Burette reading (initial and final) must be given to two decimal places. Volume of pipette used must be recorded but no account of experimental procedure is required. All calculations must be done in you answer book.
A is a solution containing 6.3 g dm\(^{-3}\) of HNO\(_3\), B is a solution Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\)
(a) Put A Into the burette and titrate it against 20.0 cm\(^3\) portions of B using methyl orange indicator. Record the volume of your pipette. Repeat the titration to obtain consistent titres. Tabulate your burette readings and calculate the average volume of A used. The equation for the reaction involved in the titration is:
2HNO\(_{3(aq)}\) + Na\(_2\)CO\(_{3(aq)}\) \(\to\) 2NaNO\(_{3(aq)}\) + CO\(_{2(g)}\) + H\(_{2}\)O\(_{(l)}\)
(b) From your results and information provided above, calculate the;
(i) concentration of B in mol dm\(^{-3}\)
(ii) concentration of B in g dm\(^{-3}\):
(iii) mass of sodium ions in 1:0 dm\(^{-3}\) of B
[H = 1; C = 1; O = 16; N = 14; Na = 23]
Credit will be given for strict adherence to the instructions, for observations precisely recorded and accurate inferences. All tests, observations and inferences must be clearly entered in your als book, in ink, at the time they are made.
C is a mixture of an inorganic and organic compounds. Carry out the following exercises on C: Record your.observations and identity any gases evolved. State the conclusion you draw from the result of each test.
(a) Put all of C into a beaker and add 10 cm\(^3\) of distilled water: Stir the mixture thoroughly and filter. Keep both the filtrate and residue.
(b)(i) Test the filtrate with litmus paper.
(ii) To about 2 cm\(^3\) of the filtrate, add BaCI\(_{2(aq)}\) followed by dilute HCI:
(iii) To another 2 cm\(^3\) portion of the filtrate add NaOH and heat.
(c) Transfer the residue into a boiling tube and add few drops of iodine solution
(a) Consider the following compounds: MnO\(_2\), NaHCO\(_3\), Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\), NH\(_4\)CI cnd Pb(NO\(_3\))\(_2\) Select the compound(s) which;
(i) has a black colour
(ii) is a basic oxide:
(ii) sublime on heating
(iv) dissolves in water to give a solution of pH less than 7.
(b) State the colour of each af the following aqueous Solutions:
(i) Calcium hydroxide;
(ii) iron (III) trioxonitrate (V):
(ii) Copper (II) tetraoxosulphate (VI);
(iv) Poassium heptaoxodichromate (VI).
(c) Give one example of a neutral oxide which is a colourless liquid at room temperature.
(d) Draw and label a diagram for a set-up that can be used for the separation of two immiscible liquids
(a)(i) Draw the energy profile diagram for the reaction
H\(_{2(g)}\) + I\(_{2(g)}\) —> 2HI\(_{(g)}\) \(\Delta\) = —13 kJmol\(^3\)
(ii) If the concentration of HI increases from 0 to 0.001 mol dm\(^3}\) in 50 seconds, what is the rate of the reaction?
(b) State the type of salt represented by each of the following compounds:
(i) K\(_4\)Fe(CN)\(_6\) (ii) (NH\(_4\))\(_2\)Fe(SO\(_4\))\(_2\)6H\(_2\)O (iii) Mg(OH)NO\(_3\) (iv) NaH\(_2\)PO\(_4\).
(c) Explain, giving equations, the following observation: When carbon (IV) oxide is passed into lime water, it turns milky initially but turns clear with excess carbon (IV) oxide.
(d)(i) Give one use for each of the following compounds: CaCO\(_3\), CaSO\(_4\), NaHCO\(_3\).
(ii) State a drying agent for each of the following gases: i. NH\(_3\), II. HCI Ill. SO\(_4\).
(iii) Write an equation to illustrate the reaction of ammonia as a reducing agent.
(e) An industrial raw material has the following composition by mass:
Iron = 28.1%
Chlorine = 35.7%
Water of crystallization = 36.2%
Calculate the formula for the material. [ H = 1, 0 = 16, Cl = 35.5, Fe = 56 ].
(a)(i) Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the preparation and collection of dry chlorine gas in the laboratory.
(ii) List two uses of chlorine.
(b)(i) Explain why river water flowing through an industrial town may be unsafe for drinking.
(ii) State the use of each of the following substances in water treatment: I. Sand, II. Chlorine, III. Calcium oxide, IV. Alum
(c)Consider the reaction represented by the following equation:
2Na\(_2\)CI\(_{(s)}\) + H\(_2\)SO\(_{4(aq)}\) \(\to\) Na\(_2\)SO\(_{4(aq)}\) + 2HCI\(_{(g)}\)
Calculate the volume of HCI gas that can be obtained at s.t.p. from 5.85 g of sodium chloride. [H = 1, Na = 23, CI = 35.5, Molar volume a 22.4 dm\(^3\) at s.t.p]
(d) Give one example in each case of a (i) metal that is a liquid at room temperature. (ii) non-metal that is a iiquid at room temperature, (iii) gas at room temperature that is monatomic.
(e) State two differences between metals and nom metals with respect to their: (i) physical properties; (ii) chemical properties.
(a) A solution of CuSO\(_4\) was electrolyzed between pure copper electrodes and the following results were obtained:
Mass of copper anode before experiment = 7.20 g
Mass of copper anode after experiment = 4.00 g
Mass of copper cathode before experiment = 5.75 g
From the information provided,
(i) calculate the mass of the cathode, after the experiment.
(ii) write an equation for the reaction at the I. anode, II. cathode.
(iii) state whether the colour of the solution would change during the electrolysis. Give a reason for your answer.
(iv) if the electrolysis was carried out for 1 hour 20 minutes with a current of 2.0 amperes, determine the value of the Faraday.
(b) Consider the reaction represented by the following equation:
MnO\(^-_4\) + I\(^-\) + H\(^+\) \(\to\) I\(_2\) + H\(_2\)O + Mn\(^{2+}\)
Write balanced half equation for the (i) oxidation reaction, (ii) reduction reaction.
(c)(i) Describe briefly how tin can be extracted from its ore.
(ii) State one use of tin.
(iii) Mention one property that makes tin suitable for the use stated in (c)(ii)
(d)(i) What is meant by the term pollution?
(ii) Explain why it is dangerous to run a generator in a closed room.
(a) State the following laws of chemical combination: (i) Law of constant composition (ii) Law of multiple’ proportion.
(b) Copper reacts with oxygen to form two oxides X and Y. On analysis, 1.535 g of X yielded 1.365 g copper and 1.450 g of Y yielded 1.160 g of cooper.
i) Determine the chemical formula of X and Y.
(ii) Calculate the mass of copper which can react with 0.500 g of oxygen to yield I. X II. Y.
(iii) Which of the laws of chemical combination is illustrated by the result in (b)(i) above. [ = 16, Cu = 63.51]
(c) Write the structure of the product responsible for the observation in each of the following reactions:
(i) A mixture of butanoic acid and ethanol warmed in the presence of concentrated H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) gives off a fragrant odour.
(ii) Sodium dissolves in propan-2-ol with effervescence to give a solution which on evaporation to dryness leaves a white precipitate.
(d) Consider the compound CH\(_3\)CH\(_2\)COOCH\(_2\)CH\(_3\).
(i) Name the compound (ii) Write the structural formula of the compound (iii) State the reagents and conditions for the formation of the compound.
(a)(i) State two differences betwecii the properties of solids and gases
(ii) What process does each of X, Y and Z represent in the changes shown below?
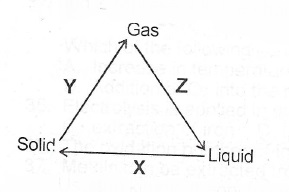
(b)(i) State Charles’ Law (ii) Draw a sketch to graphically illustrate Charles’ Law.
(c) 60 cm of hydrogen diffused through a porous membrane in 10 minutes. The same volume of a gas G diffused through the same membrane in 37.4 minutes. Determine the relative molecular mass of G. [ H = I ]
(d)(i) State two assumptions X of the kinetic theory.
(ii) Consider the reaction represented by the Solid of Liquid following equation:
H\(_{2(g)}\) + Cl\(_{2(g)}\) \(\to\) 2HCI\(_{(g)}\)
Use the kinetic theory to explain how the rate of formation of HCI\(_{(g)}\) would be affected by I. increase in temperature; II. decrease in pressure.
(e) Given different examples, mention one metal in each case vihich produces hydrogen on reacting with (i) dilute mineral acid; (ii) cold water; (iii) steam; (iv) hot, concentrated alkali.
a) Define each of the following terms and indicate one use of each:
(i) Nuclear fission; (ii) Nuclear fusion.
(b) Alpha particle emission by \(^{293}_{25}U\) proceduces an element A. Beta particle emission by the particle A produces another element B. Element B also undergoes alpha particle emission to produce \(^{227}_{89}AC\). Write balanced equations to represent the above statement.
(c) The models below represent the filling of orbitals in an atom.
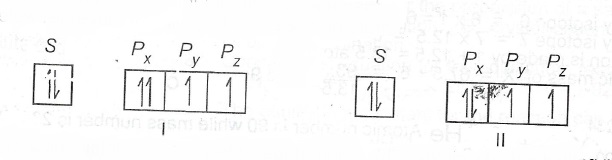
State which rule(s) is/are violated or obeyed by each model.
(d) Explain why the boiling point of H\(_2\)S with relative molecular mass of 34 is lower than that of H\(_2\)O with relative molecular mass of 18.
(e) HCI is passed into each of the following solvents:
(i) water;
(ii) methylbenzene. I. State the effect of each solution on blue litmus paper II. Compare the electrical conductivities of the two solutions.
(f) Zinc dust is added to copper (II) tetraoxosulphate (VI) solution. State;
(i) what is observed; (ii) the type of reaction that occurs.
Which of the following equations represents a substitution reaction?
- A. C 2H10(g) + CI 2(g) → C4H9 CI(g) + HCI(g)
- B. C 2H4(g) + HCI (g) → C 2H5 CI(l)
- C. C2H2(g) + 2H 2(g) → C 2H6(g)
- D. C 3H4(g) + 402(g) → 3CO2(g) + 2H 2O(g)
The ammonium compound used in the manufacture of dry cells is
- A. NH4NO3
- B. (NH4)SO4
- C. NHCI4
- D. (NH4)2CO3
Which of the following substance is an ore of iron?
- A. Bauxite
- B. Cassiterite
- C. Haematite
- D. Steel
Waste plastics accumulate in the soil and pollute the environment because plastic materials are
- A. insoluble in water
- B. non -biodegradable
- C. easily affected by heat
- D. inflammab,le
Greenhouse effect can be reduced by controlling
- A. water evaporation
- B. burning wood and fossil fuel
- C. the use of aerosols
- D. the use of artificial fertilizers
What is CaHb in the following equation? C a
H b + 5O2 → 3CO 2 + 4H2O
- A. C 3H4
- B. C3H6
- C. C3H8
- D. C 5H 10
Which of the following compounds is an alkanoate?
- A. CH3COOH
- B. CH3COOCH3
- C. CH3CH2OH
- D. CH3CH2COOH
What type of reaction occurs between vegetable oil and plant ash extract?
- A. Displacement
- B. Dehydration
- C. Neutralization
- D. Saponiflication
Which of the following industrial processes is chlorines not used?
- A. Production of polyvinylchloride (PVC)
- B. Manufacturing of hydrochloric acid
- C. Manufacturing of common salt
- D. Manufacturing of domestic bleach
In the reaction represented by the equation. 5Fe 2+ (aq) + MnO– 4(aq) + 8H+ (aq) → 5Fe3+(aq) + Mn2+(aq) + 4H2O(l) which species is reduced?
- A. Fe2+
- B. MnO-4
- C. H+
- D. Fe3+
Consider the reaction: 2AI(s) + 6H+ (aq) → 2AI3+ (aq) + 3H2(g). What is the total number of moles of electrons transferred from the aluminium atoms to the hydrogen ions?
- A. 3
- B. 4
- C. 5
- D. 6
Metals can be extracted from their ores by a process involving
- A. reduction
- B. oxidation
- C. hydrolysis
- D. decomposition


