(a)(1) Define covalent bond.
(ii) Give two properties of covalent compounds
(ii) With the aid of a diagram, show how ammonia molecule is formed
(iv) Illustrate with a diagram the formation of ammonium ion?
(v) What type of bond(s) exist(s) in I. ammonia, H. ammonium ion? (\(_1\)H\(_7\)N)
(b)(i) Write three subatomic particles with their corresponding relative masses. CH\(_2\)OH
(ii) Name the possible states in which water can exist.
(c) (i) State Graham’s law of diffusion
(ii) Arrange the following gases, He, CH\(_4\) and N\(_2\) in order of increasing rates of diffusion. Give a reason for the order. [ H = 1, He = 4, C = 12, N = 14 ]
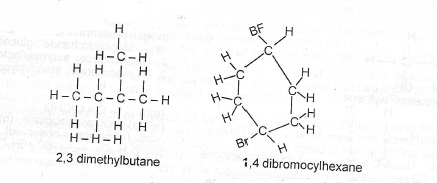
(d) Draw the structures of the following compounds:
(i) 2,3-dimethylbutane;
(ii) 1,4-dibromocyclohexane.
Explanation
(a)(i) Covalent bond is a bond between two atoms in which each of the atoms contribute to the shared pair of electrons.
(ii) (a) Non-conductors of electricity (b) Insoluble in water/soluble in non-polar solvents. (c) Have low melting or boiling point.
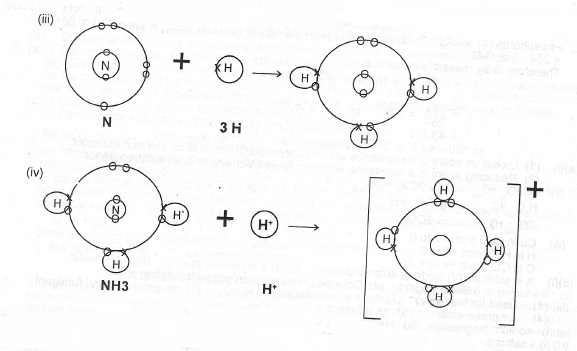
(v) (a) covalent bond (b) covalent bond dative or coordinate covalent bond
(b)
|
Particles |
Relative Masses Proton |
| Proton | 1 |
|
Neutron |
1 |
| Electron | 1 |
| 1840 |
(c)(i) Graham's law of diffusion states that a constant temperature and pressure, the rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its vapour density or molecular mass.
(ii) N\(_2\), CH\(_4\), He : the smaller the molecular mass the faster the rate at which the gas diffuses or the larger the molar mass the slower the rate at which the gas diffuses.
(d)