(a) Consider the following reaction sequence.
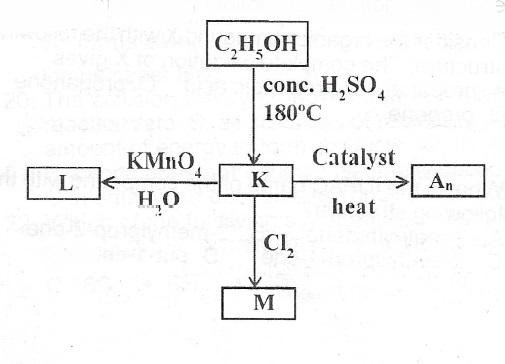
(i) What process leads/tathe formation of K?
(ii) Write the formula of K.
(iii) Write the structural formula of L and name L.
(iv) Name A\(_n\)
(v) Write the structure of M and name M.
(b)(i) What are carbohydrates?
(ii) Give one example each of a I. monosaccharide; II. disaccharide; III. polysaccharide.
(c) Consider the following structure of a simple sugar :
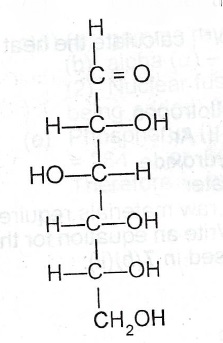
(i) Which functional group makes the compound a reducing agent?
(ii) State what would C = O be observed when I. the compound is mixed with Fehling’s solution and boiled;
I. few drops of concentrated H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) is added to the sample of the compound. H—C—OH
(iii) Write an equation for the reaction in (c)(ii)(II).
(d) A hydrocarbon Z with molecular mass 78 on combustion gave 3.385 g of CO\(_2\) and and 0.692 g of H\(_2\)O. Determine the molecular formula of Z. [ H = 1, C = 12, O = 16]
Explanation
(a)(i) Dehydration
(ii) C\(_2H_4\)
(iii)

(iv) Polythene/Polythene
(b)(i) Carbohydrates are (naturally occurring) organic compounds containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen with the hydrogen and oxygen present in the ratio of 2:1 (as in water).
(ii)1. Monosaccharide : glucose/fructose 2. Disaccharide: sucrose/lactose/maltose. 3. Polysaccharide : starch/glycogen/cellulose.
(c)(i)
(I) (a) brick red precipitate (b) black/charred mass (of carbon is observed).
(iii) C\(_6\)H\(_{12}\)O\(_6\) \(\to\) 6C + 6H\(_2\)O
(d) Mass of hydrogen in Z = \(\frac{12}{8 \times 0.692}\) = 0.077g
Mass of carbon in Z = \(\frac{12}{44}\) x 3.385 = 0.923g.
C H
0.923 0.077
12 1
0.077 0.077
0.077 0.077
0.077 0.077
Empirical formula of Z = CH
(CH)\(_n\) = 78
13\(_n\) = 78
n = \(\frac{78}{13}\)
= 6
molecular formula of Z = C\(_6\)H\(_{16}\)

