What would be observed when aqueous ammonia is added in drops and then in excess to a solution of copper(II) ions?
- A. blue precipitate is formed which is soluble in excess ammonia
- B. brick red precipitate is produced which is insoluble in excess ammonia
- C. white precipitate is formed which is excess in ammonia
- D. green precipitate is formed which is insoluble in excess ammonia
The basic property of salts used as drying agents is by?
- A. efforescence
- B. high melting point
- C. hygroscopy
- D. low solubility
What number of moles of oxygen would exert a pressure of 10 atm at 320 K in an 8.2 dm\(^{2}\) cylinder?
[R = 0.082 atm dm\(^{3}\) mol\(^{-1}\) K\(^{-1}\)]
- A. 0.32
- B. 1.56
- C. 3.13
- D. 31.25
The most common method of preparing insoluble salts is by
- A. filtration
- B. decomposition
- C. neutralization
- D. double decomposition
A molecular of phosphorus is
- A. diatomic
- B. triatomic
- C. tetraatomic
- D. monoatomic
Which of the following gasses is highly soluble in water at room temperature
- A. ammonia
- B. carbon (IV) oxide
- C. chlorine
- D. nitrogen
The formation of ethene from dehydration of ethanol can be described as——-
- A. an addition reaction
- B. an elimination reaction
- C. an oxidation reaction
- D. a substitution reaction
Study the graphs below and use them to answer the question below

Which of the graphs illustrates the variation of the solubility of a salt in water (y-axis), with an increase in temperature (x-axis) if the dissolution process is exothermic?
- A. I
- B. II
- C. III
- D. IV
Study the graphs below and use them to answer the question below

Which of the graphs illustrates the variation of the pH of a given volume of strong acid solution (y-axis) with the volume of strong base titrated against its (x-axis)?
- A. I
- B. II
- C. III
- D. IV
Study the graphs below and use them to answer the question below

Which of the following illustrates the variation of the rate of evolution of gas from a given length of magnesium ribbon (y-axis) with an increase in the concentration of the added (x-axis)?
- A. I
- B. II
- C. III
- D. IV
Which of the following pairs of compounds would form a precipitate when their aqueous solutions are mixed?
- A. NaCl and KNO\(_{3}\)
- B. KCL and NaNO\(_{3}\)
- C. K\(_{2}\)SO\(_{4}\) and BaCl\(_{2}\)
- D. NH\(_{4}\)NO\(_{3}\) and CO\(_{3}\)
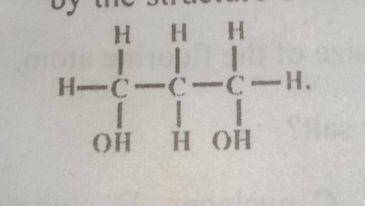
The alkanol represented by the structure above is
- A. primary and dihydric
- B. secondary and monohydric
- C. tertiary and dihydric
- D. secondary and dihydric
If humid air is polluted by chlorine discharged, the air can be restored by sprinkling
- A. solid MnO\(_{2}\)
- B. acidified KMnO\(_{4}\)
- C. acidified FeSO\(_{4}\)
- D. saturated NaCl(aq)
Cathodic protection of metals is based on
- A. standard electrode potential of hydrogen
- B. its electrical conductivity
- C. nature of oxides formed
- D. relative tendencies of oxidation
What is the relative molecular mass of the compound below?
[H = 1.0; C = 12.0; O = 16.0]
- A. 137
- B. 136
- C. 64
- D. 59
The ratio of carbon atoms of hydrogen atoms in a hydrocarbon is 1:2. If its molecular mass is 56, what is its molecular formula?
- A. C\(_{3}\)H\(_{6}\)
- B. C\(_{4}\)H\(_{8}\)
- C. C\(_{2}\)H\(_{4}\)
- D. CH\(_{2}\)
Which of the following oxide causes acid rain?
- A. CO
- B. NO
- C. H\(_{2}\)O\(_{2}\)
- D. NO\(_{2}\)
The hydrolysis of proteins by diluting mineral acids produces
- A. sucrose
- B. glucose
- C. amino acids
- D. fatty acids
Aqueous solutions of zinc chloride, calcium chloride iron (lII) tetraoxosulphate (VI) and lead (II) trioxonitrate (IV) are contained in four separate bottles whose labels have been lost. Using aqueous ammonia solution only, show how you would identify the content of each bottle.
Carry out the following exercises on sample C. Record your observations and identify any gases evolved. State the conclusion you draw from the result of each test.
(a) Put about half of sample C into a conical flask and add about 5cm\(^3\) of tetrachloroethane followed by 15cm\(^3\) of water. Shake vigorously for about one minute. Put the resulting mixture into a burette and allow to stand until two layers separate. Run the two layers into two separate conical flasks and label them accordingly.
(b) Using the following reagents only, bench sodium hydroxide solution, aqueous ammonia solution, aqueous lead (II) trioxonite (V) solution, silver trioxonitrate (V) solution. bench trioxonitrate (V) acid. Identify the ions present in the upper layer solution
(c) Add 2 – 3 drops of the lower layer solution to about 2cm\(^3\) of starch solution from your result, name the substances which dissolved in the upper and lower layers.
A solution of a mineral acid containing 0.10 mol of the acid per dm of solution. B IS a solution Containing 1.325g of anhydrous sodium trioxocarbonate (IV) per dm of solution.
(a) Put A into the burette and titrate with 20cm\(^3\) or 25cm\(^3\) portions of B using methyl orange as an indicator. Record the volume of your pipette
(b) From your results and the information is given, calculate;
(i) The number of mole of acid in the average titre
(ii) The number of mole of sodium trioxocarbonate (IV) in the volume of B pipette,
(iii) The mole ratio of acid to base in the reaction [H = 1, C = 12, O = 16, Na 23]
(c) Suggest what the acid in (a) Could be giving reasons for your answer. Hence, write the equation for the reaction.


