(a) (i) What is diffusion?
(ii) State Charles’ law:
(iii) Sketch a graph to illustrate Charles’ law.
(iv) A given mass of a gas occupied 150 cm3 at 27 °C and a pressure of 1.013 x 105 Nm\(^{-2}\). Calculate the temperature at which its volume will be doubled at the same pressure.
(v) Arrange the three states of matter in order of increasing: (i) kinetic energy; (ii) forces of cohesion.
(b) (i) State Le Chatelier’s principle. (ii) A metal M forms two oxides containing 11.1% and 20.0% of oxygen. Show that these figures agree with the law of multiple proportion.
(c) The table below shows the physical properties of substances A, B and C.
|
Substance |
Melting point/°C | Boiling point/°C |
Solubility in water at 25°C |
| A | 30 | 117 | Insolube |
| B | 31 | 160 | Insoluble |
| C | 1200 | 1200 | Insoluble |
(i) If A and B are miscible when melted and B and C react when heated, describe how a mixture of A, B, and C could be separated.
(ii) When 25.25g of the mixture A, B and C was separated, 7.52 g of A and 8.48 g of B were recovered. Assuming i there was no loss of components during separation, calculate the percentage by mass of C in the mixture
Explanation
(a)(i) Diffusion is the movement of particles from the region of higher concentration to the region of lower concentration
(ii) Charles' Law states that the volume of a given mass of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature at a constant pressure.
(iii)
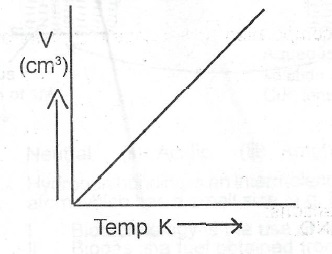
OR
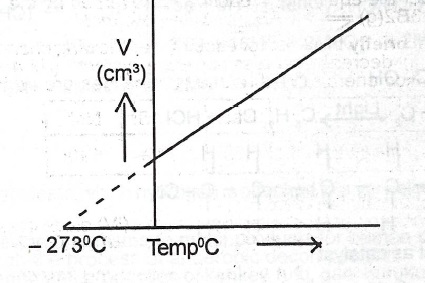
(iv) \(\frac{V_1}{T_1} = \frac{V_2}{T_2}\) \(T_2 = \frac{T_1V_2}{V_1}\)
\(T_2 = \frac{300 \times 300}{150} = 600k\)
(v)(i) Solid < liquid < gas / solid, liquid, gas
(ii) Gas < liquid < Solid / gas, liquid, solid
b)(i) In a reversible reaction at equilibrium, if any will of the factors affecting the equilibrium is altered, the position of equilibrium will change so as to annul the effect of the change
(ii) Oxide I
% of O\(_2\) = 11.1 %
% by mass of metal = 88.9%
11.1 of O\(_2\) combined with 88.9 of metal
100 of O\(_2\) = \(\frac{100}{88.9}\) = 800.9g
Oxide II
% of O\(_2\) = 20%
% by mass of metal = 80%
20 of O\(_2\) combined with 80 of metal
100 of O\(_2\) = \(\frac{100}{ 80}\) = 400g
Ratio of metal in both oxides = 800. 9 : 400
2 : 1
(c)(i) Add water to mixture A, B and C and stir.
— C dissolves
— Filter to obtain C as filtrate and A and B as residue
— Heat residue until melted.
— Separate by simple distillation
— Evaporate filtrate to dryness to obtain solid C
— Pure A is collected at 117°C and pure B at 160°C
(ii) Mass of mixture = 25.25g
Mass A + B = 7.52g + 8.48g
= 16.00g
Mass of C = 25.25 - 16.00g
= 9.25g
% of C in mixture = \(\frac{9.25}{25.25}\) x 100
= 36.6%

