain your ansv.er in (d)(i) above.
(iii) State the products formed when ammonia reacts with excess chlorine.
(a)(i) List three observable changes that take place when a dilute solution of copper (II) chloride is electrolysed using platinum electrodes. Stage III
(ii) Calculate the quantity of electricity used during electrolysis when a current of 0.21 ampere flows for 2 hours.
(iii) State what is meant by the term preferential discharge of ions in electrolysis
(iv) Give one factor which influences the preferentia! discharge of ions during electrolysis.
(v) State one Q difference between-a conductor and an electrolyte.
(b) Consider the reaction represented by the equation below: Na\(_2\)S\(_2\)O\(_{3(aq)}\) + 2HCI\(_{(aq)}\) \(\to\) 2NaCI\(_{(aq)}\) + H\(_2\)O\(_{(l)}\) + SO\(_{2(g)}\) + S\(_{(s)}\)
(i) List two factors that can affect the rate of this reaction.
(i) Which of the products can be readily used to measure the rate of the reaction. Give a reason for your answer.
(iii) Name two instruments that can be used to measure factors in (b)(i) above.
(c)(i) State the reasons for regarding rusting and burning as oxidation processes.
(ii) I. Write the balanced half equations for the following redox reaction: Mg\(_{(s)}\) + Fe\(^{2+}_{(aq)}\) —-> Mg\(^{2+}_{(aq)}\) + Fe\(_{(s)}\)
II. Which of the reactants is the oxidizing agent?
Ill. State the change in the oxidation number of the oxidizing agent.
(d)(i) State one ore from which each of the following metals can be extracted. I. Tin II. Iron (ii) List two uses of copper (iii) Name one alloy of tin.
(i) Write the structure of 2—chloro-2—methylpropane.
(ii) Consider the compound X represented by the structure below:
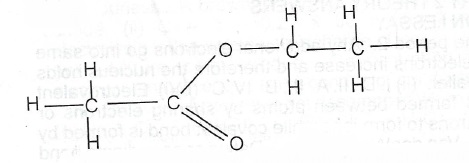
I. State the functional group in X; II. Give the IUPAC name of X; Ill. State the homologous series to which X belongs. IV. Give the names of two compounds from which X is formed. V. State one physical characteristt of X.
(b)(i) List two products obtained from fractional distillation of petroleum;
(ii) State one use of each product in (b)(i) above,
(iii) Mention one disadvantage of crude oil production
(c)(i) Mention the monomer of protein (ii) A compound has an empirical formula of CHO\(_2\) and its molar mass is 90. Deduce the molecular formula of the compound. [H = 1, C = 12, O = 16].
(d) Use the reaction scheme below to answer questions (i).— (iv).

(i) State the reagents needed for stages II and V;
(ii) Nanie the product Q of reaction in stage IV;
(iii) State the conditions required for stage III;
(iv) Give the names of the processes in stages I, II, Ill and V respectively.
(a)(i) State Graham’s law of diffusion
(ii) If 100 cm\(^3\) of oxygen diffused in 4 seconds and 50cm\(^3\) of gas Y diffused in 3 seconds, calculate the relative molecular mass of gas Y. (0 = 16)
(b) Consider the following equilibrium reaction: X + 2Y\(_{(g)}\) \(\rightleftharpoons\) XY\(_{2(9)}\) \(\Delta\)H = -52KJ mol\(^{-1}\)
(i) State what happens to the yield of XY\(_2\) when the temperature is increased
(ii) Explain the effect of decrease in pressure on the equilibrium position.
(iii) State the effect of a catalyst on the I. position of equilibrium II. activation energy
(c)(i) State the differences between the solubilities of solids and gases in liquids.
(ii) Name the physical-properties used it choosing separation techniques for the following mixtures:
I. kerosene and petrol II. calcium trioxocarbonate (IV) and potassium chloride. III. ammonium chloride and sodium chloride.
(d)(i) State a method of preparing each of the following salts:
| Acid | Basicity |
| H\(_3\)PO\(_4\) | |
| CH\(_3\)COOH | |
| HNO\(_2\) |
(iii) State the difference between anhydrous and hydrated salts.
(a) The electronic configurations of atoms of elements A, B, C and D are given as follows: A. Is\(^2\)2s\(^2\)2p\(^2\); B. 1s\(^2\)2s\(^2\)2sp\(^1\) ; C. 1s\(^2\)2s\(^2\) 2p\(^1\) ; D. 1s\(^2\) 2s\(^2\)
(I) Arrange the elements in order of increasing atomic size, giving reasons
(ii) State which of the elements I. is divalent II. contains atoms with two unpaired electrons in the grouped state. Ill, readily loses one electron from its atom during chemical bonding IV. belongs to group Ill in the Periodic Table.
(b)(i) State one difference between electrovalent and covalent bonds.
(ii) Name two other bonds apart from the ones in (b)(i) above which bind atoms and molecules together.
(iii) State two characteristics of a covalent compound.
(c)(i) What is isotopy?
(ii) Illustrate with suitable example
(iii) Two isotopes of Z with mass numbers 18 and 20 are in the ratio 1:2 Determine the relative atomic mass of Z.
(d)(i) Which of the following elements: calcium, fluorine, iodine neon, magnesium and helium are I. halogens II. noble gases Ill. alkaline earth metals.
(ii) Write a balanced equation for the bombardment of \(^7_3Li\) with protons to produce \(^8_4\beta\) and \(\gamma\)-rays
(iii) State one use of radioactive isotopes.
In which of the following processes is biotechnology not applied?
- A. Manufacture of drugs
- B. Treatment of domestic sewage
- C. Production of alcoholic beverages
- D. Electroplating of metals
Which of the following substance is an alloy of lead?
- A. Brass
- B. Duralumin
- C. Stainless steel
- D. Soft solder
Which of the following pairs of solutions will produce a precipitate when mixed?
- A. Pb(NO3)2(aq) and NaCI(aq)
- B. MgSO4(aq) and HCI(aq)
- C. ZnCI2(aq) and NaSO4(aq)
- D. NaOH(aq) and HNO3(aq)
Hardness in water can be removed by adding
- A. copper (ll) tetraoxosulphate (IV)
- B. sodium trioxocarbonate (IV)
- C. sodium chloride
- D. alum
Ethyne undergoes the following reactions except
- A. polymerisation
- B. addition
- C. substitution
- D. esterification
Fats are classified as
- A. hydrocarbons
- B. alkanoates
- C. alkanols
- D. carbohydrates
The colour of the solution formed when ethyne reacts with an acidic solution of potassium tetraoxomanganate (VII) is
- A. purple
- B. colourless
- C. green
- D. pink
Which of the following substances is a non-reducing sugar?
- A. Sucrose
- B. Glucose
- C. Fructose
- D. Maltose
What is the major product formed when C2H5OH reacts with CH3COOH?
- A. C2H5COOCH3
- B. C2HCOCH3
- C. CH3COOC2H5
- D. C3H7COOH
Reaction undergone by compounds with the general formula Cn H2n+2 include
- A. addition
- B. esterification
- C. substitution
- D. dehydration
Determine the mass of copper deposited by 4.0 moles of electrons in the reaction represented by the equation below: Cu2(aq) + 2e– → Cu(s)
- A. 32
- B. 64
- C. 128
- D. 256
The main difference between a primary cell and a secondary cell is that the primary cell
- A. is an electrolytic cell but the secondary is not
- B. cannot be recharged but the secondary cell can
- C. can be recharged but the secondary cell cannot
- D. contains electrodes but the secondary cell does not


