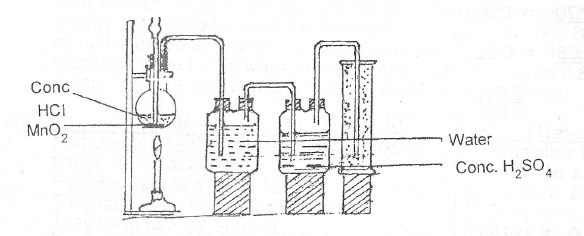
(a)(i) Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the preparation and collection of dry chlorine gas in the laboratory.
(ii) List two uses of chlorine.
(b)(i) Explain why river water flowing through an industrial town may be unsafe for drinking.
(ii) State the use of each of the following substances in water treatment: I. Sand, II. Chlorine, III. Calcium oxide, IV. Alum
(c)Consider the reaction represented by the following equation:
2Na\(_2\)CI\(_{(s)}\) + H\(_2\)SO\(_{4(aq)}\) \(\to\) Na\(_2\)SO\(_{4(aq)}\) + 2HCI\(_{(g)}\)
Calculate the volume of HCI gas that can be obtained at s.t.p. from 5.85 g of sodium chloride. [H = 1, Na = 23, CI = 35.5, Molar volume a 22.4 dm\(^3\) at s.t.p]
(d) Give one example in each case of a (i) metal that is a liquid at room temperature. (ii) non-metal that is a iiquid at room temperature, (iii) gas at room temperature that is monatomic.
(e) State two differences between metals and nom metals with respect to their: (i) physical properties; (ii) chemical properties.
Explanation
(a)(i) Draw the diagram in the marking scheme.
(ii) (1) It is used as germicide or disinfectant or sterilizing agent
(2) It is used as bleaching agent.
(3) It is used commercially to produce HCL
(4) It is used to produce polymers like PVC
(5) It is used as chlorinated chemicals during water treatment.
(b)(i) The water may be polluted or contaminated with industrial wastes.
(ii) Sand – for filtration or removal of suspended particles Chlorine – to destroy bacteria or kill germs.
Calciumoxide – to reduce acidity or adjust pH Alum – coagulate colloidal particles.
(c) 2NaCl\(_{(s)}\) + H\(_2\)SO\(_{4(aq)}\) \(\to\) Na\(_2\)SO\(_{4(aq)}\) + 2HCl\(_{(aq)}\)
Molar mass of NaCl = 23 + 35.5 = 58.5.
No. of moles of NaCl used = \(\frac{5.85}{58.58}\) = 0.1 mole
Moles of HCl produced = Moles of NaCI used
Volume of HCI at s.t.p. = 0.1 x 22.4 dm\(^3\) = 2.24 dm\(^3\)
(d)(i) Mercury (ii) Bromine (iii) Helium, Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon and radon.
(e)
|
Property |
Metals | Non-metals |
|
(1) Physical
|
1. Good conductors of heat. 2. Good conductors of electricity. 3. Possess metallic lustre. 4. It is ductile. 5. It is malleable |
1. Poor conductors of heat. 2. Poor conductors of electricity. 3. Dull in appearance. 4. Non-ductile or brittle. 5. Non-malleable. |
| (ii) Chemical |
1. Forms basic oxides. 2. Reacts with acids or water to produce hydrogen. 3. Generally tend to form ionic compounds. |
1. Forms basic oxides. 2. Reacts with acids or water to. produce hydrogen. 3. Generally tend to form ionic compounds. |

