(a)(i) Define hard water
(ii) Name two substances responsible for hardness in water
(iii) Give two methods for the removal of hardness in water.
(b)(i) What are the raw materials require for the manufacture of tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid by the contact process?
(ii) Write an equation for tr reaction that requires a catalyst in the contact process (iii) State the catalyst used in (b)(ii).
(c)(i) Give two uses of sodium tetraoxosulphate (VI) Consider the reaction represented by the following equation:
Na\(_2\)SO\(_4\).10H\(_2\)O\(_{(s)}\) \(\to\) Na\(_2\)SO\(_4\).H\(_2\)O + 9H\(_2\)O\(_{(g)}\)
(ii) What name is given to this type of reaction?
(iii) Calculate the solubility of Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\) at 25°C. if 30.0 cm\(^3\) of its saturated solution at that temperature gave 1.80 g of the anhydrous salt. [C = 12, 0 = 16, Na = 23]
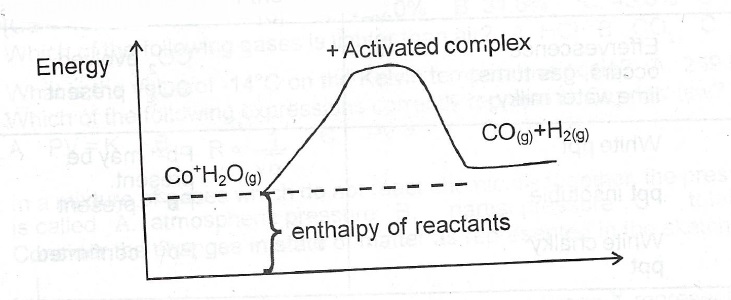
(d)(i) Define the term activated complex
(ii) State one reason why a collision may not produce a chemical reaction
(iii) The formation of water gas is represented by the following equation:
C\(_{(s)}\) + H\(_2\)O\(_{(g)}\) \(\to\) CO\(_{(g)}\) + H\(_{2(0)}\) \(\Delta\)H= + 131 kJmol\(^{-1}\)
Draw an energy profile diagram for the reaction showing the I. activated complex, II. enthalpy of reactants.
Explanation
(a)(i) Hard water is water which will not readily form lather with soap.
(ii) 1. Calcium tetraoxosulphate (IV) 2. Calcium hydrogen trioxocarbonate (IV) 3. Magnesium tetraoxosulphate (VI) 4. Magnesium hydrogen trioxocarbonate (IV).
(iii)(a) Heating the water to boiling/distillation (b) Addition of calculated amount of calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)\(_2\)] (c) Addition of washing soda crystals to the water [Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\)] (d) Ion exchange resin/permutit method.
(b)(i) Sulphur air or oxygen
(ii) 2SO\(_{2(g)}\) +O\(_{2(g)}\) \(\rightleftharpoons\) 2SO\(_{3(g)}\)
(iii) V\(_2\)O\(_5\) / Vanadium (V) oxide.
(c)(i) Use of Na\(_2\)SO\(_4\)
(a) Water softener (b) In glass or paper manufacturing (c) As analytical reagent (d) As purgative (e) In the manufacture of detergents .
(ii) Mass of salt per 30 cm\(^3\) of saturated solution = 1.80g.
1000 cm\(^3\) of saturated solution contains = \(\frac{1000 \times 1.80}{30}\)
= 60g.
Molar mass of Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\) = 23 x 2 + 12 x 1 + 16 x 3 = 106g.
Solubility of Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\) = \(\frac{60}{106}\) = 0.566 mole dm\(^3\).
(d)(i) Activated complex is the intermediate (complex) that reactants must attain in order to form a product or it is a temporary species formed by reactant molecules as a result of collision before the products are formed.
(ii) A collision may fail to produce a chemical reaction if the energy of the colliding particles is less than activation energy / if the reactant are not properly aligned.