a) Define the following in term:. of electron transfer: (i) oxidation; (ii) reduction.
(b)(i) Determina the oxidation stale of phosphorus in each of the following structures: I. POCI\(_3\) II. PH\(_3\).
(ii) State with reasons whether the following compounds will form acidic, neutral or basic aqueous solutions: I. NaNO\(_3\) II. Na\(_2\)H\(_4\)CI; Ill. Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\).
(c) Consider the set-up
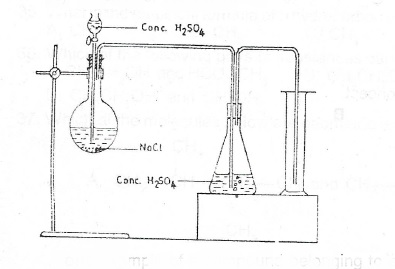
(i) What is the gas produced in the experiment illustrated by the set-up above?
(ii) Name the method of collection of gas
(iii) Give a reason for your answer in (c)(ii) above
(iv) State the function of the concentrated H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) in the conical flask
(v) Give of collection of the gas one I. physical property; II. chemical property of the gas
(vi) State one chemical test to identify the gas.
(d) A 4.3 g hydrated sodium tetraoxosulphate (VI) (Na\(_2\)SO\(_4\).xH\(_2\)O) was heated to remove the water of crystallization. The remaining anhydrous salt had a mass of 2.12 g. Calculate the value of x in the t I hydrated salt. [H = 1; O = 16; Na = 23; S = 32 ]
Explanation
(a)(i) Oxidation is the process of electron loss. Reduction is the process of electron gain
(b)(i) POCI\(_3\)
O.N of P + O.N of oxygen + (O.N of CI) x 3 = 0
P + —2 + —1 x 3 = 0
—P — 2 — 3 = 0
P = — 5
(ii) I. NaNO\(_3\) is neutral because it is a salt of a strong acid and a strong base, its ions do not undergo hydrolysis.
II. NH\(_4\)CI is acidic because it is a salt of a strong acid and a weak base. The NH\(^+_4\) undergoes hydrolysis.
III. Na\(_{4}\)CO\(_3\) is basic because it is a salt of weak acid and ntrong base. The CO\(^{2-}_3\) undergoes hydrolysis.
(c)(i) Hydrogen chloride gas
(ii) downward delivery or upward displacement of air.
(iii) The gas is denser than air
(iv) drying the gas.
(v) Physical properties
— denser than air — very soluble in water — colourless gas — fumes in moist air
Chemical Properties
— gives cloud or white fumes in contact with ammonia vapour
(vi) Pass the gas into AgNO\(_{3(aq)}\) a white precipitate of AgCl is formed wihich is soluble in aqueous ammonia but insoluble in HNO\(_3\)
(d) Mass of water = 4.30 — 2.12 = 2.18g
Mass of Na\(_2\)SO\(_4\) = 23 x 2 + 32 + 16 x 4 = 142
Molar mass of H\(_2\)O = 2 + 16 = 18
2.12g of anhydrous salt contain 2.18g of water
142g of anhydrous salt contain \(\frac{2.18 \times 142}{ 2.12}\)
= 146.018
X(H\(_2\)O) = 146
18x = 146
x = \(\frac{146}{18}\)
= 8

