(a)(i) What is a functional group?
(ii) State the functional group in each of the following compounds: I. CH\(_3\)CH\(_2\)CH(CH\(_3\))OH; II. CH\(_3\)CH\(_2\)CH\(_2\)COOH.
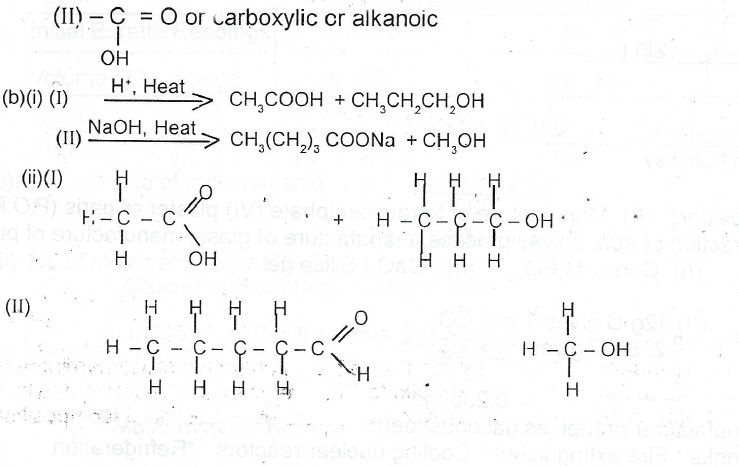
(b)(i) Complete the following equations:
(ii) Draw the structure(s) of the product(s) formed in (b)(i) above.
(c)(i).Write an equation for the prepzration of butan-2-ol from butene.
(d) (i) Give the reagents required for the following conversions to take place: I. CH\(_2\) = CH\(_2\) to CH\(_3\)CH\(_2\)OH; II. CH\(_3\)CH\(_2\)OH to CH\(_3\)COOH; Ill. CH\(_3\)COOH to CH\(_3\)COOCH\(_2\)CH\(_3\).
(e) Consider the following organic structure; CH\(_3\)OHCHCH = CHCOOH
(i) State what would be observed when the organic compound is treated with each of the following reagents: I. cold NaHCO\(_{3(aq)}\); II. hot solution of I\(_2\) in NaOH\(_{(aq)}\); Ill. bromine water.
Explanation
(a)(i) It is an atom or group of bonded atoms that is responsible for the chemical behaviour of an organ compound
(ii)(I) — OH or hydroxyl group or alkanol
(C) C\(_4\) H\(_8\) + H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) \(\to\) C\(_4\)H\(_8\)HSO\(_4\)
C\(_4\)H\(_9\)HSO\(_4\) + H\(_2\)O \(\to\) C\(_4\)H\(_8\)OH + H\(_2\)SO\(_4\)
OR
CH\(_2\) = CHCH\(_2\)CH + H\(_2\)O \(\to\) CH\(_3\)OHCHCH\(_2\)CH\(_3\)
OR
C\(_4\)H\(_8\) + H\(_2\)O \(\to\) C\(_4\)H\(_8\)OH
(d)(i) (I) Conc. H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) / H\(_3\)PO\(_4\)
(II) Acidified KMnO\(_4\) / K\(_2\)Cr\(_2\)O\(_7\) / Na\(_2\)Cr\(_2\)O\(_7\)
(Ill) Ethanol and Conc. H\(_2\)SO\(_4\)
(e)(i) (I) Effervescence occurs (II) Yellow precipitate (III) Bromine water decolourized
(ii) (I)
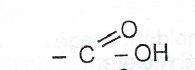 or — COOH or alkanoic group
or — COOH or alkanoic group
(II) CH\(_3\)CHOH / CH\(_3\) adjacent to CHOH
(III) C = C or carbon — carbon double bond

