The multiplier is defined as
- A. The ratio of the change in income to the change in investment
- B. The change in investment divided by the change in income
- C. \(\frac{1}{MPC}\)
- D. \(\frac{1}{1-\text{MPS}}\)
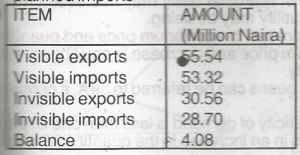
The amount, N4.08 million, shown as balance in the table represents
- A. terms of payments
- B. balance on current accounts
- C. balance of trade
- D. terms of trade
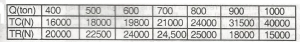
The table gives the various levels of output (Q) and its corresponding total cost of production. (ITC) and total revenue (TR) for a firm. Which output level Q results in maximum profit?
- A. 400
- B. 500
- C. 600
- D. 700
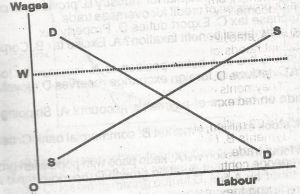
In the diagram above what happens when the minimum wage is fixed at OW?
- A. Unemployment is reduced
- B. Unemployment results
- C. The demand schedule will shift
- D. the supply schedule will become steeper
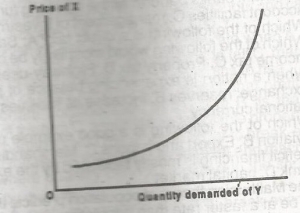
If the curve above shows the relationship between the price of commodity X and the quantity demanded of commodity Y then X and Y are
- A. complementary goods
- B. substitutes
- C. inferior goods
- D. luxury goods
The primary goal of development planning in Nigeria is to?
- A. increase profitability of enterprises
- B. achieve a rapid increase in the welfare and standard of living of Nigerians
- C. increase the level of gross domestic product
- D. make Nigeria a super-power
A sustained increase in the per capita income of a country over a period of time is called?
- A. economic growth
- B. economic development
- C. structural change
- D. stagflation
If C stands for consumption expenditure, I for investment, X for exports, and M for imports, then national income is?
- A. C + I + X + M
- B. C + I +X - M
- C. C + I - X + M
- D. C + I + X
The value of the total output produced within Nigeria by all residents (citizens and non-citizens) is referred to as the?
- A. gross national product
- B. disposable income
- C. national income
- D. gross domestic product
The difference between gross national product and net national product is equal to?
- A. gross investment
- B. net investment
- C. net foreign income
- D. capital depreciation
The group of people engaged in banking or insurance services by occupational distributions are classified as?
- A. primary producers
- B. secondary producers
- C. tertiary producers
- D. technical producers
Optimum population is the population level at which?
- A. death rate is at a minimum
- B. per capita income is at a maximum
- C. population is at a maximum
- D. death rate is equal to birth rate
International and inter-regional trade differ primarily because?
- A. comparative advantage is relevant to the former but not to the latter
- B. products flow across national boundaries
- C. there are different resources supplies among countries of the world
- D. of regulation from GATT
The law of comparative advantage states that a country should specialize in the production of a commodity
- A. for which local demand is greatest
- B. in which its oportunity cost is lower than that of the trade partner
- C. for which foreign demand is greatest
- D. for which there is abundant supply of raw materials
By using exchange controls, a country tries to eliminate a balance of payments deficit by?
- A. limiting her imports to its currency value of exports
- B. reducing the nation's domestic price level
- C. limiting her exports to its currency value of imports
- D. overvaluing the country's currency
A balance budget is defined as a condition of?
- A. balance of payments equilibrium
- B. equality of planned aggregate demand supply
- C. equality of planned receipts and planned expenditure
- D. equality of planned exports and planned imports
A perfect example of a public good is?
- A. air
- B. education
- C. water
- D. transport
The main objectives of public expenditure does NOT include?
- A. stabilization of national economy
- B. achievement of a more equitable income distribution
- C. meeting the social needs of the people
- D. revenue sharing and profit maximizationn
The three groups of government revenue are?
- A. investment income, direct tax and indirect tax
- B. imports duties, excise tax and export duties
- C. company tax, personal income tax and import duties
- D. company tax, import duties and excise tax
Government intervention in an economy is often justified on the group that?
- A. wants are unlimited while resources are scarce
- B. productivity is higher in the public than in the private sector
- C. free market may not work, or produce desirable results
- D. opportunity cost of government expenditure is zero
A tax is defined as regressive if?
- A. the proportion of income paid as tax increase as the income level increases
- B. all income group pay the same percentage of their income as tax
- C. the proportion if income taen by the tax falls as income increases
- D. the proportion of income taken by the tax is a fixed nominal amount of income for all income groups


