All your burette readings (initials and final) as well as the size of your pipette must be recorded but no account experimental procedure is required. All calculations must be done in your answer booklet.
A is 0.100 mol dm\(^{-3}\) HNO\(_3\). B is a solution containing 2.50 g of a mixture of Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\) and Na\(_2\)SO\(_4\) in 250 cm\(^3\) of solution.
(a) Put into the burette and titrate it against 20.0 cm\(^3\) or 25.0cm\(^3\) portions of B using methyl orange as indicator. Repeat the exercise to obtain consistent titre values. Tabulate your readings and calculate the average volume of acid A used. The equation of reaction is Na\(_2\)CO\(_{3(aq)}\) + 2HNO\(_{3(aq)}\) \(\to\) NaNO\(_{3(aq)}\) + H\(_2\)O\(_{(l)}\) + CO\(_{2(g)}\)
(b) From your results and the information provided, calculate the:
(i) concentration of B in moldm\(^{-3}\);
(ii) concentration of Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\) in B in gdm\(^{-3}\);
(iii) percentage of Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\), in the mixture. [Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\) = 106]
Credit will be given for strict adherence to the instructions, for observations precisely recorded and for accurate inferences. All tests, observations, and inferences must be clearly entered in your answer book, in ink, at the time they are made.
C and D are inorganic salts. E is a solution of an organic compound. Carry out the following exercises on C, D and E. Record your observations and identify any gas(es) evolved. State the conclusion you draw from the result of each test.
(a) To all of C, add about 2 cm\(^3\) of distilled water in a boiling tube. Shake to dissolve and test the solution with litmus paper.
(b)i) Test E with litmus paper.
(ii) Add all of E to the solution obtained in (a).
(c)(i) Add about 5 cm\(^3\) of distilled water to D in a test tube and shake thoroughly. Divide the resulting solution into two portions.
(ii) To the first portion, add few drops of BaCl\(_{2(aq)}\) followed by excess dil. HCl.
(iii) To the second portion, add HNO\(_{3(aq)}\) in drops and then in excess.
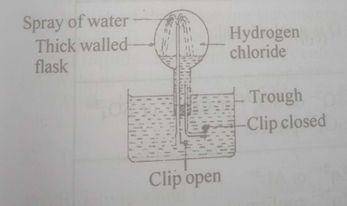
(a) Consider the following diagram ABOVE.
(i) Give the name of the experiment.
(ii) What does the experiment demonstrate?
(iii) Name one gas that could be used in place of HCl gas.
(iv) What colour could be observed in the flask during the spray of water?
(v) Could the gases used in the experiment be collected over water?
(vi) Explain briefly your answer in (a)(v).
(b) A solid substance U when strongly heated decomposes to give a white solid V and carbon (IV) oxide. When water is added to V, W is produced W can be used to test for carbon (IV) Oxide. Identify U, V and W.
(a) Define electrochemical cell.
(b) Aluminium can be prepared commercially by the application of electrolysis. Name the: I. electrolyte used in the process; II. ore from which the electrolyte is obtained; III. electrodes used in the electrolysis.
(ii) Give two reasons why cryolite, NaAl F\(_6\) is added to the electrolyte?
(c)(i) List the two gaseous fuels produced from coke.
(ii) Which of the two gases listed in (c)(i) is a better fuel?
(iii) Give a reason for your answer in (c)(i)
(iv) Write a balanced equation for the production of each gaseous fuel.
(d)(i) For each of the following reactions, state what would be observed when: I. chlorine gas is bubbled through aqueous sodium iodide; II. chlorine gas is passed over heated iron in a hard glass tube; III. aqueous silver trioxonitrate (V) is added to aqueous sodium bromide.
(ii) Write a balanced chemical equation for each of the reactions in (d)(i).
(a)(i) Name two gases that could be used to perform the fountain experiment.
(ii) State the physical property which makes the gases suitable for the experiment in (a)(i)
(b)(i) Define each of the following terms: I. solubility; II. saturated solution.
(ii) State two factors that affect the solubility of a solid in a liquid.
(iii) A salt Z of mass 10.2 g was dissolved in 15.4 cm\(^3\) of distilled water at 40°C. Calculate the solubility of Z in moldm\(^3\) at 40°C. [Mr (Z) = 331].
(c)(i) Town water supplies that have passed through iron pipes contain P and Q ions. In the presence of air, P ions are slowly converted to Q ions.
I. Identify P and Q ions. II. Write a balanced equation for the reaction between P ions, hydrogen ions and oxygen to give Q ions and water.
(ii) Explain briefly a test to confirm the purity of water.
(iii) State the effect of:
I. boiling a temporally hard water. II. adding sodium trioxocarbonate (IV) crystals to permanent hard water;
(iv) Write a balanced equation for the process in (c)(iii)I.
(a)(i) Give three characteristics of homologous series.
(ii) Name two groups of compounds which form such a series.
(b) A saturated organic compound A containing two carbon atoms reacted with ethanoic acid in the presence of a mineral acid to form a compound B with a sweet smell. (i) Name the functional group present in A.
(ii) Draw the structure of A.
(iii) Write a chemical equation to show the formation of B.
(iv) Name the compound B.
(c)(i) Write a balanced equation for the reaction between ethyne and excess bromine.
(ii) Give IUPAC name of the product of the reaction in (c)(i)
(iii) State two conditions under which cracking takes place
(d)(i) Outline the preparation of ethanol from starch.
(ii) Give two properties of starch.
(iii) Give a reason why starch does not reduce Fehlings solution
(iv) Describe briefly a chemical test to confirm the presence of starch.
(a) Consider the following table; (i) Which of the elements:
| Element | Atomic Number | Mass Number |
| J | 9 | 19 |
| Q | 13 | 27 |
| R | 16 | 32 |
| X | 19 | 39 |
| Y | 24 | 52 |
I. is a halogen?
II. is most likely to be attracted by a magnet?
III. belongs to group I?
IV. would readily form an ion with a double negative charge?
(ii) What type of bond would exist between J and X when they combine?
(iii) How many neutrons are there in Q?
(iv) Write the formula of the compound formed when R combines with X.
(v) State the element which exists as diatomic molecule..
(vi) Select the element which belong to the d-block of the periodic table.
(b)(i) Explain briefly the term atomic orbital
(ii) I. State three prostulates of Dalton’s atomic theory.
II. List two limitations of this theory in the study of the atom
(iii) Describe briefly the structure of sodium chloride in its solid state.
(c) A sample of carbon is burnt at a rate of 0.50g per second for 30 minutes to generate heat.
(i) Write a balanced equation for the reaction
(ii) Determine the:
I. volume of carbon (IV) oxide produced at s.t.p.
II. moles of oxygen used up in the process at s.t.p. [C = 12.0, O = 16.0, Molar volume V\(_m\) = 22.4 dm\(^3\)].
(a) Define esterification.
(b) State two properties of plastic.
(c) Name the components of duralumin.
(d) What is meant by each of the following terms?
(i) Raw material.
(ii) Primary product.
(e) State Charles’ law.
(f) List four pieces of protective equipment in the laboratory.
(g) Give two uses of ammonia.
(h) Name the:
(i) process by which lighter hydrocarbons are obtained from heavier ones;
(ii) products formed from the reaction between ethanol and sodium metal.
(i) Determine the oxidation number of sulphur in H\(_2\)SO\(_4\).
(j) Write the IUPAC name for each of the following compounds: (i) NaClO\(_3\); (ii) CuSO\(_4\)5H\(_2\)O.
Consider the following equilibrium system:
2SO2(g) + O2(g) \(\rightleftharpoons\) 2SO3(g)
The addition of more O2(g) to the system will shift the equilibrium position to the
- A. Right leading to the production of more SO3(g)
- B. Right leading to the production of more SO2(g)
- C. Left leading to the production of more SO2(g)
- D. Left leading to the production of more SO3(g)
The correct balanced equation for the reaction between aluminium metal and hot concentrated tetraoxosulphate(VI)acid is ?
- A. 2AI(s) + 6H2SO4(1) \(\to\) AI2(SO4)3(aq) + 6H2O(1) + 3SO2(g)
- B. 2AI(s) + 3H2SO4(1) \(\to\) AI2(SO4)3(aq) + 6H2O(1) + 3SO2(g)
- C. 2AI(s) + 4H2SO4(1) \(\to\) AI2(SO4)3(aq) + 8H2O(1) + 3SO2(g)
- D. 2AI(s) + 5H2SO4(1) \(\to\) AI2(SO4)3(aq) + 8H2O(1) + 3SO2(g)
Which of the following gases is monoatomic?
- A. Argon
- B. Chlorine
- C. Nitrogen
- D. Oxygen
Which of the following polymers in thermosetting?
- A. Bakelite
- B. Nylon
- C. Polypropene
- D. Polystyrene
Which of the following products of biotechnology can be used as a fuel in place of petrol?
- A. Butane
- B. Ethanol
- C. Ethene
- D. Propanol
A substance responsible for the sour taste of unripe orange is
- A. Alkene
- B. Alkanol
- C. Alkanoic acid
- D. Alkanoate
Which of the following process does not take place in domestic water treatment?
- A. Chlorination
- B. Flocculation
- C. Neutralization
- D. Sedimentation
Which of the following substances is a heavy chemical?
- A. Ammonia
- B. Barim Hydroxide
- C. Hydrochloric acid
- D. Tetraoxosulphate(VI)acid
Which of the following compounds is a secondary alkanol?
- A. Ethanol
- B. 2-methylbutan-2-ol
- C. 3-methylpentan-2-ol
- D. Propan-1-ol
Starch could be converted to glucose by the process of
- A. Condensation
- B. Dehydration
- C. Fermentation
- D. Hydrolysis
Which of the following reactions would take place when concentrated sodium hydroxide solution is added to palm oil?
- A. Esterification
- B. Neutralization
- C. Polymerization
- D. Saponification
A compound has an empirical formular CH2O and molecular mass of 90.
[H = 1.00, C = 12.0, O = 16.0]
- A. C4H10O2
- B. C3H10O2
- C. C3H6O3
- D. C2H2O4
The complete hydrogenation of benzene gives
- A. Cyclohexene
- B. Cyclohexane
- C. Hexene
- D. Hexane


