(a)(i) List two characteristics of homologous series.
(ii) Consider the compound represented by the following formula: CH\(_3\)(CH\(_2\))\(_2\)CH\(_3\). I. Which homologous series does the compound belong? II. Write the structures of three possible isomers of the coumpound. III Name the three possible isomers in (a)(ii)II.
(b) Write the structure of the major product formed in each of the following reactions: (i) ethanol with excess acidified potassium tetraoxomanganate (VII);
(ii) excess ethane with chlorine in the presence of sunlight;
(iii) ethanol with propanoic acid in the presence of few drops of concentrated tetraoxosulphate(VI) acid.
(c) Name the major product in each reaction in (b).
(d) Consider the following organic compounds:

(i) Give the IUPAC name of each compound.
(ii) State a chemical test for the functional group in each compound.
(e) An organic compound with relative molecular mass 136 contains 70.57% carbon, 5.90% hydrogen and 23.53% oxygen. Determine its: (i) empopirical formula; (ii) molecular formula. [H= 1.00, C= 12.0, H = 16.0]
Explanation
(a)(i) List two characteristics of a homologous series:
(1) They can be represented by a gener molecular formula. (2) They have similar chemical properties. (3) They have same functional group (4) They can be prepared by a general method. (5) Each consecutive member differ by – CH\(_2\) group (6) Increase intensity of physical properties with increase in molar mass.
(ii) Consider the compound represented by the following formula: CH\(_3\)(CH\(_2\))2CH\(_3\) I. Which homologous series does the compound belong? Ans: Alkanes
II. Write the structures of 3 possible iscmers of the compound.
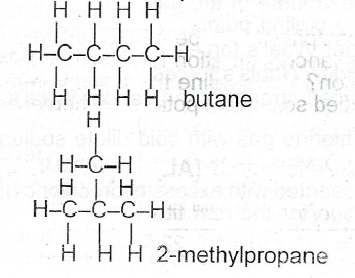
(b) Write the structure of the major product forn I in each of the following reactions:
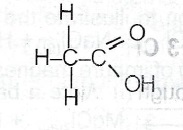
(i) Ethanol with excess acidified KMnO\(_4\)
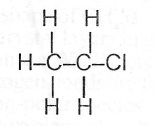
(ii) Excess ethane with chlorine in the presence of sunlight.
(iii) Ethanol with propanoic acid in the presence of few drops of concentrated tetraoxosulphate(VI)acid.
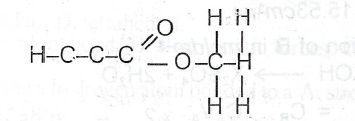
(c) Name the major product in each reaction in (b): (i) Ethanoic acid. (ii) Chloroethane. (iii) Ethylpropanoate.
(d) Consider the following organic compounds:
X — (CH\(_3\))\(_3\)COH

(i) Give the IUPAC name of each compound.
X is 2-methylpropan-2-ol.
Y is phenylmethanoic acid/benzoic acid.
(ii) State a chemical test for the functional group in each compound.
To sample X add some PCl\(_5\). Steaming white fumes of HCI will be observed.
OR
Add an organic acid to sample X and few drops of concentrated H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) or dry HCI gas and heat. A pleasant/fragrance/fruity smell is produced, confirms — OH in X.
OR
Add (saturated solution) of NaHCO\(_3\)/Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\) to sample Y. Effervescence of colourless, odourless gas which turns lime water milky.
OR
To sample Y, add an alkanol in the presence of conc. H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) or dry HCI. A pleasant/fragrance/fruity smell is produced, confirms — COOH in Y.
(e)(i)
moles = C; \(\frac{70.57}{12}\) H; \(\frac{5.90}{1}\) O; \(\frac{23.53}{16}\)
moles = C; \(\frac{5.88}{1.471}\) H; \(\frac{5.90}{1.471}\) O; \(\frac{1.471}{1.471}\)
emperica formula = C\(_4\)H\(_4\)O
(ii) (C\(_4\)H\(_4\)O)n = 136
68n = 136
n = \(\frac{136}{68}\)
n = 2
molecular formula - C\(_8\)H\(_8\)O\(_2\)

