(a)(i) Give the two reasons why soda lime is used instead of caustic soda in the preparation of methane.
(ii) List two physical properties of methane.
(iii) A hydrocarbon with a vapour density of 29 contains 82.76% carbon and 17.24% hydrogen. Determine the: I. empirical formula; II. molecular formula of the hydrocarbon. [ H = 1.00 C = 12.00 ]
(b)(i) What is meant by the term isomerism?
(ii) Draw the structures of the two isomers of the compound with the molecular formula C\(_2\)H\(_6\)O.
(iii) Give the name of each of the isomers in (b)(ii).
(iv) State the major difference between the isomers.
(c) Give three deductions that could be made from the qualitative and quantitative analysis of a given organic compound.
(d) Give one chemical test to distinguish between propene and propane.
Explanation
(a)(i) - sodalime does not attack glass apparatus, unlike caustic soda - sodalime is not, deliquescent unlike caustic soda.
(ii) - it is a gas at room temperature. - colourless gas. - odourless gas. - slightly soluble in water. -less dense than air.
(iii) I. % Carbon Hydrogen
82.76 17.24 82.76 17.24
12 1.00
6.90 17.24
6.90 6.90
1 2.5
2 5
II. Emperical formula = C\(_2\)H\(_5\)
Molecular formula = C\(_2\)H\(_5\)n = VD x 2
[(12 x 2) + (1 x 5)]n = 58
29n = 58
n = 2
molecular formula = (C\(_2\)H\(_5\))\(_2\) = C\(_4\)H\(_{10}\)
(b) (i) Tha existence of two or more compounds with the same molecular formula but different molecular structures/different arrangement of atoms.
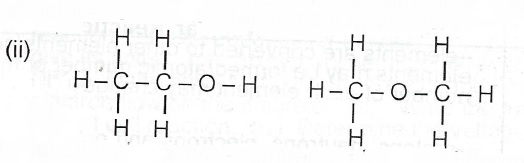
(iii) ethanol methoxymethane
(iv) The two isomers belong to different homologous series/they have different functional groups.
(c) - functional groups - number of atoms of different elements - types of elements - types of bonds - percentage composition of the elements in a compound - spatial arrangements of atoms in a molecule
(d) Pass each of the gases into (acidified) KMO\(_4\)/ bromine water/bromine inCCl\(_4\)/ bromine propene decolourizes bromine water/KMnO\(_4\)/bromine in CCI\(_4\)/bromine whereas propane does not.

