(a)(i) Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the preparation and collection of dry chlorine gas in the laboratory.
(ii) State two uses of chlorine.
(b) Describe the preparation of hydrogen from water gas.
(i) Name the chief ore of aluminium.
(ii) Why is the ore purified?
(iii) Name the electrode used in the electrolysis.
(iv) Give one reason why cryolite, NaAlF\(_6\), is added to the electrolyte.
(c) Name three products obtained directly from the destructive distillation of coal.
Explanation
(a)(i) 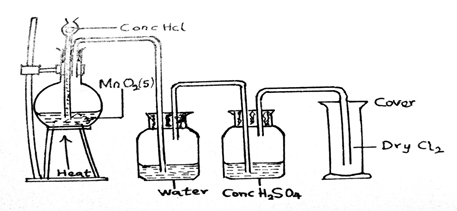
(ii) - used as germicide/disinfectant/sterilization/antiseptic/insecticides
- bleaching of materials/wood pulp/textiles
- commercial production of HCl
- production of polymers/PVC/plastics
- production of chlorinated chemicals e.g. CHCl\(_3\), CCl\(_4\)
- in medicine
- production of dyes
(b) Water gas is CO + H\(_2\) steam is mixed with water gas and passed over heated catalyst of iron (III) oxide or chromium (III) oxide at 450\(^o\) C
The CO in water gas is converted to CO\(_2\) with further yield of hydrogen
The CO\(_2\) is removed by dissolving the mixture in water / NaOH/KOH/Ca(OH)\(_2\) solutions under pressure
(c) (i) Bauxite
(ii) - To produce aluminium oxide/alumina.
- To prevent poisoning of the electrode.
(iii) Carbon/ graphite
(iv) - It is added to reduce some of the energy (costs) involved in extracting aluminium
- to increase the electrical conductivity of alumina
- to lower the melting points to of the alumina
(d) Coke
- Coal tar
- Coal gas
- ammoniacal liquor

