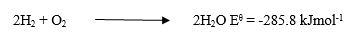All your burette readings (initials and final) as well as the size of your pipette must he recorded but no account of experimental procedure is required. All calculations must be done in your booklet.
State the observation that would be made when each of the following reactions is carried out in the laboratory:
(a) Addition of 2 cm\(^3\) of bench H\(_2\)SO\(_{4(aq)}\) to 2 cm\(^{3}\) of barium chloride solution;
(b) Addition of 2 cm\(^3\) of dilute hydrochloric acid to 1g of powered iron(II) sulphide (FeS):
(C) Addition of 2 cm\(^3\) of dilute hydrochloric acid to 1g of iron filings and allowed to stand for sometime.
All your burette readings (initials and final) as well as the size of your pipette must be recorded but no account of experimental procedure is required. All calculations must be done in your booklet.
C and D are inorganic salts. Carry out the following exercises on them. Record your observations and identify any gas(es) evolved. State the conclusions you draw from the result of each test.
(a) Put all of C in a test tube and add about 5 cm of distilled water. Shake thoroughly and test the resulting solution with Litmus paper. Divide the solution into three portions.
(i) To the first portion, add NaOH\(_{(aq)}\) in drops, then in excess.
(ii) To the second portion. add NH\(_{3(aq)}\) in drops. then in excess.
(iii) To the third portion. add AgNO\(_{3 (aq)}\) followed by HCl\(_{(aq)}\)
(b)(i) Put all of D in a test tube and add about 5 cm\(^3\) of distilled water. Shakę thoroughly and feel the test tube.
(ii) To about 2 cm\(^3\) of the solution, add HCl\(_{(aq)}\)
All your burette readings (initials and final) as well as the size of your pipette must he recorded but no account of experimental procedure is required. All calculations must be done in your booklet.
A solution of potassium tetraoxomanganate( VII). B is a solution of iron(II)chloride containing 4.80g of the salt in 250 cm\(^{3}\) of solution.
(a) Put A into the burette. Pipette 20.0cm\(^3\) or 2.50.0 of B into a conical flask, add 20.0 cm\(^3\) of H\(_2\)SO4\(_{(aq)}\) and titrate with A. Repeat the titration to obtain concordant titre values. Tabulate your results and calculate the average volume of A used. The equation of the reaction is: MnO\(_{4(aq)}\) + 5Fe\(^{3+}_{ (aq)}\) + H\(_2\))
(b) From your results and the information provided, calculate the;
(i) concentration of B moldm\(^{-3}\):
(ii) concentration of A in moldm\(^{-3}\)
(iii) number of moles of Fe\(^{2+}\) in the volume of B pipetted. [FeCl\(_2\) = 127 gmol\(^{-1}\)] Credit will be given for strict adherence to the instruction, for observations precisely recorded and for accurate inferences. AlI tests, Observations and inferences must be clearly entered in the booklet in ink at the time they are made.
(a) (i) List two gaseous pollutants that can be generated by burning coal.
(ii) Explain briefly why coal burns more easily when it is broken into pieces than when it is in lumps.
(iii What gas is responsible for most of the explosions in coal mines?
(iv) Name the non-volatile residue left behind after the destructive distillation of coal.
(b) State one oxide in each case which:
(i) is used in bleaching;
(ii) oxidizes hot concentrated HCl to chlorine;
(iii) dissolves in water to give a solution with pH greater than 7;
(iv) reacts with NaOH and also with HCl;
(v) is a reddish-brown gas.
(c) (i) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between chlorine gas and iron(II) chloride solution.
(ii) State the type of reaction in (c)(i).
(iii) Give a reason for your answer in (c)(ii).
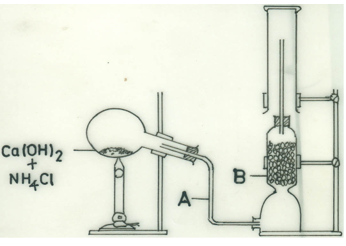
(d) Consider the following set-up:
(i) Identify A and B.
(ii) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
(iii) Name the gas produced.
(iv) Why was the flask tilted downwards?
(v) What is the:
(I) function of B in the experiment;
(II) method of collection of the gas?
(e) Give one product obtained from refining petroleum that is solid.
(a) Outline the procedures for the treatment of water for town supply.
(b) (i) State two main impurities present in bauxite.
(ii) Give one reason why bauxite is usually preferred as the ore for the extraction of aluminium.
(iii) Outline the manufacture of aluminium form purified bauxite.
(c) (i) Explain briefly the term fine chemical industry.
(ii) State two differences between a fine chemical and a heavy chemical.
(d) (i) Write a balanced chemical equation for the combustion of coal.
(ii) If 5.4 g of coal is burnt completely, calculate the amount of oxygen measured at s.t.p. that would be required for the combustion.
[C = 12.0, O = 16.0, Molar volume of a gas at s.t.p. = 22.4 dm\(^3\)]
(e) Name two substances which can be used as electrodes during the electrolysis of acidified water.
a) (i) Describe, using the kinetic theory of matter, what happens when potassium chloride dissolves in water.
(ii) Give a reason why the process in (a) (i) is endothermic.
(b) (i) An underground iron pipe is less likely to corrode if it is bonded at intervals with magnesium rods. Give reasons for this observation.
(ii) State the stages involved in the rusting of iron.
(iii) State the condition for the rusting of iron in water.
(c) (i) What is a spontaneous reaction?
(ii) State two conditions that could make a reaction spontaneous.
(iii) Explain briefly why one gramme of sodium reacts more rapidly with water at 250C than one gramme of calcium at the same temperature.
(iv) Write equations for the reactions in (c)(iii).
(d) What mass of lead (II) trioxocarbonate (IV) would contain 35.0 g of lead?
[C=12.0, O = 16.0, Pb = 207.0]
(e) Name the type of intermolecular force present in:
(i) fluorine;
(ii) hydrogen fluoride.
(a) A compound of carbon, hydrogen and chlorine contains 0.48 g of carbon, 0.08 g of hydrogen and 1.42 g of chlorine.
(i) Determine the empirical formula of the compound.
(ii) If the molar mass of the compound is 99, calculate the molecular formula of the compound.
[H = 1.0, C = 12.0, Cl = 35.5]
(b) State three properties of NaCl (s) which shows that it is ionic.
(c) Consider the following reaction equation:
(i) On the same diagram, sketch and label a reaction profile for a catalysed and uncatalysed reaction between H\(_2\) and O\(_2\).
(ii) Indicate the possible positions of the activated complexes for the reaction profiles in (c)(i).
(d) The petrochemical industry produces addition polymers using one of the fractions obtained from crude oil.
(i) Name the fraction used as a raw material for the process.
(ii) What process is used to obtain the fraction from crude oil?
(iii) Name two gaseous hydrocarbons that can be used in making polymers.
(iv) Describe briefly how these hydrocarbons can be obtained.
(v) Name the polymer produced from one of the hydrocarbons named in (d)(iii).
(a) Arrange the three states of matter in order of decreasing:
(i) kinetic energy;
(ii) force of cohesion.
(b) Consider the redox reaction equation:
(i) State the change in oxidation number of:
I. magnesium;
II. hydrogen.
(ii) Which of the species is being:
I. oxidized;
II. reduced?
(iii) Identify the oxidizing agent.
(c) (i) State two differences between boiling and evaporation.
(ii) What will be the effect of reduction of atmospheric pressure on the boiling point of water?
(d) For a given chemical equilibrium system, what is the significance of the equilibrium constant K?
(e) Consider the following organic compounds:
C\(_3\)H\(_7\)COOH; (CH\(_3\))\(_3\)COH.
Give the IUPAC name of each compound.
(f) Why are organic compounds classified on the basis of functional groups?
(g) State three differences between the solubility of solids in liquids and gases in liquids.
(h) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between fluorine and water.
(i) Define the term basicity of an acid.
(a) (i) State the collision theory of reaction rates.
(ii) Using the collision theory, explain briefly how temperature can affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
(b) (i) Sketch a graphical representation of Charles’ law.
(ii) Calculate the volume of oxygen that would be required for the complete combustion of 2.5 moles of ethanol at s.t.p.
[molar volume at s.t.p = 22.4 dm\(^3\)]
(c) (i) Define esterification.
(ii) Give two uses of alkanoates.
(iii) Give the products of the alkaline hydrolysis of ethyl ethanoate.
(d) A tin coated plate and a galvanized plate were exposed for the same length of time.
(i) Which of the two plates corrodes faster?
(ii) Explain briefly your answer in 2 (d) (i).
(a) (i) Name the ore mostly used in the extraction of aluminium.
(ii) Name two major impurities in the ore named in (a)(i).
(iii) Name the material used in making the electrodes in the extraction of aluminium.
(iv) Give two reasons why aluminium is commonly recycled.
(v) Explain briefly why the anode has to be replaced at regular intervals during the extraction of aluminium.
(b) A current of 0.75 amperes was passed through an electrolysis containing chromium ions for one hour and four minutes. If the mass of chromium deposited was 0.52 g, calculate the:
(i) quantity of electricity passed;
(ii) moles of chromium deposited;
(iii) quantity of electricity required to deposit one mole of chromium;
(iv) charge on the chromium ion.
[Cr = 52.0, 1 F = 96500 C]
(c) In the contact process for the manufacture of tetraoxosulphate(VI) acid, the following reaction occurs:
2SO\(_2\)\(_{(g)}\) + O\(_2\)\(_{(g)}\) 2SO\(_3\)\(_{(g)}\) H = – 197 kJ mol\(^{-1}\)
(i) Name the catalyst used in the reaction;
(ii) State the optimum temperature for this reaction;
(iii) What would be the effect on the yield of SO\(_3\) if a temperature higher than the optimum is used?
(d)(i) State two chemical methods by which temporary hardness of water can be removed.
(ii) Write a balanced chemical equation for each of the methods stated in (d)(i).
(a)(i) Describe briefly the laboratory preparation of hydrogen gas from the action of steam on iron.
(ii) Write the equation for the reaction in (a)(i).
(iii) List three methods for the industrial preparation of hydrogen gas.
(b)Consider the following reaction equation:
CO(g) + 2H\(_{2(g)}\) CH\(_3\)OH\(_{(g)}\) + 201 kJmol-J
Predict the effect of each of the following factors on the position of equilibrium:
(i) decrease in temperature;
(ii) increase in pressure;
(iii) increase in concentration of CO\(_{(g)}\).
(c) (i) Define condensation polymerization.
(ii) Name two condensation polymers.
(iii) Write the formula of ethylethanoate.
(d) (i) Define the term allotropy.
(ii) Name two crystalline allotropes of carbon.
(iii) State one use of each of the allotropes named in (d)(ii).
(e) State two differences between nitrogen (I) oxide and oxygen.
(a) Explain the statement, the standard electrode potential of zinc is -0.76 v.What is meant by the term periodic property of elements?
(b) Consider the following standard electrode potentials:
Zn\(^{2+}\)\(_{(aq)}\) + 2e\(^-\) Zn(s) Eᶿ = – 0.76 V
Cu\({2+}\)\(_{(aq)}\) + 2e\(^-\) Cu(s) Eᶿ = + 0.34 V
When the two half cells are connected:
(i) write the reaction equation at each electrode;
(ii) write the overall cell reaction equation;
(iii) state the type of reaction occurring at each electrode;
(iv) calculate the e.m.f. of the cell.
(c) (i) Name two chemical industries.
(ii) State two factors that should be considered when siting a chemical industry.
(iii) List two effects of a chemical industry on the community in which it is sited.
(d) Using chemical equations, explain briefly what would happen when hydrogen peroxide is added to:
(i) silver oxide;
(ii) chlorine gas.
(e) List three physical properties of nitrogen.
1. (a ) Define the term compound.
(b) State two conditions necessary for the cracking of petroleum fractions.
(c) Name two transition elements that are used as catalyst.
(d) (i) Write an equation for the reaction between zinc dust and trioxonitrate (V) solution.
(ii) Which of the reactants in 1(d)(i) is:
I. reduced;
II. oxidized.
(e) Two isotopes of oxygen 16O and 18O have relative abundance of 90 % and 10 % respectively. Calculate the relative atomic mass of oxygen.
(f) List two ores of iron.
(g) (i) What is biotechnology?
(ii) Name one product that can be obtained using biotechnology.
(h) Define the term element.
(i) State two sources of methane in the atmosphere.
(j) Explain briefly why the trend of the boiling points for group VII elements is in the order I\(_2\) > Brl\(_2\)> Cl\(_2\).
(a) (i) List the two gaseous fuels produced from coke.
(ii) Which of the two fuels listed in 5(a)(i) is a better fuel?
(iii) Give reasons for your answer in 5(a)(ii)
(iv) Write a balanced equation for the production of each of the fuels. [9 marks]
(b)(i) Differentiate between thermosets and thermoplastics.
(ii) Give one example of:
I. thermosets;
II. thermoplastics.
(iii) State three properties of plastics.
(c)(i) State the method of collecting gases which are denser than air.
(ii) Name two gases that could be used to perform the fountain experiment in the laboratory.
(iii) State the physical properties of the gases named in 5(c)(ii) which makes them suitable for the experiment. [4 marks]
(d) (i) State two compounds that could be used to test for water.
(ii) Give three disadvantages of hard water.
(a) (i) Define the term fermentation
(ii) Name the catalyst that can be used for this process
(b) Name two factors which determine the choice of an indicator for an acid-base titration
(c) Consider the following reaction equation: Fe + H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) \(\to\) FeSO\(_4\) + H\(_2\). Calculate the mass of unreacted iron when 5.0g of iron reacts with 10cm\(^3\) of 1.0 moldm\(^3\) H\(_2\)SO\(_4\), [Fe = 56.0]
(d) Name one:
(i) Heavy chemical used in electrolytic cells
(ii) Fine chemical used in textile industries
(e) Explain briefly how a catalyst increases the rate of a chemical reaction.
(f) (i) Write the chemical formula for the product formed when ethanoic acid reacts with ammonia
(ii) Give the name of the product formed in (f)(i)
(g) List three properties of aluminum that makes it suitable for the manufacture of drinks cans
(h) State two industrial uses of alkylalkanoates
(i) Name two steps involved in the crystallization of a salt from its solution
(j) List two effects of global warming
(a)(i) State two industrial uses of hdrogen.
(ii) Consider the equation below. Mg(HCO\(_3\))\(_{2(aq)}\) \(\to\) MgCO\(_{3(g)}\) + H\(_2\)0\(_{(l)}\) + CO\(_{2(g)}\)
1. State the type of hardness of water being removed as shown by the above equation.
2. Give two disadvantages of hardness of water.
(b)(i) In the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis, graphite electrodes are used. State the disadvantages of using this type of electrode.
(ii) Calcuim oxide reacts with water to form slaked line: I. Write a balanced equation for this reaction; II. State one use of slaked line.
(c)(i) What is meant by saponification?
(ii) List the raw materials needed for the manufacture of soap.
(iii) Name the main by-product obtained from the manufacture of soap.
(d) With the aid of chemical equations explain briefly how iron is extracted in the blast furnace using iron ore, coke and limestone as raw materials at the:
(i) bottom of the furnace; (ii) middle of the furnace (iii) top of the furnace.
(a)(i) Draw and label a diagram for the laboratory preparation of a dry sample of sulphur(IV)oxide.
(ii) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction in (a)(i).
(iii) State the precaution that must be taken in the preparation of the gas stated in (a)(i).
(iv) Give a reason why the precaution stated in (a)(ii) must be taken.
(b)(i) State Dalton’s law of partial pressures.
(ii) The volume of a sample of methane collected over-water at a temperature of 12°C and a pressure of 700 mmHg was 30cm\(^3\). Calculate the volume of the dry gas at s.t.p. [Saturated vapour pressure of water at 12°C is 10 mmHg] •
(c)(i) Write an equation for the reaction between chlorine and water.
(ii) Why does litmus paper turn red when put in the resulting solution in (c)(i)?
(d)(i) State the trend in the boiling points of chlorine, bromine and iodine.
(ii) Explain briefly why water has a higher boiling point than ammonia.
(a)(i) Draw the structure of the sixth member of the alkenes.
(ii) Calculate the relative molecular mass of the sixth member of the alkene.
(iii) State one difference between cracking and reforming in the petroleum industry. [H = 1, C = 12]
(b)(i) Define the term enthalpy of neutralization.
(ii) Describe briefly how the enthalpy of neutralization of the reaction of dilute hydrochloric acid and aqueous potassium hydroxide could be determined.
(c) An electrochemical cell is constructed with copper and silver electrodes.
(i) State which of the electrodes will be the: 1. anode; II. cathode.
(ii) Give the reason for your answer in 3(c)(i).
(iii) State the type of reaction occurring at each electrode.
(iv) Write a balanced equation for the overall cell reaction.
(d)(i) Name the compound formed when iron is exposed to moist air for a long time.
(ii) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction in 3(d)(i).
(iii) Name one ore of iron.
(a)(i) Sketch a graphical representation of Charles’ law.
(ii) Calculate the volume of oxygen that would be required for the complete combustion of 2.5 moles of ethanol at s.t.p. [molar volume at s.t.p. = 22.4 dm\(^3\)]
(b)(i) State the collision theory of reaction rates.
(ii) Using the collision theory, explain briefly how temperature can affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
(c)(i) Define esterification.
(ii) Give two uses of alkanoates.
(iii) Give the products of the alkaline hydrolysis of ethyl ethanoate.
(d) A tin coated plate and a galvanized plate were exposed for the same length of time.
(i) Which of the two plates corrodes faster
(ii) Explain briefly your answer in 2(d)(i)
Particles in a solid exibit
- A. vibrational motion
- B. vibrational and translational motion
- C. vibrational and random motion
- D. random and translational motion
Which of the following properties would not influence electrovalent bond formation?
- A. Electronegativity
- B. Electron Affinity
- C. Ionization potential
- D. Catalytic ability